What is Buffing?
Buffing is a surface finishing process to shine metal, wood, or composites. It levels out the residues or excess products to provide a smooth surface and look. The buffing process usually uses a cloth wheel impregnated with loose abrasives as cutting compounds. The cloth buff carries the abrasive compound which removes the superficial material and imperfections to create a glossy uniform surface.
Buffing Process
The buffing operation is usually performed in two steps; an initial cut buff and then a finish buff.
Cut Buffing:
Cut buffing is the coarsest buffing operation. This is the preliminary buffing operation to remove major discontinuities and surface roughnesses. Surface preparation is required before the buffing operation to get better surfaces. With a very good surface preparation, the cutting buff will remove pits, course abrasive lines, deep scratches, etc.
Finish Buffing:
It is the final buffing operation after cut-buffing is performed. This step produces a very good luster on the surface and removes the fine lines generated during cut buffing. Finish buffing is usually quicker, easier, and less pressure process as compared to cut buffing.
Buffing Wheels
Buffing wheels that carry the required abrasive compounds are the transferring agent between the workpiece and the abrasive compound. To get the desired surface smoothness, the construction of the buff should match the workpiece. A harder buff is more aggressive and not flexible and so, usually used for flat surfaces. Whereas a softer buff is ideal for complex shapes as it is less aggressive.
As mentioned earlier there are two types of buffing operations; cut buffing and finish buffing. Both of these operations use different kinds of buffs. Cut buffing operation uses spiral sewn, set up wheels, sisals, and treated airways type of buffs. On the other hand, finish buffs use loose buffs, concentric sewn, airway, and Flannel types of buffs.
Buffing Compound
Buffing compound which is made of binders and abrasives comes in a solid bar or liquid form. Animal fats, grease-less waxes (glue and water), and petroleum-based products are normally used as binders. Proper use of a binder is very important for appropriate buffing operation as the binder decides the cutting ability, hardness, adhesion ability, and lubrication of the buff.
Common abrasive compounds for buffing operation are Aluminum Oxide, Tripoli, Iron Oxide, Silicon Carbide, Calcined Alumina, and Chrome Oxide. The following table in Fig. 1 provides some typical specifications of abrasives used in the buffing process:
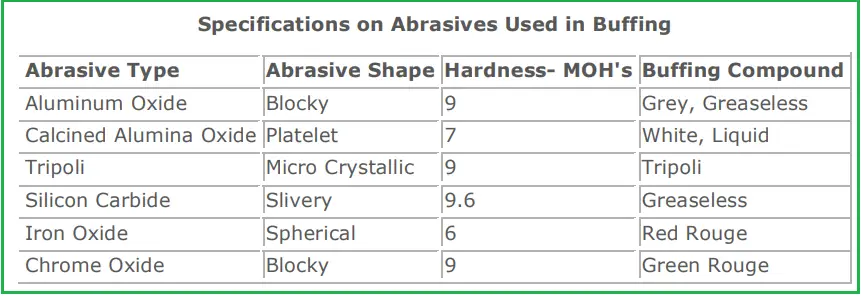
In general, Greaseless Compound, Stainless Compound, and Tripoli are used for cut buffing; while Green Rouge, White Rouge, Reg Rouge, and Calcined Alumina are used for finish buffing.
Surface Speed for Buffing
The surface speed is one of the important parameters for the buffing process as it decides the work rate speed, the pressure required, heat build-up, and the actual finish that will be produced. Depending on the material of the buffing operation, the surface speed for the buffing operation is decided. Buffing speed is usually measured in feet per minute or SFM unit. The following table in Fig. 2 provides some typical speed recommendations for various material types.
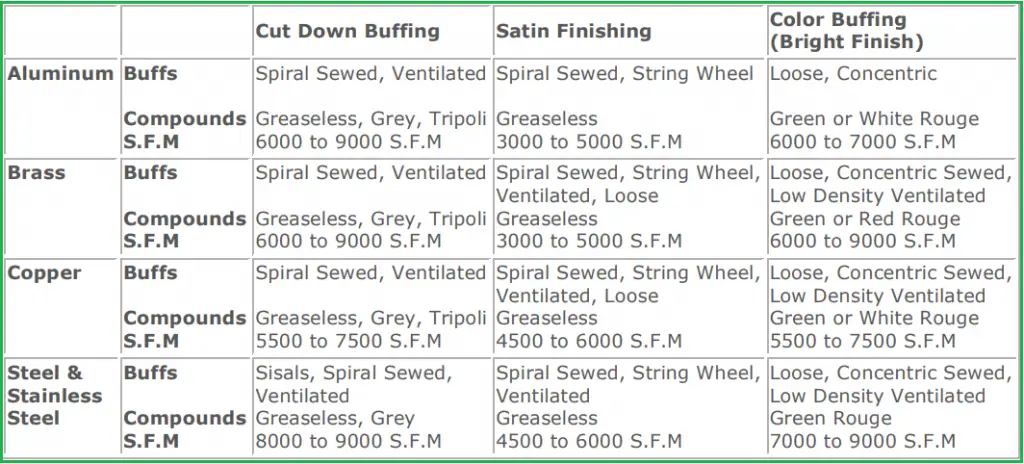
What is Polishing?
Polishing is also a surface finishing process performed using abrasives that are secured with glue or other adhesives to the wheel. Polishing is believed to be a more aggressive finishing process as compared to buffing. It has the ability to remove more superficial material from the workpiece surface which in turn allows for a brighter and more polished finish.
Differences between Buffing and Polishing | Buffing vs Polishing
The main differences between buffing and polishing are:
- Both buffing and polishing are surface finishing processes. Buffing uses loose abrasives on the wheel whereas polishing uses abrasives that are secured to the wheel.
- Polishing is usually performed using a high-grit abrasive whereas buffing is normally performed using a low or medium-grit abrasive.
Applications of Buffing and Polishing Process
The buffing and polishing process is widely used for removing scratches, coatings, oxides, imperfections, pits, etc from the surface of the workpiece. Major applications of the buffing and polishing process are found in:
- Tools, fixtures, and sports industries
- Household utensils and appliances sector
- Automobile, bicycle, motorcycle parts.








very valuable information.
Do you know if silicon car wax works on pipe exteriors?