Sample Coolers cool the sample from a process/chemical stream to the required temperature conditions for safe analysis. They are basically small, compact shell and tube heat exchangers. Sample coolers form one of the most critical components of a sampling system. They are widely used for most applications in liquid, gas, or steam process.
The process sample requiring cooling passes through the tube side of the cooler. Whereas the cooling fluid (mostly water) passes through the shell side. The cooled sample is then collected from the tube side outlet and taken to a laboratory for analysis. Sometimes the sample is piped to in-line process instrumentation when continuous monitoring of process fluid properties such as conductivity, pH, or other chemical constituents is required.
Sample coolers are also used to temper the sample to the required temperature for the analysis. This is very important as the fluid temperature can directly affect the analysis results. Usually, the sample is allowed to flow for a while before collection. This ensures that a true sample with proper temperature is collected for analysis.
Sample coolers are usually designed and constructed based on BS 5500, ASME Section Vlll, or TEMA standards. The selection of a sample cooler is usually done considering the application, specific type of fluid, temperature, pressure, and flow conditions.
Applications of Sample Coolers
Sample coolers are widely used in chemical process industries. The industries where sample coolers are frequently found are:
- Oil & Gas
- Refinery
- Power generation (boiler sample cooler)
- Fertilizer
- Chemical and Petrochemical plants
- Pharmaceutical
- Process water sampling.
- Sugar, Paper
- Textile, Cement, Steel, etc.
Basic Design of Sample Cooler
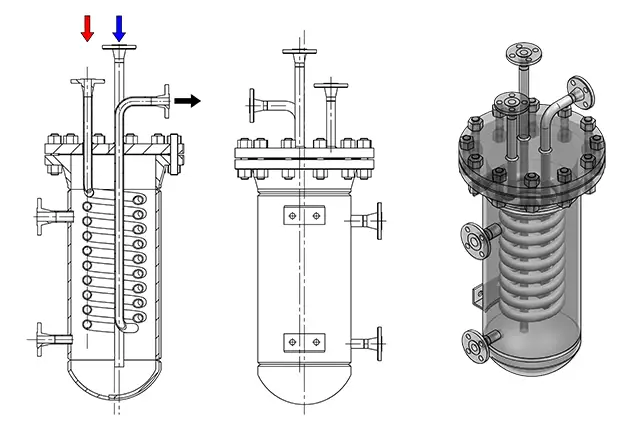
Depending on the application, Sample coolers are designed in numerous sizes and configurations. In general, they consist of a single, one-piece heat transfer tube, wound as a coil. The tube is then housed in a cylindrical container called a shell. The process fluid stream is usually admitted to the coil from the top. The cooling fluid flows through the sample cooler shell in an opposite direction. This opposing flow ensures optimum efficiency for the sample cooler. The heat of the process sample is transferred to the cooling fluid making a decrease in the sample temperature.
The shell is mounted using flanged connections so that it can be removed without disturbing the sample lines. To facilitate convenient operation and collection, the sample cooler is installed as close as possible to the system take point. The sample coolers are usually installed in the vertical position.
Characteristic Features of a Sample Cooler
A sample cooler must possess the following characteristics:
- They must be safe in operation.
- They should provide an accurate sampling.
- Highly efficient. The sample temperature from the cooler outlet shall be very close to the desired temperature.
- Shall be robust to handle high pressure & high-temperature samples.
- There should not be welded joints in the coil. Sample coolers shall be designed as a complete single-piece coil as this ensures trouble-free operations without risks of failure of joints inside the shell.
- Sample coolers shall be made from corrosion-resistant materials.
- Counter-current flow shall be achieved at a very close temperature approach of the sample to the cooling fluid.
- The cooling fluid requirement must be minimum.
- The size of the sample cooler must be small and compact to make the installation easy and minimize the cooling fluid utilization.
- They should be mounted with proper access for easy maintenance. Installation should be such that the coils can be cleaned or replaced without any difficulty.
- In-built safety relief valves are sometimes provided to prevent accidents in case of any unlikely coil failure.
- The design shall be Self-draining to eliminate sample retention (the usual design is an inlet from the top and an outlet from the bottom).
- Sample cooler shell must be possible to be easily removed without disconnecting the sample lines, for inspection or maintenance purposes.
- It must be a low-pressure-drop system.
Sample Cooler Ordering Information
For ordering a sample cooler the following information should be mentioned in the datasheet:
- Application of the cooler.
- Continuous or intermittent operation.
- Temperature and Pressure ranges.
- Flow rate
- Any associated valve requirement.
- Material of shell, tube, and coils.
- Required cooling capacity.
- Inlet and Outley sizes.
- Any pressure drop criteria
- Pressure equipment directive (CE marking) requirements if any
Types of Sample Coolers
Depending on the construction of sample coolers, there are three types of sample coolers:
- Single helical tube sample coolers.
- Spiral tube sample coolers, and
- Dual tube coil sample coolers.
Installation of Sample Coolers
For safety and efficient operation, a sample cooler needs to be installed as specified by the purchaser. While installing, the equipment should be isolated from all connected piping and depressurized. Sometimes, a relief valve is installed in the cooler line to protect against excessive pressure rise.