Plumbing systems play a vital role in our homes, ensuring the delivery of clean water and the proper disposal of waste. While the functionality of plumbing largely depends on a network of pipes, it’s crucial to understand that not all pipes are created equal. Different types of plumbing pipes offer varying levels of durability, longevity, and suitability for specific applications. In this article, we will explore the most common types of plumbing pipes and their unique characteristics to help you make informed decisions for your plumbing needs.
Copper Pipes
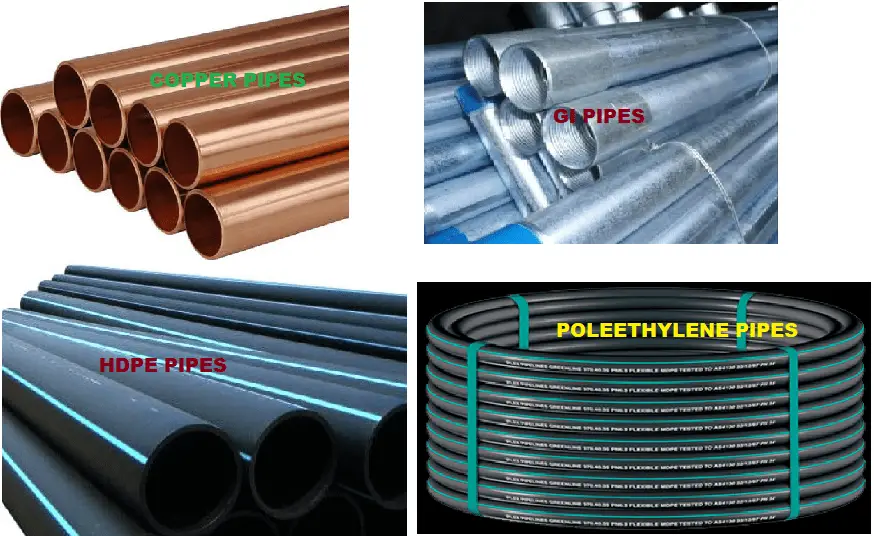
Copper pipes have long been the gold standard in plumbing due to their excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and versatility. They are available in rigid or flexible forms, making them suitable for both water supply and drainage systems. Copper pipes are known for their longevity, often outlasting the lifespan of other plumbing materials. They are also resistant to high temperatures, making them ideal for both hot and cold water applications. However, copper pipes can be relatively expensive and may require skilled labor for installation.
Advantages of Copper Pipes
Here are some key features and advantages of copper pipes:
- Corrosion Resistance: Copper pipes are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for carrying water and other fluids. They do not rust or deteriorate over time, ensuring long-lasting performance and reliability.
- Durability: Copper pipes have a long lifespan and can often outlast the buildings they are installed in. They are strong and can withstand high water pressures without bursting or leaking. Copper pipes are also resistant to UV rays, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Heat Resistance: Copper pipes have excellent heat resistance, making them ideal for both hot and cold water supply systems. They can effectively handle high-temperature water without warping or degrading. This heat resistance makes copper pipes suitable for applications such as hot water heaters and radiant heating systems.
- Flexibility: Copper pipes can be easily shaped and bent to fit various plumbing layouts and configurations. They are available in both rigid and flexible forms, providing versatility in installation. Copper pipes can be soldered or joined using compression fittings, allowing for secure and leak-free connections.
- Antibacterial Properties: Copper has natural antibacterial properties, which can help inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi in the plumbing system. This can contribute to maintaining a clean and hygienic water supply.
- Recyclability: Copper is a highly recyclable material. When copper pipes reach the end of their useful life, they can be recycled and repurposed, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
Applications of Copper Pipes
Copper pipes are commonly used in various plumbing applications, including:
- Water Supply Lines: Copper pipes are widely used for both residential and commercial water supply systems. They are suitable for carrying potable water, ensuring clean and safe drinking water for households and buildings.
