Harmonic analysis is the dynamic analysis used to predict the steady-state dynamic response of the piping system subjected to sinusoidally varying loads. All kinds of externally applied loads like nodal, elemental, gravity, and thermal loads can be included as load input. Accordingly, load cases are required to prepare and included in the solution. Load components in each load case use the same factor and phase angle. Different load cases may have different factors and phase angles, but the frequency for all loads is the same. The points that will be covered in this article are:
- Introduction
- Reviewing the Static Model
- Creating the Harmonic input
- The Harmonic Analysis
- Result Review
- Acoustic vibration and resonance are caused by Positive displacement pumps
Introduction to Harmonic Analysis
The harmonic analysis considers the effect of a harmonic load being applied to the system. The load is usually applied as a sinusoidal function (Fig. 1), e.g. pressure pulsation from reciprocating equipment. Being of a cyclic nature, harmonic loading relates to the fatigue allowable of the design code and should be considered. Care should be taken when undertaking a harmonic analysis for the accuracy of input data. Information relating to existing field problems can be derived from the measurement of pressure pulsation, deflection, forces, etc.
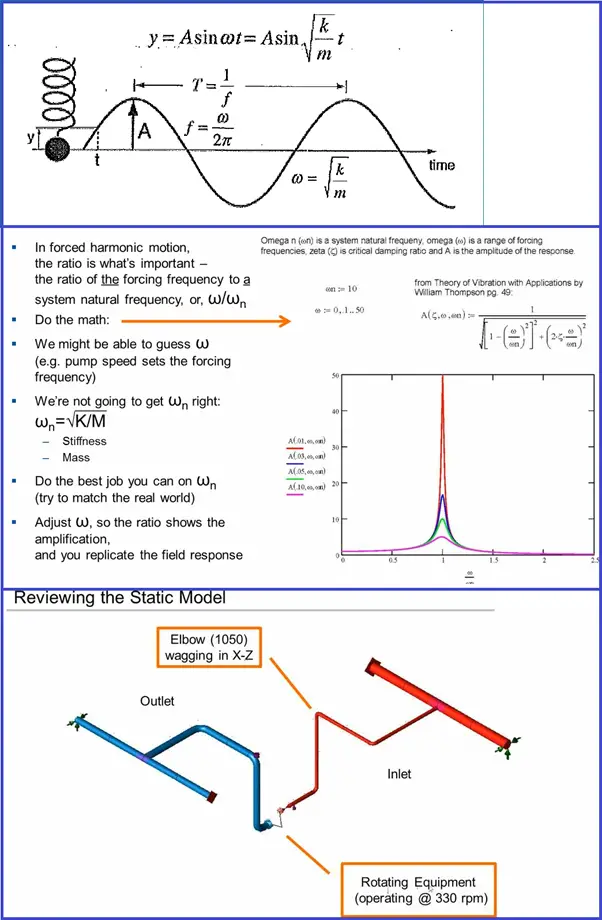
Reviewing the Caesar II Static Model for Harmonic Analysis
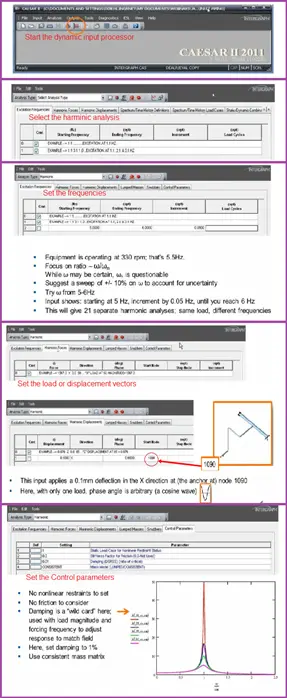
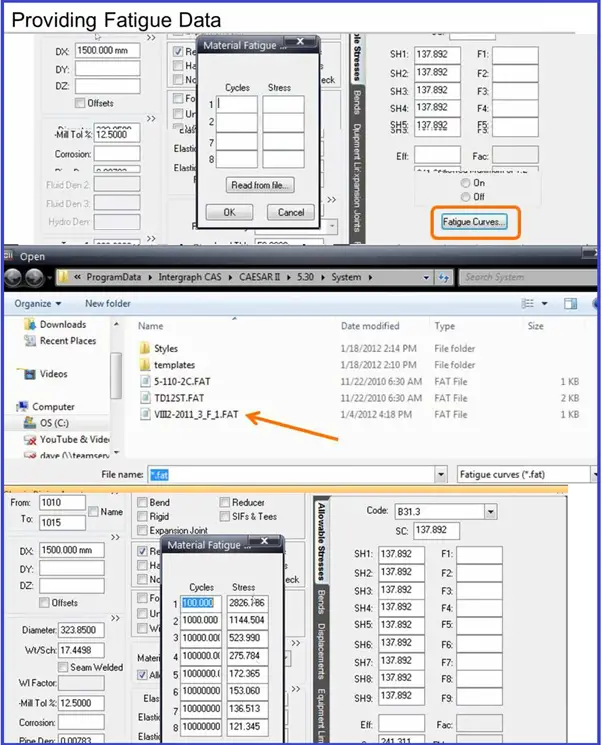
Creating harmonic Input for Analysis in Caesar II
Follow the steps shown in Fig. 2
