Nuts are one of the most widely used common types of fasteners. Wing-nut is a type of nut having two large metal wings to tighten or loosen using the hands. Wingnuts are also popularly known as butterfly nuts. Wing-nuts consists of a metal piece with a threaded hole. To hold two or more objects together, they are used with a wing bolt or wing screw. To assemble, the wing bolt is inserted through the objects, after which a wingnut is inserted on the end of the bolt and tightened by turning it. ASME B18.17 or DIN 315 provides the specifications relating to wing nuts (Fig. 1).
Characteristics of Wing Nuts
- The metal wings characterize this special type of not. They got their name from the presence of the tabs or wings.
- Usually, they are hexagonal in shape.
- Wingnuts have internal threads to engage with a bolt.
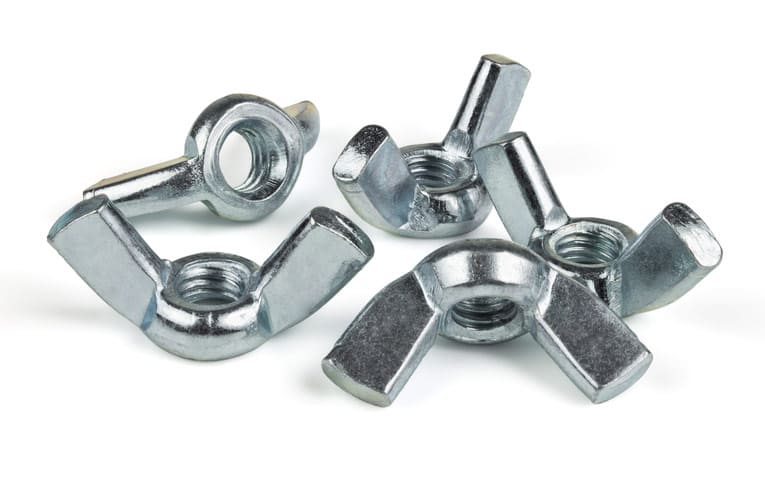

Working of Wing Nuts
The working of wingnuts is similar to other nuts. The basic function of holding two or more objects together is achieved when assembling the nut and bolt together. The main advantage of wing nuts lies in their easy installation and removal procedure. The presence of wings in wingnuts, help operators to grip and tighten easily. Wing nuts protrude from an integral round base with a flat bearing surface and are placed 180 degrees apart.
Types of Wing Nuts
Wingnuts are classified based on style and manufacturing method. ASME B18.6.9 classifies wing nuts into the following four types.
| Wing Nut Types | Manufacturing Method | Remarks |
| Type A | Cold-forged or cold-formed | Type A wing nuts are produced in regular, light, and heavy dimensional series |
| Type B | Hot forged | Type B wingnuts are available in three different wing styles. |
| Type C | Die-cast | Type C wing nuts are produced in regular, and heavy dimensional series |
| Type D | Sheet metal stamped | Type D wingnuts are available in three different wing styles. |
Stamped wing nuts have hollow wings that are open at the top while cold-forged wing nuts are solid parts.
Materials of Wing Nuts
Wing nuts can be manufactured from various materials. Some of the common materials are stainless steel, copper, brass, aluminum, plastic, steel, and other ferrous alloys. They may be zinc plated to increase corrosion resistance.
Size of Wing Nuts
The nominal thread diameter decides the size of a wing nut. Common sizes range from about #6 to 3/4″. Sizes less than 1/4″ are listed as a number size while sizes that are 1/4″ and larger are specified in inches, usually fractional rather than decimal. Not all types are available in all sizes. With the size of the wing nut, their dimensions vary. The following table in Fig. 2 provides typical dimensions of wing nuts.
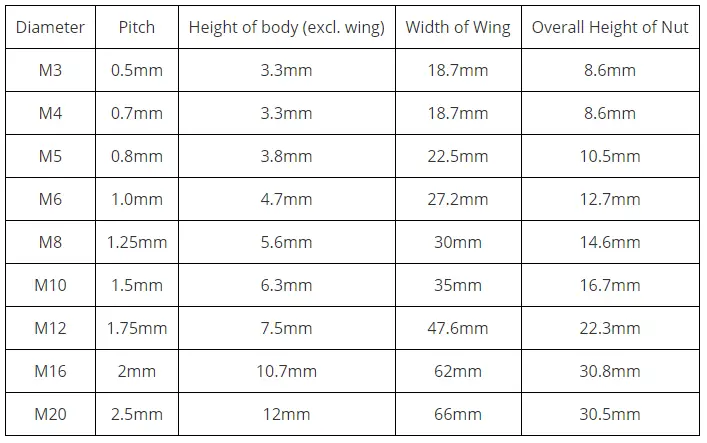
Application of Wing Nuts
Wing nuts are suitable for parts requiring frequent assembly and disassembly. They are mostly used for applications requiring less torque as wing nuts are hand-turned without using any tool. Depending on the application requirement, wing nuts can have a standard or metric thread. Common applications of wing nuts include:
- Car batteries
- Furniture
- Bicycle wheels
- Drum kits
- Boat accessories, etc
Advantages of Wing Nuts
Wing nuts provide a number of benefits like:
- Easy engagement and removal.
- Lower torque requirement for tightening.
- Easy tightening by hand without the need for a tool.
- Usually does not require heat treatment.
- Wingnuts can be used with or without washers.
Disadvantages of Wing Nuts
However, there are a few drawbacks of wing nuts. Some of the disadvantages are:
- Not suitable for vibrating applications.
- Not suitable for heavy load applications.

Classic
Explain me Strength test during Hydro test in Piping
I’ma attaching angle iron to angle iron. One of the pieces may be subject to considerable stress. I would like to use a wing nut. Your site states they are not for heavy use…but isn’t it the bolt that is subject to the stress and not the wing nut?
Excellent article. I want to thank you for this informative read. Good job, keep it up.