- Plumbing Fixtures: Copper pipes are used to connect plumbing fixtures, such as faucets, showers, toilets, and sinks, to the main water supply lines. Their flexibility allows for easy installation in tight spaces.
- Heating Systems: Copper pipes are often used in hydronic heating systems and radiant floor heating systems. Their heat conductivity and resistance make them efficient for distributing hot water throughout the system.
It’s important to note that copper pipes can be more expensive than other types of plumbing pipes. They also require skilled labor and specialized tools for installation. Additionally, in areas with aggressive water conditions or high acidity, copper pipes may require additional protective measures, such as water treatment or pipe insulation.
Overall, copper pipes are a popular choice for plumbing systems due to their durability, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and longevity. When properly installed and maintained, copper pipes can provide a reliable and efficient water supply and contribute to the overall functionality of the plumbing system.
PEX Pipes
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) pipes have gained popularity in recent years due to their flexibility, ease of installation, and affordability. PEX pipes are highly resistant to freezing temperatures and are less likely to burst compared to copper or rigid plastic pipes. They can be easily bent and curved around obstacles, reducing the need for complicated fittings. PEX pipes are commonly color-coded to differentiate between hot and cold water lines. It’s worth noting that PEX pipes should not be exposed to direct sunlight as it can degrade the material over time.
Benefits of PEX Pipes
Here are some key features and benefits of PEX pipes:
- Flexibility: PEX pipes are highly flexible, allowing for easy installation in various plumbing layouts. They can be bent and curved around obstacles, reducing the need for complex fittings and minimizing the potential for leaks. The flexibility of PEX pipes also makes them suitable for retrofitting or remodeling projects.
- Freeze Resistance: PEX pipes have excellent freeze resistance, making them ideal for cold weather climates. They can expand and contract without cracking or bursting when exposed to freezing temperatures. This feature reduces the risk of costly water damage and simplifies winterization procedures.
- Durability: PEX pipes are highly durable and resistant to common plumbing issues such as corrosion, scale buildup, and pitting. They can withstand high water pressures and are less likely to develop pinhole leaks over time. PEX pipes also have excellent resistance to chemicals, ensuring a long lifespan.
- Easy Installation: PEX pipes are relatively easy to install, even for individuals with basic plumbing knowledge. They can be cut with a simple tubing cutter and require fewer fittings compared to rigid pipes. PEX pipes can be connected using various methods, including crimping, clamping, or push-fit fittings, which simplifies the installation process.
- Versatility: PEX pipes are suitable for a wide range of plumbing applications. They can be used for both hot and cold water supply lines, including potable water distribution. PEX pipes are also commonly used for radiant floor heating systems and hydronic heating applications.
- Reduced Noise Transmission: PEX pipes have natural sound-dampening properties, minimizing the noise associated with water flow. This makes them an excellent choice for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as residential buildings or multi-story structures.
It’s important to note that while PEX pipes are highly versatile, they should not be exposed to direct sunlight for extended periods as they can degrade the material. UV-resistant PEX pipes or proper insulation should be used for outdoor or exposed installations.
When working with PEX pipes, it’s crucial to follow local plumbing codes and guidelines. Proper tools, fittings, and installation techniques should be used to ensure secure and watertight connections. It’s advisable to consult with a professional plumber or plumbing engineer if you have specific questions or concerns about using PEX pipes for your plumbing project.
In summary, PEX pipes offer a flexible, durable, and freeze-resistant solution for plumbing systems. Their ease of installation and suitability for various applications make them a popular choice among homeowners and professionals alike.
PVC Pipes
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) pipes are widely used for drainage systems and non-potable water applications. They are lightweight, durable, and resistant to chemicals, making them suitable for various plumbing needs. PVC pipes are relatively inexpensive and easy to install. However, they are not recommended for hot water applications as they can warp under high temperatures. Additionally, PVC pipes may become brittle over time, especially when exposed to extreme cold.
