The Indian Boiler Regulations (IBR) are a crucial set of standards that ensure the safe and efficient operation of boilers and pressure vessels in India. Designed to protect life, property, and the environment, these regulations are a cornerstone of industrial safety and operational excellence. The IBR applies to all industries, both public and private, that use boilers. This includes sectors involved in various processes, heating, and power generation.
What is IBR (Indian Boiler Regulation)?
The Indian Boiler Regulation, or IBR, is an independent body that provides boiler manufacturing guidelines in India and regulates them. Indian Boiler Regulation falls under the IBR Act 1950. This law is accepted all over India except Jammu & Kashmir. The IBR is basically a construction code that specifies the design, material, fabrication, inspection, and testing requirements for boiler and boiler-connected parts for use in India.
The Indian Boiler Regulations (IBR) set standards for the materials, design, construction, inspection, and testing of boilers and their components in India. These standards are developed and regularly updated by the Central Boilers Board to keep pace with advances in boiler technology.
Manufacturers of materials and components used in boilers, such as piping, mountings, fittings, and valves, must adhere to the Indian Boiler Regulation of 1950 (IBR). The IBR also covers:
- Steam receivers,
- Steam separators,
- Steam traps,
- Accumulators and similar vessels
- Heat exchangers,
- Converters,
- Evaporators and similar vessels in which steam is produced
The IBR is enforced by the Indian government, and any imported materials or equipment must come with a certificate proving compliance with these regulations. This certificate must be issued by an authorized inspecting authority designated by the Indian government.
IBR or Indian Boiler Regulation Scope
The Indian Boiler Regulation or IBR covers the below-mentioned industrial equipment in steam services:
- Boilers along with the feed piping from the feed pump
- Full Steam piping
- Steam receivers
- Heat exchangers
- separators
- converters
- steam traps
- evaporators and similar vessels in which steam is generated
- accumulators and similar vessels
What is a boiler?
As per IBR, any vessel exceeding 22.5 liters (five gallons) & generating steam is considered a Boiler
Why IBR approval is required?
The primary objectives of the Indian Boiler Regulations are:
- Safety: To ensure that boilers and pressure vessels are designed, constructed, and operated in a manner that minimizes risks to life and property.
- Efficiency: To promote efficient operation and maintenance practices that enhance the performance and longevity of boilers.
- Compliance: To establish clear and enforceable standards that align with international best practices and legal requirements.
If these norms as per the IBR regulation are violated, then legal action may be taken against the concerned by the IBR authorities. In case any accident occurs at the site and then IBR norms are not followed, the matter will be complicated, so it is required that IBR piping is designed, fabricated, erected, & hydro-tested as per the latest IBR code.
Manufacturers and suppliers of boilers and associated components must comply with the Indian Boiler Regulations if those items are used in India. The boiler construction has to be under the supervision of an Inspecting Officer and must be inspected at all stages of construction.
Advantages of IBR Approval
There are various advantages of IBR Boilers as listed below:
- As the complete system is manufactured using IBR-approved materials, the Risk of an explosion is minimized.
- As approved by IBR, there will not be Legal complications which in turn ensures peace of mind
- IBR design and construction compliance ensures longer tube life & lesser breakdown
- Finally, Overall Safety Assurance. Indian Government-certified third-party inspection.
Which piping services follow IBR rules?
Services that follow the IBR rules are steam, condensate, & boiler-feed water.
The above services are further classified as follows:
STEAM Piping
- 1) High-high pressure steam (HHP).
- 2) High-pressure steam (HP).
- 3) Medium-pressure steam (MP).
- 4) Low-pressure steam (LP)
CONDENSATE Piping
- 5) High-pressures Condensate (HC).
- 6) Medium pressures Condensate (MC).
- 7) Low-pressures Condensate (LC).
BOILER FEED WATER Piping
- 8) High-pressure boiler feed water (HP)
- 9) Medium-pressure boiler feed water (MP)
- 10) Low-pressure boiler feed water (LP)
The following conditions should be fulfilled to follow IBR norms.
