What is a Drip Leg in Steam Piping?
Drip Legs are vertical piping pockets installed in steam piping to collect condensate. Installing drip legs in the proper location serves the purpose of a successful, water-hammer-free, system start-up.
Purpose of Drip Legs
Drip Legs are installed in steam mains to serve the following purposes:
- Drip Legs are used for removing entrained moisture from the steam transmission and distribution lines to ensure high-quality steam for use in various plant applications, while also preventing damaging and dangerous water hammer.
- As steam travels at high velocity through piping, moisture forms as the result of piping heat losses and/or improper boiler control resulting in condensate carryover.
- Drip legs are therefore located at points where condensate may accumulate to allow for drainage by gravity down to a steam trap for proper discharge from the system. Since condensate drains by gravity, drip legs must be located on the bottom of the piping and designed with diameters large enough to promote the collection.
Drip Leg Installation guidelines
Due to heat loss and system start-up energy consumption, condensate is formed inside the steam pipes. For proper working of the steam system, this condensate must be drained by installing drip legs in main lines at appropriate locations.
- Drip legs should be located at Vertical Lifts, Drops, or at the end of the steam line.
- In the straight run of piping every 30 to 50 meters.
- Installed directly ahead of the regulating or control valve, Manual Valves Closed for a Long Time.
- Ahead of expansion joints or elbows.
- Provide proper support (no sagging)
- Provide slope towards Drip legs.
Drip Leg Categories
- DRIP Applications: drip traps
- PROCESS Applications: process traps
- TRACING Applications: tracer traps. Steam tracing refers to using steam to indirectly elevate the temperature of a product using jacketed pipes or tubing filled with steam
Drip Leg Configuration
Because condensate drainage from steam systems is dependent upon gravity, the drip leg (Fig. 1) diameter is critical for optimum removal – larger is better.
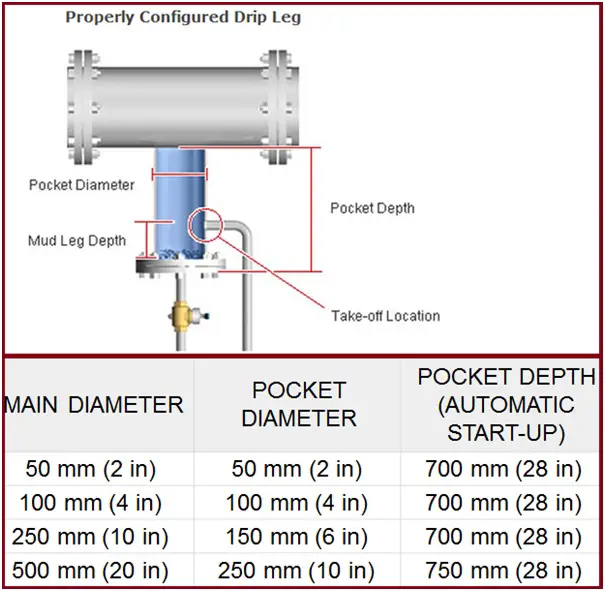
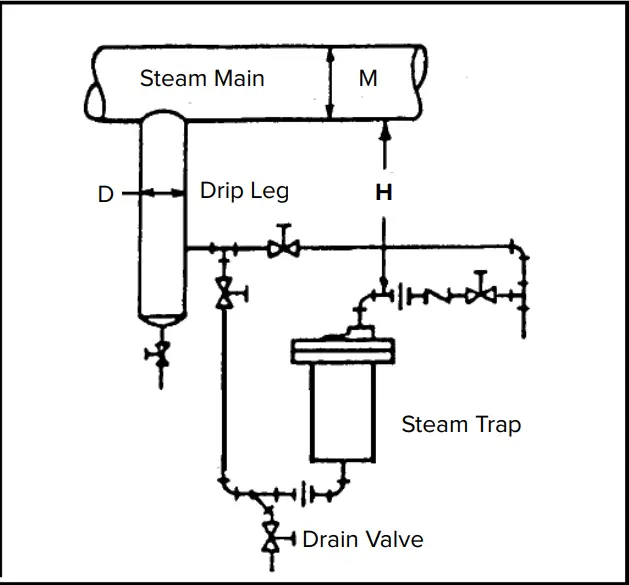
Fig. 2 below shows a typical loop used in a drip leg.