Advantages of PVC Pipes
Here are some key features and benefits of PVC pipes:
- Affordability: PVC pipes are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of plumbing pipes. This makes them a cost-effective option for plumbing projects, whether it’s for residential, commercial, or industrial applications.
- Durability: PVC pipes are highly durable and resistant to corrosion, rust, and chemical degradation. They can withstand high water pressures without leaking or bursting, providing a long-lasting plumbing solution.
- Lightweight: PVC pipes are lightweight, which makes them easy to handle and install. Their lightness reduces the strain on the overall plumbing system and simplifies transportation during construction or renovation projects.
- Easy Installation: PVC pipes are easy to work with and install. They can be cut to desired lengths using a saw or PVC pipe cutter and joined together using solvent cement or compression fittings. PVC pipes require fewer fittings and connections, resulting in simpler and quicker installation.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC pipes have excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for a wide range of plumbing applications. They can withstand exposure to various household chemicals and are commonly used for both potable water supply and drainage systems.
- Insulation: PVC pipes have good thermal insulation properties, which means they help maintain the temperature of the fluid flowing through them. This can be beneficial in both hot and cold water applications, helping to conserve energy and improve efficiency.
- Wide Range of Applications: PVC pipes are versatile and used in various plumbing applications. They are commonly used for water supply lines, drainage systems, wastewater disposal, irrigation systems, and venting applications.
However, it’s important to note that PVC pipes have temperature limitations. They are not suitable for carrying hot water above a certain temperature threshold, as high temperatures can cause the material to deform or weaken. For hot water applications, alternative materials like CPVC (chlorinated polyvinyl chloride) pipes may be more appropriate.
When working with PVC pipes, it is important to follow local building codes and guidelines. Proper solvent cementing techniques and appropriate fittings should be used to ensure leak-free connections. Additionally, PVC pipes should be protected from prolonged exposure to direct sunlight as ultraviolet (UV) rays can degrade the material over time. Outdoor installations should be done with UV-resistant PVC pipes or appropriate pipe insulation.
In conclusion, PVC pipes are a popular choice for plumbing systems due to their affordability, durability, and ease of installation. They provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for various plumbing needs, making them widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
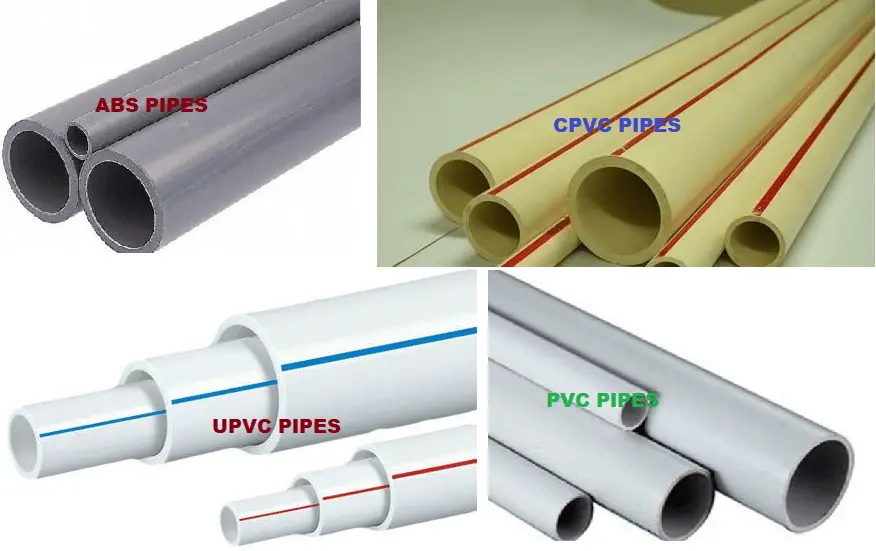

CPVC Pipes
Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) pipes are a variant of PVC pipes that have been treated with chlorine to increase their temperature resistance. CPVC pipes are commonly used for hot water supply lines and are suitable for both residential and commercial applications. They offer excellent corrosion resistance and are relatively easy to install. However, it’s important to note that CPVC pipes require specific solvent cement for proper joint connections.