1) < 3.5-kg/cm2 IBR approval is not required. <10” ID
2) < 3.5-kg/cm2 IBR approval is required. >10” ID
3) > 3.5 kg/cm2 IBR approval is required. <10” ID
Applicable pressure, Temperature, and Hydrotest for the above category of services are as below
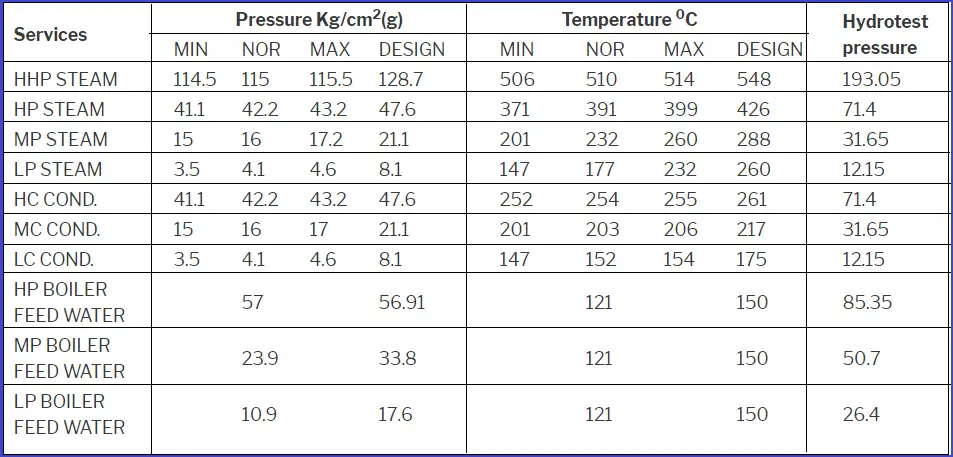
What is the procedure for Indian Boiler Regulation (IBR) approval?
The procedure of IBR is as under
- IBR packages to be prepared
- Necessary drawing and inspection fees as per IBR
- Drawings are to be sent to the divisional boiler inspector.
- Construction can start work on fabrication & erection only when the drawing is in the approval stage.
- After drawing approval, respective contractors have to get fabrication permission & welder approval. After taking an introductory letter, the contractor can start work.
- After getting approval, the material used for the job has to be offered to the divisional boiler inspector
- After completion of work NDT (Non-destructive testing), approval is to be taken from CIB (chief inspector of boiler)
- After NDT approval, lines are to be offered for Hydrotest to the divisional boiler inspector
- After the hydro test, the job can be considered as work completed.
- The design engineering team is responsible for complete approval from the drawing stage still Hydrotest & final closeout of the job.
Documents attached in an IBR package are as mentioned below:
- Drawing Index
- Pipe data
- IBR Design packages general notes.
- Pipe wall thickness table.
- Pipe wall thickness calculation sheet.
- Piping class report.
- Pipe Drawings.
The material should be used with an IBR stamp. The material used for IBR are same as per ASTM STD e.g. A106 Gr B or A671Gr CB60 for pipes but the only difference is that the material must come with the following certificate
- Form IIIA for pipes.
- Form IIIC for fittings.
The above materials must be inspected by the boiler inspector in the vendor shop at that stage & stamped.
As per Indian boiler regulation, all pipes shall be commercially straight and free from longitudinal seaming, grooving, blistering, or other injuries and surface marks. The ends of the pipes shall be cut square. The installed pipes shall be adequately supported.
As the Indian Government has strictly enforced the IBR, all equipment and materials must be imported into India with an accompanied certificate confirming that all imports meet the IBR.
What does IBR service mean?
IBR services mean the inspection, testing, and certifying services that include but are not limited to:
- Design review and approval of pipe fittings and valves (Form III-C) in IBR services
- Inspection, testing, and certification of pipes (Form III-A) in steam services
- Inspection, testing, and certification of materials (Form IV-A)
- Witnessing tests required by the Indian Boiler Regulation 1950, or the Code approved by the Central Boilers Board for specific products, for IBR purposes only
- Supervision of the Fabrication process and weld quality inspections
- Witnessing the welding of the test specimen for the procedure and/or welder certification
- Witnessing all nondestructive and destructive tests of welded test pieces in laboratory
- Certification of welders qualification and welding procedures
- Re-certification of welders (Form XII and XIII)
There are some approved agencies that provide IBR services.
Note that the Indian boiler regulations are periodically updated to reflect technological advancements and changes in industry practices. Recent amendments have focused on enhancing safety measures, incorporating advanced technologies, and aligning with international standards. Keeping abreast of these updates is essential for operators and industry professionals to ensure ongoing compliance.
To sum up, the Indian boiler regulations play a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of boilers and pressure vessels across various sectors. By adhering to these regulations, industries not only comply with legal requirements but also contribute to a culture of safety and operational excellence. Whether you are a boiler operator, a maintenance professional, or an industry stakeholder, understanding and implementing the IBR is essential for safeguarding lives, protecting assets, and enhancing performance.
