In the dynamic world of oil and gas production, centrifugal pumps play a pivotal role in moving fluids efficiently and safely. To ensure the reliability, performance, and consistency of these critical components, the American Petroleum Institute (API) developed API 610, a globally recognized standard for centrifugal pumps used in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries. In this article, we will dive into the fundamentals of API 610 and its significance in maintaining operational excellence and safety.
What is API 610?
API 610 is a technical standard that outlines the minimum requirements for the design, manufacturing, and testing of centrifugal pumps used in the petroleum, petrochemical, and natural gas industries. Established by the API, an influential body representing the oil and gas sector, API 610 ensures that the pumps adhere to high-quality and performance standards. The primary objective of this standard is to promote pump reliability, longevity, and safety in the challenging environments encountered within these industries.
Key Features and Scope
Types of Pumps Covered:
API 610 covers various types of centrifugal pumps, including single-stage overhung, between bearings, and multistage pumps. The standard also addresses vertical and horizontal pumps, providing a comprehensive range of applications.
Design and Construction:
The standard set rigorous criteria for pump design and construction, including material selection, shaft design, impeller balance, and hydraulic performance. This ensures that pumps can withstand the demanding conditions prevalent in oil and gas operations.
Hydrostatic Testing:
API 610 mandates hydrostatic testing to verify the structural integrity of pumps, ensuring they can handle the specified pressure and remain leak-free during operation.
Operating Ranges:
The standard specifies the pump’s permissible operating ranges, which are essential for efficient and safe performance. These ranges include parameters like flow rate, head, temperature, and speed.
Reliability and Maintenance:
API 610 emphasizes reliability-centered maintenance, promoting practices that enhance pump life and minimize unplanned downtime. It offers guidance on maintenance intervals, inspection procedures, and failure analysis.
Why is API 610 Important?
Safety and Environmental Compliance:
The oil and gas industry operates under stringent safety and environmental regulations. API 610-compliant pumps help minimize the risk of accidents and leaks, safeguarding workers and the environment.
Reliability and Performance:
The harsh conditions in oil and gas installations demand pumps capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, pressures, and corrosive fluids. API 610 ensures the pumps’ reliability, reducing the chances of operational disruptions.
Global Standardization:
API 610’s international acceptance ensures that oil and gas companies worldwide adhere to the same quality and safety standards, fostering seamless integration and compatibility of equipment.
Long-term Cost Savings:
High-quality, API 610-compliant pumps generally have a longer service life and lower maintenance costs. This leads to considerable cost savings over the pump’s lifecycle.
API 610 Pump Types
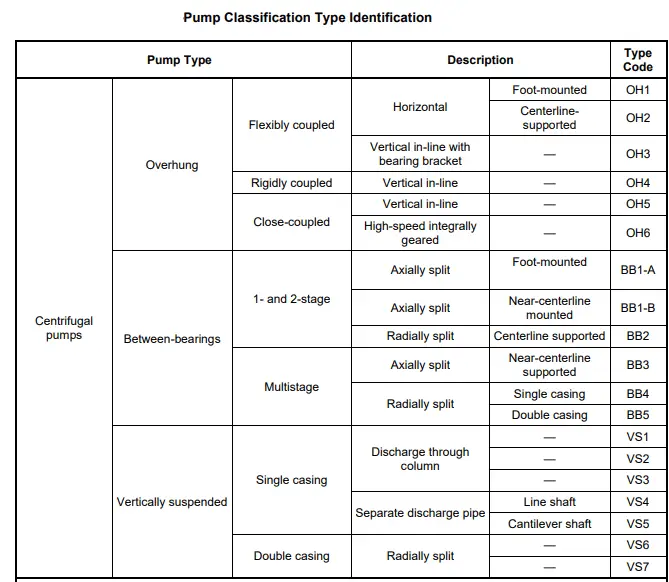
API 610 classifies centrifugal pumps used in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries into different types based on their design and construction. These classifications are essential as they provide a standardized way of categorizing pumps and specifying their characteristics for specific applications. The main API 610 classifications are as follows:
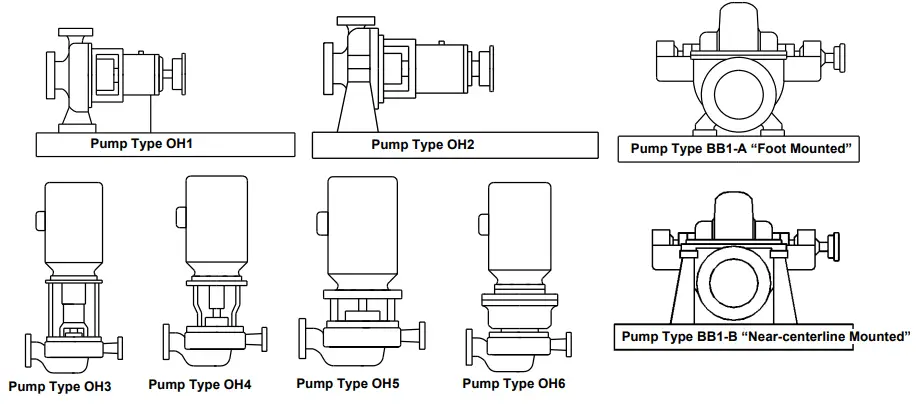
- Type OH: Overhung Pumps (Pump Type OH1 to OH6-Refer to Fig. 2)
- These pumps have a single-bearing housing supporting the impeller and are typically used for low to medium-flow and head applications.