Benefits of CPVC Pipes
Here are some key features and benefits of CPVC pipes:
- Temperature Resistance: CPVC pipes are designed to withstand higher temperatures compared to standard PVC pipes. They can handle hot water at temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) without deforming or weakening, making them suitable for hot water supply lines.
- Corrosion Resistance: CPVC pipes are highly resistant to corrosion from hot water and aggressive chemicals. They are less prone to scaling, pitting, and degradation, ensuring a long lifespan and reliable performance in hot water applications.
- Durability: CPVC pipes are known for their strength and durability. They can withstand high water pressures and mechanical stresses without leaking or bursting. CPVC pipes also have good impact resistance, reducing the risk of damage during installation or use.
- Chemical Resistance: CPVC pipes have excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for various applications where hot water is in contact with chemicals or aggressive substances. They can handle a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents commonly found in plumbing systems.
- Easy Installation: CPVC pipes are lightweight and easy to install, similar to PVC pipes. They can be cut, joined, and connected using solvent cement or mechanical fittings. CPVC pipes require fewer supports compared to metal pipes due to their lightweight nature.
- Cost-Effective: CPVC pipes offer a cost-effective solution for hot water plumbing systems. They are generally more affordable than metal pipes such as copper or stainless steel, making them a popular choice for residential and commercial projects.
Applications of CPVC Pipes
CPVC pipes are commonly used in a range of hot water applications, including:
- Hot Water Supply Lines: CPVC pipes are suitable for carrying hot water from the water heater to faucets, showers, and other hot water fixtures. They provide a reliable and efficient distribution system for hot water in residential and commercial buildings.
- Industrial Applications: CPVC pipes are used in various industrial processes that involve hot water transport, such as in manufacturing plants, chemical processing facilities, and food production facilities.
- Sprinkler Systems: CPVC pipes are also used in fire sprinkler systems, where hot water or a mixture of water and antifreeze is circulated to provide fire protection.
It’s important to note that CPVC pipes should not be used for drinking water applications, as they can impart a slight taste or odor to the water. For potable water supply lines, it’s recommended to use CPVC pipes for hot water lines only and use approved materials like PVC or copper for cold water lines.
When working with CPVC pipes, it is crucial to follow manufacturer instructions, local plumbing codes, and guidelines. Proper solvent cementing techniques and appropriate fittings should be used to ensure secure and leak-free connections. Consulting with a professional plumber or plumbing engineer is advisable for specific projects or complex installations.
In summary, CPVC pipes are specifically designed for hot water applications, offering excellent temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and durability. They provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for distributing hot water in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing systems.
Galvanized Steel Pipes: Galvanized Iron Pipes
Galvanized steel pipes were once a popular choice for plumbing, but they are now less commonly used due to their drawbacks. These pipes are coated with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. While galvanized steel pipes are durable and have a long lifespan, they are prone to rust and can accumulate mineral deposits over time, leading to reduced water flow. Moreover, galvanized steel pipes are challenging to work with and may require professional assistance for installation or repairs.
Advantages of Galvanized Iron Pipes
Here are some key features and characteristics of galvanized iron pipes:
- Corrosion Resistance: The primary purpose of galvanizing is to provide corrosion resistance to the underlying iron or steel material. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial layer, protecting the iron or steel from rust and corrosion caused by exposure to water and other corrosive substances. This corrosion resistance makes galvanized iron pipes suitable for plumbing systems, particularly in areas with high levels of moisture.
- Durability: Galvanized iron pipes are known for their durability and ability to withstand high water pressures. They have a long lifespan and can handle demanding plumbing applications.
