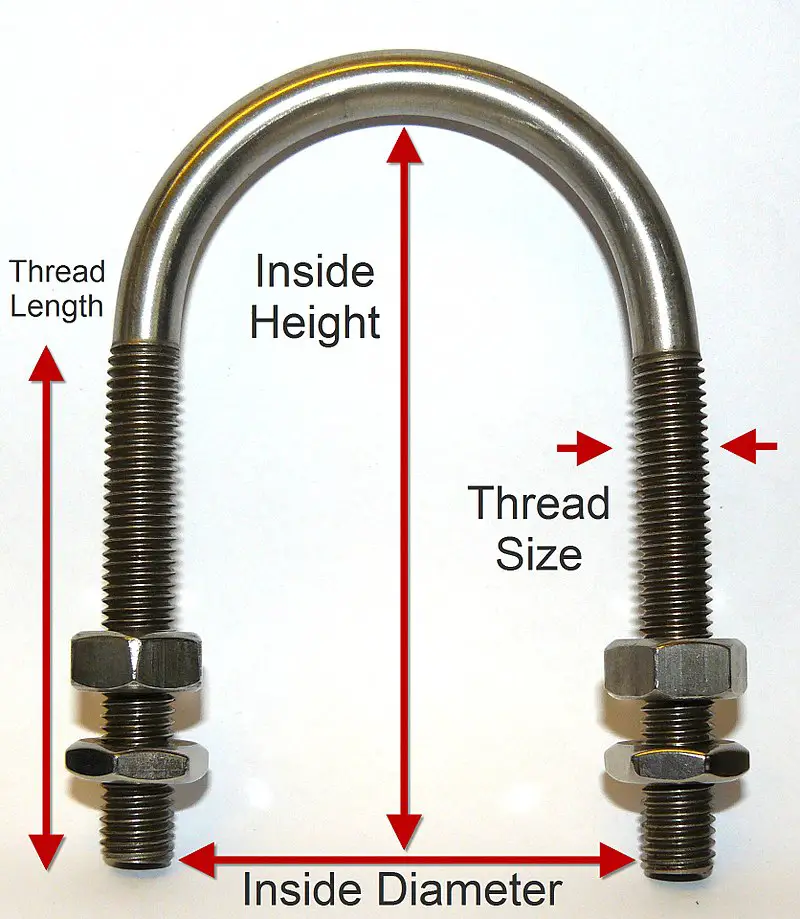
A u-bolt is a u-shaped curved bolt having threads on each end used as support in the piping and pipeline industry. U-Bolts are one of the simplest and most widely used types of piping support. They work mainly as Rest+Guide+Hold down support; though with a little installation, changes can be made to work as line stops as well. U-bolts with their curved shape fit nicely around the pipes which are then secured with a secondary member using nuts. They are easily available in various sizes and thicknesses. The important dimensions of a u-bolt are shown in Fig. 1 below:
Applications of U-bolts
U-bolts have an extended range of applications. They are widely used as piping support solutions. The common uses of u-bolts in piping solutions are:
Use of u-bolt as pipe supports:
They are used to provide lateral restraints to pipes. For small-bore piping systems, u-bolts are the most simplest and widely used type of piping support. In any plant, for supporting bare pipes lesser than 8-inch size, u-bolts are extensively used. As already stated they function as rest+guide+hold down. U-bolts are capable to suppress line vibrations by providing rigidity to the system. For supporting vertical elevated runs of pipe, U-bolts are a good choice.
Uses of u-bolts for pipe shipping:
In the pipe and pipeline shipping industry, u-bolts are used to avoid pipe movement and breakage. U-bolts prevent haphazard pipe movements due to transportation loads.
Materials of U-bolts
Even though u-bolts can be manufactured from any type of strong and durable materials; in the piping industry, the following materials are widely used.
- Plain Carbon Steel, and
- Stainless steel.
Sometimes, protective coatings are added to prevent corrosion. Some of the usual u-bolt coatings are:
- Zinc Plating
- Hot-Dip Galvanization
- Thermoplastic coating
- Fluoropolymer coating
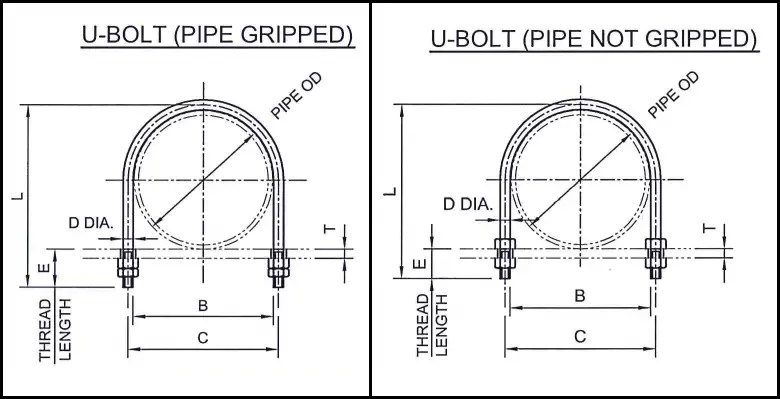
Types of U-bolts: Gripped vs Non-gripped U-bolts
In general, u-bolts are used as guide+hold down. However, they can be used to work like anchors as well. Depending on these u-bolt functions, they are classified into two groups; Gripped u-bolt and non-gripped u-bolt.
Non-gripped U-bolt: U-bolt as Guide
Non-gripped u-bolt is the most common and simple installation to work as the pipe guide. It does not restrict axial movement. In non-gripped pipe u-bolt installation, one nut is placed on the top and the other on the bottom of the support beam. Both nuts are fixed, keeping a gap in between the pipe and the u-bolt surface.
Gripped U-bolt: U-bolt as Anchor
In gripped u-bolt configuration, the u-bolt work as an anchor and stop pipe movement at the support location. To work the pipe u-bolt as an anchor, the u-bolt needs to be installed such that there is no space between the pipe and u-bolt. Both bolts are placed at the bottom of the secondary support structure and tightened to snug against the pipe. The friction force in between the clamp and pipe surfaces restricts the pipe movement in the axial direction to work as a directional anchor. However, with an increase in line stops axial forces, the frictional force may not be able to withstand the axial force and may slip. This is the reason the use of u-bolt as anchors is limited to lower-size pipes; usually up to 6-inch pipes.
Installation of U-bolts
Installing a pipe U-bolt is very easy. The size of u-bolts is decided based on the pipe OD. All properly sized u-bolts come with threads and nuts. The only job is to drill the hole in the support beam, properly align the bolt through those holes, and tighten the nuts depending on the support type (anchor type or guide type).

Appreciate your efford sir. Keep posting.
Why we need double nut ?
Would be more useful if you gave some load data and recommended torque info.
What would you recommend for larger pipe say 14″ to 20″?