Selection of Drip Leg Sizes
The selection of drip leg sizes for draining the main steam line depends on the types of warm-up methods as mentioned below:
- Supervised Warm-up Method: Warming up of the power plant principal piping normally follows this method. Such lines are warmed up only once in a lifetime and hence long drip leg is not required.
- Automatic Warm-Up Method: Such a warm-up method is used for frequent steam use leading to the requirement of bigger drip legs. A static head (dimension H in Fig. 2) is used in such cases.
Fig. 3 below provides the recommended Drip leg Sizes (Drip Leg Diameter and Leg Length) with respect to the main steam piping size.
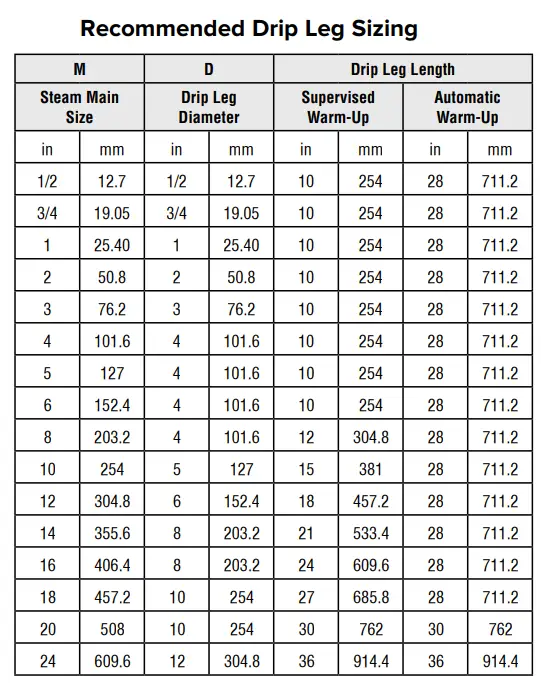
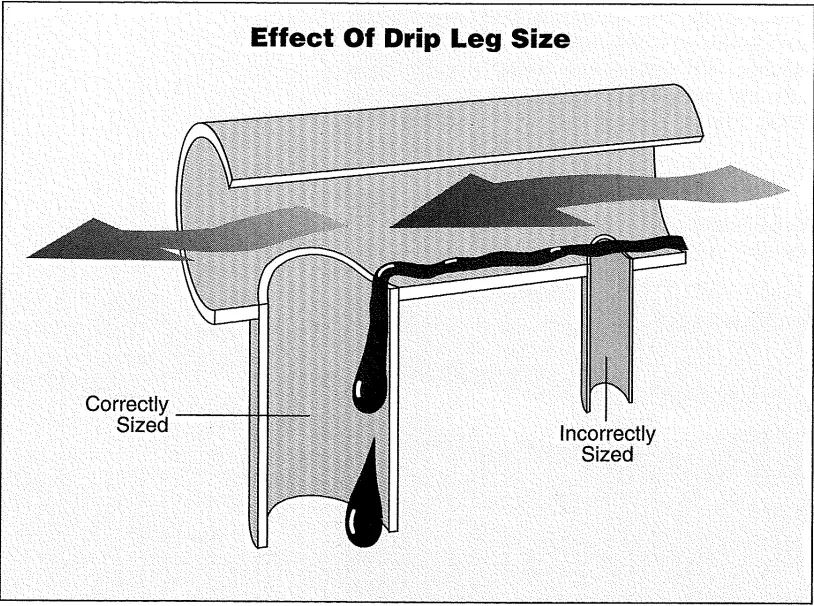
A carefully designed drip leg enables steam traps to effectively drain the condensate from steam mains. For that, the drip legs should be large enough to allow the condensate to drop out of the steam at the pipe bottom. Recommended drip leg sizing table (Fig. 3) provides a good reference for such a scenario. In case the drip leg is not sized properly, the condensate will blow along with the steam without separating out as shown in Fig. 4.
Click here to know about Steam Traps: Steam Traps: Definition, Types, Selection, Features, Codes & Standards

Helpful material …
useful information , and thanks for your post.
Hi Anup,
Drip length on every 50m straight length will be too short, Recommend on 100m straight piece of pipe.
The guide is 30m to 50m for Steam pit traps (Drip-leg).
Mathematical calculation of drip leg sizing & pocket depth and distance between drip leg assembly on pipe rack. please guide.
Why there should be drain line? Is it an absolute necessity??
Your effort is very much appreciated as you are doing awesome work for society. In this topic, I want to know about the selection of drip leg length and its effect on steam trap action….
I mean to ask the please elaborate if possible.