- Strength: Galvanized iron pipes are strong and rigid, making them suitable for applications where structural integrity is essential. They can withstand heavy loads and are commonly used for water distribution in buildings and outdoor plumbing installations.
- Temperature Resistance: Galvanized iron pipes have good temperature resistance and can handle both hot and cold water. However, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause the zinc coating to deteriorate, leading to reduced corrosion protection.
- Installation Challenges: Galvanized iron pipes can be challenging to work with during installation due to their weight and rigidity. They often require threaded fittings for connections, which can be time-consuming and may require professional assistance. Additionally, the threads on galvanized pipes can be prone to leakage over time.
- Maintenance Considerations: Over time, the zinc coating on galvanized iron pipes may wear away or develop cracks, exposing the underlying iron or steel to corrosion. Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to identify and address any signs of corrosion, such as rust stains or leaks.
It’s important to note that the use of galvanized iron pipes for potable water systems is no longer recommended in many jurisdictions due to potential health concerns. As the zinc coating ages, it can release small amounts of zinc into the water, which may pose health risks if consumed over time. Modern plumbing standards often require the use of alternative materials, such as copper, PVC, or PEX, for potable water supply.
In summary, galvanized iron pipes were once a common choice for plumbing systems due to their corrosion resistance and durability. However, their use has declined in recent years due to potential health concerns, installation challenges, and the availability of more advanced materials. It’s advisable to consult with a professional plumber or adhere to local plumbing codes and regulations when considering the use of galvanized iron pipes in plumbing projects.
Polyethylene Pipes
Polyethylene (PE) pipes are commonly used for underground water supply lines and irrigation systems. They are highly resistant to chemicals, corrosion, and abrasion. PE pipes come in various types, such as HDPE (high-density polyethylene) and MDPE (medium-density polyethylene), each with different strengths and applications. These pipes are lightweight, flexible, and relatively easy to install. However, they are not suitable for hot water applications due to their lower temperature resistance.
Benefits of Polyethylene Pipes
Here are some key features and benefits of polyethylene pipes:
- Durability: Polyethylene pipes are known for their exceptional durability. They have high resistance to cracking, impact, and abrasion, making them suitable for challenging environments and underground installations. PE pipes have a long lifespan and can withstand prolonged exposure to harsh conditions, including UV rays and chemicals.
- Corrosion Resistance: Polyethylene pipes are highly resistant to corrosion and chemical attack. They do not rust or corrode like metallic pipes, making them suitable for transporting various substances, including potable water, wastewater, chemicals, and gases.
- Flexibility: PE pipes are flexible, which allows for easy installation and versatility in plumbing applications. They can be coiled and bent to accommodate changing terrain or irregular layouts. The flexibility of PE pipes reduces the need for multiple fittings and joints, reducing the potential for leaks.
- Lightweight: Polyethylene pipes are lightweight compared to metallic pipes, which makes handling and installation easier and more cost-effective. The reduced weight also contributes to lower transportation costs and less strain on the overall plumbing system.
- High Flow Capacity: PE pipes have smooth internal surfaces that facilitate excellent flow characteristics. They offer low friction losses and allow for efficient fluid transport, ensuring optimal performance in plumbing systems.
- Thermal Insulation: Polyethylene pipes provide some degree of thermal insulation. They have low thermal conductivity, which helps to maintain the temperature of the fluid being transported. This feature can be advantageous in applications where temperature control is important, such as chilled water systems.
- Leak Resistance: The joints and connections in PE pipes are typically fused or welded together, creating strong, leak-resistant connections. This eliminates the need for external fittings or adhesive materials, reducing the potential points of failure and ensuring a reliable plumbing system.
Applications of Polyethylene Pipes
Polyethylene pipes are commonly used in various applications, including:
- Water Supply Systems: PE pipes are widely used for water supply networks, both for potable water and non-potable water applications. They can be employed for residential, commercial, and industrial water distribution systems.
