Pipe caps are a type of pipe fitting to cover the pipe end. In the Piping, Plumbing, and Pipeline industry, pipe end caps are widely used to block the ends of pipes. They work in a similar fashion to pipe plugs or blind flanges. Even though this is a very important pipe fitting, most of the time the significance of pipe caps is overlooked. In this article, we will explain some details about pipe cap fittings; their types, materials, standards, specifications, and differences with plugs and blind flanges.
What is a Pipe Cap?
A pipe end cap is a pipe fitting that held the pipe content within itself by blocking the end parts. It acts as a protective device for the plumbing, piping, and pipeline system by not allowing outside matters to enter the inside of the pipe. Due to this pipe caps are also known as pipe end protectors. Industrial pipe caps are widely used in domestic, commercial, and industrial water supply lines, Steam pipes in power plants, and various oil, gas, and chemical lines in process and chemical industries.
Pipe Cap Materials
A range of materials is used to manufacture piping end caps. Depending on the pipe material and service, pipe cap materials are selected. Some of the common industrial pipe cap materials are:
- Carbon Steel (ASTM A234 WPB)
- Low-Temperature Carbon Steel (ASTM A420)
- Alloy Steel (ASME A234 WP1 / WP5 / WP9 / WP11 / WP22 / WP91)
- Aluminum
- Nickel Alloy (ASTM B336, Monel 400, Inconel 825, Inconel 625, Hastelloy C 276, Cupro Nickel)
- Nylon or polyamide
- Stainless Steel (ASTM A182, ASTM A403)
- Duplex Stainless Steel (ASME S815 UNS No S31803, S32205)
- Polyethylene
- Polypropylene
- Vinyl
- FRP
- Silicone rubber etc.
Shapes of Pipe Caps
Pipe caps are manufactured in various shapes to cater to various application demands. Some of the common pipe cap shapes are:
- Round
- Square
- Rectangular
- “I” Shape Cap
- Oval
- Hemispherical
- “U” Shape Cap
- Hex Cap etc.
Pipe Cap Standards
ASME B16.9 provides pipe dimensions, ratings, testing, tolerances, and marking requirements for Steel Piping cap fittings. Usual pipe end caps are manufactured from NPS 1/2 inches through 48 inches with pipe schedules 10, 20, 30, STD, 40, 60, 80, XS, XXS, 100, 120, 140, and 160 as applicable. Other pipe end caps standards are:
- ASME B16.11
- DIN 2617
- DIN 28011
- MSS SP 43
- EN 10253
Types of Pipe Caps
Pipe caps are classified based on their applications, material of construction, construction features, etc.
Depending on the construction features, the following pipe cap types are found:
- Threaded Caps: Threaded pipe caps have female threads to fit the pipe end with the caps. The thread can be straight or tapered.
- Welded Caps: Welded pipe caps can be either butt welded or socket welded caps.
- Tapered Caps: These types of pipe caps have tapered sides that help in a close fit. Tapered caps can be used as a multi-functional pipe fitting and can be used with male and female NPT threads, male straight threads, and straight tubes and bars.
- Anti-roll Caps: These pipe cap types are round in shape but with a square end to prevent pipes and tubes from rolling.
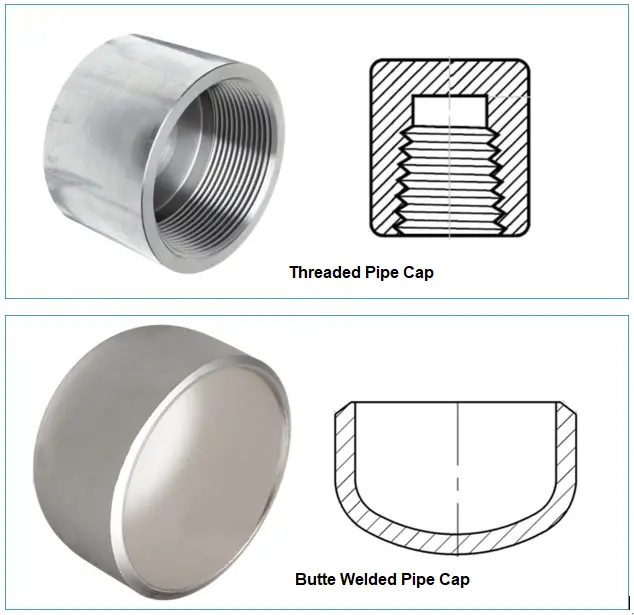
Depending on pipe cap materials, they can be classified as:
- Metallic Pipe Caps: Made from metals like Steel, Aluminum, etc. and
- Non-metallic Pipe Caps: Made from non-metals like plastics.
Specification of Pipe Caps
Pipe end caps are specified by various parameters as listed below:
- Pressure Temperature Rating
- Pipe Cap Material: Metallic/non-metallic
- Diameter: Diameter of the connection pipe
- Type: Exact type of pipe cap required.
- Shape: Shape of pipe caps (Round/Square/Rectangular)
- Head type of Round Pipe caps: (flange or slotted head, knurled or faceted head, retaining head, and tear tab)
- Length and Width for Rectangular pipe caps.
- Thread type and size: NPT/BSP/Metric
- Design Standard: ASME/DIN
- Coating/Polishing/Galvanizing Requirements
Pipe Caps vs Plugs
Plugs are piping also serve a similar function that a pipe cap serves. But there is a major difference between the pipe cap and the pipe plug. Pipe caps usually have female thread whereas pipe plugs have male threads. It means a pipe is inserted into the threads of a pipe cap whereas the plug is inserted into the pipe. Other differences between the two are:
- Purpose: A pipe cap is used to close off the end of a pipe permanently to make it a dead end, whereas a pipe plug is generally used to temporarily seal the pipe end for maintenance or testing.
- Installation: Pipe caps are can be welded or threaded while pipe plugs are generally threaded.
- Pressure rating: Pipe caps are designed to handle the system pressure but pipe plugs usually do not handle system pressure.
Pipe Caps vs Blind Flanges
A blind flange is a type of piping flange that serves a similar function as a pipe cap. However, there are some distinct differences between a pipe cap and a blind flange. These are listed below:
- Purpose: A pipe cap closes the end of a pipe permanently, but a blind flange is used to isolate a section of a pipeline or seal off a pressurized system.
- Production: Blind flanges are forged or cast components whereas pipe caps are generally made by forming.
- Installation: Pipe caps are installed by welding or screwing whereas blind flanges are generally installed by bolting and a gasket is inserted in between.
- Seal: Pipe caps provide permanent sealing whereas blind flanges are used to provide a pressure-retaining barrier with a mating flange. Blind flanges are used to connect or disconnect parts of piping or valves.
- Face type: Pipe caps have a flat or convex end face, while blind flanges have a raised face.
- Pressure testing: Blind flanges can be used for pressure testing, while pipe caps cannot.
- Maintenance: Being bolted, blind flanges can be easily removed for maintenance or repair, while pipe caps are permanent and cannot be easily removed.
- Cost: Blind flanges are typically more expensive than pipe caps due to their higher level of functionality.
Online Video Course on Piping and Pipe Fittings
To enrich yourself with piping and pipe fitting details you can opt for the following online video courses

Dear Sir,
How to select end cap thickness ?