- Type BB1: Between Bearings, Single-Stage Pumps
- These pumps have two bearings and a single-stage impeller. They are suitable for high flow, low to medium head applications.
- Type BB2: Between Bearings, Double-Suction, Twin-Volute Pumps
- Similar to BB1 pumps, they have a double-suction impeller and a twin-volute casing. These pumps are used for higher flow and medium head applications.
- Type BB3: Between Bearings, Multistage Pumps
- These pumps have two or more impellers mounted on a single shaft. They are designed for high-pressure services in refineries and petrochemical plants.
- Type BB4: Between Bearings, Axially Split, Multistage Pumps
- These pumps have axially split casings and are suitable for higher-pressure applications compared to BB3 pumps.
- Type BB5: Between Bearings, Double-Suction, Multistage Pumps
- BB5 pumps have two double-suction impellers and are used for high flow and high head applications.
- Type VS: Vertical Suspended Pumps
- These pumps have the shaft and impeller assembly suspended in the pump bowl with the motor located above the pump. They are used for various services and can be either single-stage or multistage configurations.
- Type VS1: Vertical Suspended, Single-Casing Pumps
- Similar to VS pumps, but with a single casing design.
- Type VS2: Vertical Suspended, Double-Casing Pumps
- Similar to VS1 pumps, but with an additional casing for higher-pressure services.
- Type VS4: Vertical Suspended, Vortex Pumps
- These pumps are designed to handle liquids with a high gas content or entrained gases.
- Type VS6: Vertical Suspended, Can Pumps
- VS6 pumps have a cantilevered design with the motor mounted on top, suitable for handling hazardous or toxic fluids.
The full API 610 classification for centrifugal pumps is provided in Fig. 1 below:
Differences Between API 610 Pumps and B73.1 Pumps
API 610 and ANSI B73.1 are two different standards that cover centrifugal pumps but are used in different industrial applications. Let’s explore the key differences between API 610 and ANSI B73.1 pumps:
Application and Industries:
API 610 Pumps: This standard is specifically designed for pumps used in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries. It focuses on pumps handling hydrocarbons, corrosive fluids, and high-temperature, high-pressure applications.
ANSI B73.1 Pumps: Also known as ASME B73.1, this standard covers general-purpose horizontal end suction centrifugal pumps. It is more commonly applied in industrial and commercial applications for handling water, chemicals, and other less demanding fluids.
Scope:
API 610: This standard has a broader scope and covers various types of pumps, including single-stage, multistage, and vertical pumps. It also includes more stringent requirements for materials, testing, and operational conditions to meet the challenging demands of the oil and gas industry.
ANSI B73.1: This standard primarily focuses on horizontal end suction pumps with single-stage, radially split volute casings. It is less prescriptive than API 610 and allows for more flexibility in design and materials.
Design and Construction:
API 610: Pumps meeting this standard typically have heavy-duty construction and are designed for high reliability and extended service life. They often include features like double volutes, special materials, and high-efficiency impellers.
ANSI B73.1: Pumps conforming to this standard are generally of a more standardized design with fewer specialized features. They are suitable for medium-duty applications and are often designed for ease of maintenance and cost-effectiveness.
Operating Conditions:
API 610: The standard addresses a wide range of operating conditions, including high-temperature and high-pressure applications. The pumps must be able to handle harsh and challenging environments typically found in the oil and gas industry.
ANSI B73.1: Pumps following this standard are designed for moderate operating conditions, such as handling water, chemicals, and other common industrial fluids at lower temperature and pressure ranges.
Compliance:
API 610: Compliance with this standard is often mandatory for pump applications in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, especially in critical services where safety and reliability are paramount.
ANSI B73.1: This standard is more commonly adopted in general industrial applications where specific industry regulations do not mandate API 610 compliance.
Some more insights into the differences between API 610 and ASME B73.1 pumps are given in this article: API 610 Pumps vs ANSI / ASME B73.1 Centrifugal Pumps
Conclusion
In conclusion, API 610 is a vital standard for the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries, ensuring the reliability, safety, and performance of centrifugal pumps. By adhering to this standard, companies can mitigate risks, reduce maintenance expenses, and optimize operational efficiency. As the oil and gas industry continues to evolve, API 610 remains an indispensable guide for pump manufacturers, operators, and engineers committed to delivering excellence in fluid handling systems.