- Irrigation Systems: Polyethylene pipes are well-suited for irrigation systems due to their resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and weather conditions. They are commonly used for agricultural irrigation, landscaping projects, and golf course irrigation.
- Gas Distribution: PE pipes are used for natural gas and propane distribution. They provide a safe and reliable means of transporting gas, with excellent resistance to corrosion and gas permeation.
- Industrial Applications: Polyethylene pipes find applications in various industrial sectors, such as mining, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries. They are used for transporting chemicals, slurries, and other fluids.
It’s important to note that different types of polyethylene pipes, such as HDPE and MDPE, have specific application guidelines and limitations. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations and local plumbing codes is essential to ensure proper installation and usage of PE pipes.
In summary, polyethylene pipes offer durability, corrosion resistance, flexibility, and lightweight properties, making them a versatile choice for various plumbing applications. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions and provide efficient fluid transport makes them a reliable and cost-effective option for plumbing systems.
CSST Pipes
CSST stands for Corrugated Stainless Steel Tubing. It is a type of flexible piping used for gas distribution in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. CSST pipes are made of thin-walled stainless steel tubing with a corrugated or ribbed outer layer. This corrugated design provides flexibility, allowing the pipe to be easily bent and routed around obstacles during installation.
Advantages of CSST Pipes
CSST pipes are commonly used to connect gas appliances, such as stoves, furnaces, water heaters, and fireplaces, to the main gas supply line. They offer several advantages over traditional rigid black iron or copper pipes:
- Flexibility: CSST pipes are highly flexible, making them easier to install compared to rigid pipes. They can be bent and shaped to fit around corners, through tight spaces, and around other structural elements, reducing the need for additional fittings and joints.
- Corrosion Resistance: CSST pipes are made of stainless steel, which provides excellent resistance to corrosion and rust. This makes them suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations, including areas prone to moisture or harsh environmental conditions.
- Lightweight: CSST pipes are significantly lighter than traditional rigid pipes, making them easier to handle and transport during installation. Their lightweight nature also reduces the strain on the overall gas distribution system.
- Reduced Labor and Installation Time: The flexibility and ease of installation of CSST pipes contribute to reduced labor and installation time. With fewer fittings and joints required, installation becomes quicker and more efficient, resulting in cost savings for both residential and commercial projects.
- Safety Features: CSST pipes are designed with safety features to withstand high-pressure events. They have a protective jacket or coating that helps prevent damage from external factors, such as UV rays, moisture, and chemicals. Additionally, CSST pipes are often equipped with an electrical bonding system to provide protection against potential electrical arcing caused by nearby lightning strikes.
It’s important to note that CSST pipes should be installed and handled by qualified professionals who are familiar with local building codes and regulations. Proper installation techniques, including appropriate support, bonding, and grounding, are crucial to ensure the safe and reliable operation of CSST systems.
CSST pipes have gained popularity in the gas distribution industry due to their flexibility, ease of installation, and corrosion resistance. However, it’s essential to consult with a licensed professional plumber or gas fitter to determine the suitability of CSST pipes for your specific application and to ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations.
ABS Pipes
ABS stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. ABS pipes are a type of plastic piping commonly used in residential and commercial plumbing systems. They are known for their durability, chemical resistance, and ease of installation. ABS pipes are typically black in color and have a smooth surface.
Advantages of ABS Pipes
Here are some key features and uses of ABS pipes:
- Durability: ABS pipes are known for their strength and durability. They can withstand high impact and pressure, making them suitable for various plumbing applications. ABS pipes are resistant to cracking and are less likely to shatter compared to other types of plastic pipes.
- Chemical Resistance: ABS pipes are highly resistant to chemicals, making them suitable for a wide range of plumbing applications. They can handle common household chemicals and are less likely to corrode or degrade when exposed to aggressive substances.