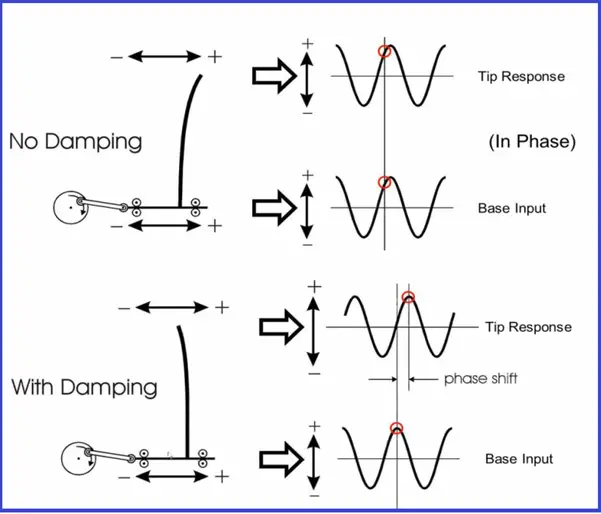
The effect of damping on the response
The Frequency-phase Dialog
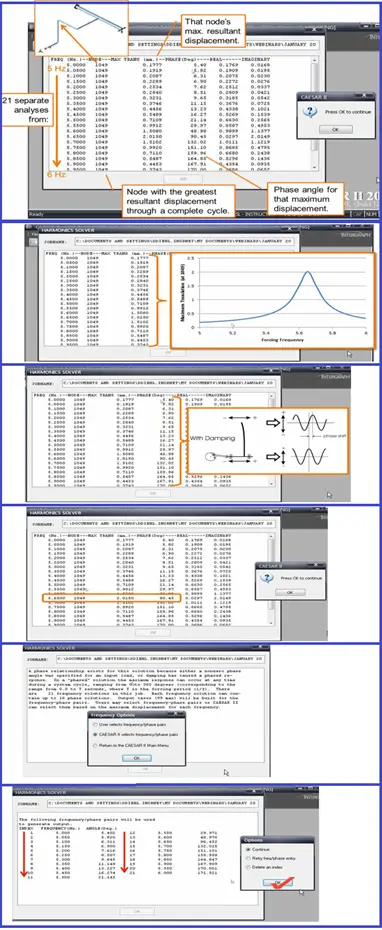
Harmonic Analysis Results Review
Results-Displacements:
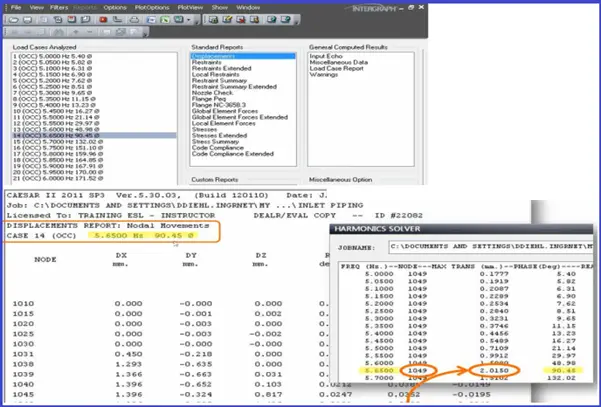
Results-Loads:
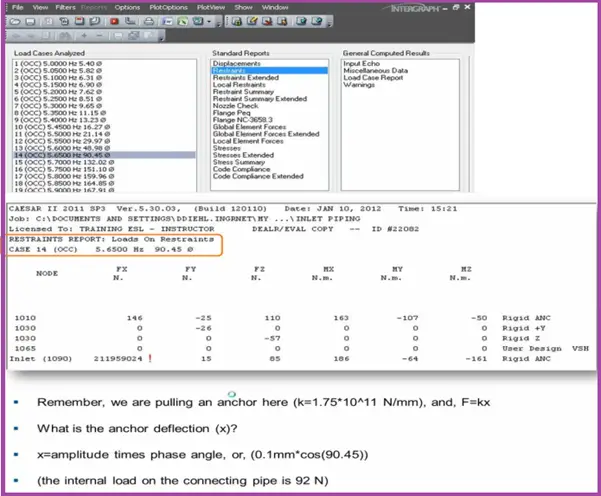
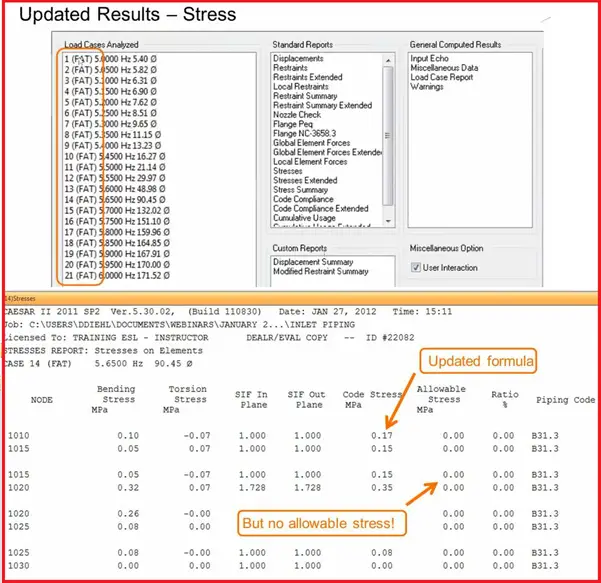
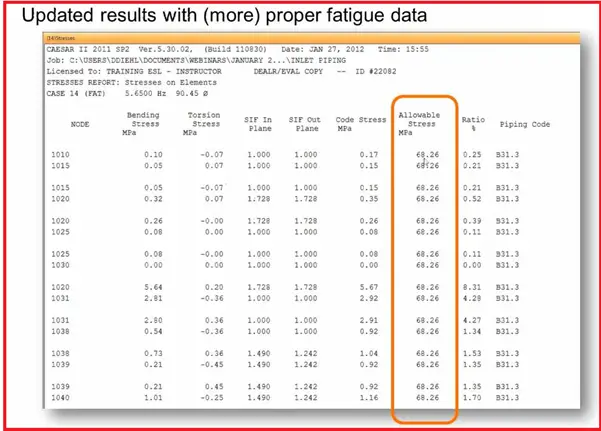
Results-Stress:
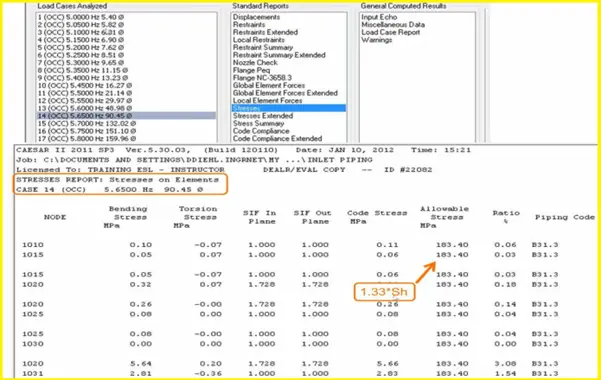

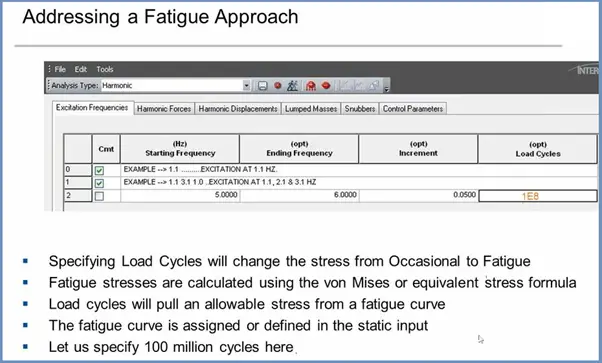
Author: This presentation is prepared by Mr. Deepak Sethia who is working in ImageGrafix Software FZCO, the Hexagon CAS Global Network Partner in the Middle East and Egypt. He has extensive experience in using Caesar II software and troubleshooting.

Good morning, excellent material, Fig. 2 was blurred if possible send to afreitas.eng@gmail.com