- Lightweight: ABS pipes are lightweight, making them easy to handle and install. This characteristic can significantly reduce labor and installation costs, especially in large plumbing projects.
- Noise Reduction: ABS pipes have excellent sound-dampening properties. They help reduce the noise caused by water flow within the plumbing system, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as residential and multi-story buildings.
- Ease of Installation: ABS pipes are relatively easy to work with and can be installed using simple tools and techniques. They can be cut, joined, and connected using solvent cement, making installation quick and efficient.
- Non-Toxic: ABS pipes are non-toxic and safe for carrying potable water. They do not leach harmful chemicals into the water supply, ensuring the delivery of clean and safe drinking water.
Applications of ABS Pipes
ABS pipes are commonly used for various plumbing applications, including:
- Drainage Systems: ABS pipes are often used for residential and commercial drainage systems, including soil and waste pipes. They effectively transport wastewater from sinks, toilets, and showers to the main sewer or septic system.
- Ventilation Systems: ABS pipes are also used for ventilation and air circulation systems. They can be installed to provide proper airflow and prevent the buildup of harmful gases, such as methane and sewer gases.
- Plumbing Fixtures: ABS pipes are suitable for connecting plumbing fixtures, such as toilets, sinks, and bathtubs, to the main plumbing system.
It’s important to note that ABS pipes are not recommended for hot water applications. They have a lower temperature resistance compared to other piping materials like CPVC or copper. Therefore, ABS pipes are primarily used for cold water supply and drainage systems.
When working with ABS pipes, it is crucial to follow local plumbing codes and guidelines and use appropriate fittings and solvent cement for secure and leak-free connections. If you are unsure about the suitability of ABS pipes for your specific plumbing needs, it is advisable to consult with a professional plumber or plumbing engineer.
Black Pipes
Black pipes, also known as black iron pipes or black steel pipes, are a type of rigid steel piping commonly used in plumbing and gas distribution systems. They are called “black” due to their dark appearance, which is a result of a black oxide scale on their surface.
Here are some key features and characteristics of black pipes:
- Material: Black pipes are typically made of mild steel, which is an alloy of iron and carbon. The carbon content gives the steel strength and rigidity, making it suitable for plumbing applications that require durability and resistance to high water pressures or gas distribution.
- Strength and Durability: Black pipes are known for their strength and durability. They can withstand high water pressures and are suitable for various plumbing applications, including water supply lines and gas distribution systems. Black pipes are often preferred for outdoor and underground installations due to their robustness and resistance to external forces.
- Corrosion Resistance: Black pipes are not inherently resistant to corrosion. Without any protective coating, they are vulnerable to rust and degradation when exposed to moisture and oxygen over time. As a result, black pipes are typically used for applications that do not require corrosion resistance, such as gas distribution, where a protective coating is unnecessary.
- Threaded Connections: Black pipes are commonly available with threaded ends, allowing for easy and secure connections using fittings. Threaded connections enable a tight seal between pipes, ensuring proper flow and reducing the risk of leaks.
- Compatibility: Black pipes are compatible with various pipe fittings, valves, and accessories commonly used in plumbing systems. This makes them versatile and adaptable for different plumbing configurations and installations.
- Gas Distribution: Black pipes are widely used for gas distribution systems, such as natural gas or propane supply lines. The strength and durability of black pipes, along with their threaded connections, make them suitable for carrying gas under pressure.
- Paintable Surface: Black pipes have a surface that can be painted or coated with protective paints to enhance their corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Adding a suitable coating can help extend the lifespan of black pipes in certain applications.
It’s important to note that black pipes are primarily used for non-potable water and gas distribution systems. They are not recommended for plumbing applications involving potable water due to the potential for rust and corrosion to affect water quality.
When working with black pipes, it’s crucial to follow local plumbing codes and regulations. Proper installation techniques, including appropriate supports, fittings, and joint connections, should be employed to ensure a safe and reliable plumbing system.
In summary, black pipes are rigid steel pipes commonly used for gas distribution systems and non-potable water applications. They offer strength, durability, and compatibility with threaded connections. While they are susceptible to rust and corrosion without protective coatings, black pipes are a reliable choice for specific plumbing and gas distribution needs.
UPVC Pipes
UPVC pipes, or unplasticized polyvinyl chloride pipes, are a type of rigid plastic piping commonly used in plumbing and drainage systems. They are made from PVC resin without the addition of plasticizers, which gives them their “unplasticized” or rigid nature. UPVC pipes offer several advantages in terms of durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation.
Here are some key features and benefits of UPVC pipes:
- Durability: UPVC pipes are known for their durability and long lifespan. They have excellent resistance to chemicals, corrosion, and abrasion, making them suitable for various plumbing applications. UPVC pipes can withstand harsh environmental conditions and are commonly used for both indoor and outdoor installations.
- Corrosion Resistance: UPVC pipes are highly resistant to corrosion caused by chemicals or corrosive substances typically found in plumbing systems. They do not rust or degrade over time, ensuring a reliable and maintenance-free plumbing solution.
- Lightweight: UPVC pipes are lightweight compared to traditional metallic pipes, making them easier to handle and install. Their lightness reduces labor and transportation costs during construction or renovation projects.
- Smooth Inner Surface: UPVC pipes have a smooth inner surface, minimizing friction losses and improving water flow efficiency. The smooth surface also prevents the accumulation of scale or deposits, reducing the risk of clogs and maintaining optimal water flow rates.
- Easy Installation: UPVC pipes are relatively easy to install due to their lightweight and rigid nature. They can be cut, joined, and connected using solvent cement or mechanical fittings. UPVC pipes require fewer supports and fittings compared to metallic pipes, simplifying the installation process and reducing overall project costs.
- Cost-Effective: UPVC pipes are generally more affordable than metallic pipes such as copper or stainless steel. Their lower material and installation costs make them a cost-effective choice for plumbing projects without compromising performance and durability.
- Insulation Properties: UPVC pipes provide some level of thermal insulation, helping to maintain the temperature of the fluid being transported. This feature can be advantageous in both hot and cold water applications, contributing to energy conservation and improved efficiency.
UPVC pipes are commonly used in various plumbing applications, including:
- Water Supply Systems: UPVC pipes are widely used for both potable and non-potable water supply lines. They provide a reliable and efficient distribution system for residential, commercial, and industrial water supply networks.
- Drainage and Sewerage Systems: UPVC pipes are commonly used for sewage and wastewater drainage systems. They have excellent resistance to chemicals and abrasion, making them suitable for transporting wastewater to the main sewer or treatment facilities.
- Ventilation Systems: UPVC pipes are also used for ventilation and air circulation systems. They are employed for removing stale air and providing fresh air exchange in residential and commercial buildings.
It’s important to note that UPVC pipes are not recommended for hot water applications due to their lower temperature resistance compared to other materials like CPVC or copper. For hot water supply lines, alternative materials should be used.
When working with UPVC pipes, it is crucial to follow manufacturer instructions, local plumbing codes, and guidelines. Proper solvent cementing techniques and appropriate fittings should be used to ensure secure and leak-free connections.
In summary, UPVC pipes offer durability, corrosion resistance, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness, making them a reliable choice for plumbing and drainage systems. Their lightweight nature and smooth inner surface contribute to efficient water flow, while their resistance to corrosion ensures a long lifespan.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right type of plumbing pipe is essential for the efficiency and longevity of your plumbing system. Each type of pipe discussed in this article has its own set of advantages and limitations. Consider factors such as cost, durability, temperature resistance, and specific application requirements when selecting plumbing pipes. Consulting with a professional plumber can also help you make informed decisions tailored to your unique needs. By understanding the characteristics of different plumbing pipes, you can ensure a reliable and efficient plumbing system for your home or business.