Latest IBR Standard
At the time of updating the article, the latest available IBR standard is IBR Amendment 2020, which was published and came into effect in September 2020. The IBR standard and all its amendments can be accessed at https://wbboilers.gov.in/boiler-regulations-1950. So, if you are interested in exploring more about IBR requirements, kindly visit this link.
Differences between IBR and ASME B31.1
The Indian Boiler Regulations (IBR) and ASME B31.1 are both critical standards for boiler and pressure vessel safety, but they serve different purposes and originate from different contexts. Here is a comparative table summarizing the differences between Indian Boiler Regulations (IBR) and ASME B31.1:
| Aspect | Indian Boiler Regulations (IBR) | ASME B31.1 |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | IBR is developed by the Central Boilers Board of India | ASME B31.1 is developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) |
| Jurisdiction | IBR is applicable specifically to India | ASME B31.1 is applicable and recognized internationally |
| Scope | It covers all types of boilers and pressure vessels used in India | ASME B31.1 focuses on power piping systems related to boilers, including design and construction |
| Focus | Safety, compliance with Indian standards, and certification requirements are the main aims of the IBR standards. | ASME B31.1 provides importance on the design, materials, fabrication, installation, and testing of power piping systems |
| Design Codes | Includes specific requirements for boiler design and construction materials in alignment with Indian standards | Specifies design, materials, and construction requirements according to ASME standards |
| Construction Requirements | IBR mandates compliance with Indian codes and certification processes | ASME B31.1 provides detailed guidelines for piping system integrity and safety |
| Inspection | Requires thorough inspections and certification by authorized Inspecting Authorities in India | Inspection and testing follow ASME guidelines, often involving third-party agencies |
| Certification | Materials and equipment must be certified to meet IBR standards; certification is required for imports | Certification is handled by accredited bodies adhering to ASME’s quality and safety standards |
| Application | Enforced by Indian regulatory authorities; applies to equipment used within India | Used internationally but primarily in the U.S. for power piping systems |
| Enforcement | IBR ensures compliance with Indian safety and operational standards | ASME B31.1 is enforced through industry practices and regulations; often adopted voluntarily |
| Legal Framework | Part of Indian legislation and regulatory framework | Part of ASME standards, which influence industry practices globally |
| Documentation Requirements | Requires specific documentation for compliance and import certification | Requires detailed documentation for design, construction, and testing of piping systems |

Need to contact u urgently,
Please call me at+91 99996 22266
Sir,
Kindly let me know what should be design pressure is working pressure of Steam is 12-15 kscg and 125 kscg respectively and in which code I can find this multiplication factors.
Dear Sir / Madam,
Is there any IBR stipulation on minimum length of Boiler Tubes (Fire Tube) for inspection and certifications / stamping by boiler inspectors.
Regards
S B Bhuyan
Hi, we have a waster hear boiler coil . At shop once equipment is tested and IBR inspected, its header manifold are required to be cut due to transportation limits, hence once it reaches at site, it will again have field weld of the manifold header which were already tested but had to cut.
Now question is once again welding is done at site, so again IBR certification is required for this equipment. can someone answer this ?
does gakset and stud &nuts in IBR lines are also need to attested form 3C.
no
Dear Sir,
We manufactured Boiler Circulation Pump outside India but this pump will be delivered to India. Our welders are certified as per country of origin. Does this mean our welders are obliged to be certified as per IBR 1950 as well as per Chapter XIII. Is it this chapter referring to Boiler itself and not the pump. Thank you for answering in advance.
Dear sir,
I need ur help regarding condensate line if comes under ibr regulation,in which ibr chapter it is mention.
why is 10.54 kg/cm2 a limiting condition for class 150
Why only steam generating vessel exceeding 22.5 liters comes under IBR? on what basis this value (22.5 litres) is decided?
Does IBR Certification is also required for Vortex flow meters for steam? If yes, where to approach. Any website reference.
For Pressure & Differential pressure transmitter IBR is required ? IF NO- Then why ? if -Yes then what is the procedure to get it done.
Dear Sir,
Please let me know if IBR is applicable for Thermowells in IBR piping.
Thank you in advance!
Siva Prasad Babu
I B R रुल्स प्रमाणे स्टीम टेस्ट बद्दल माहिती पाहिजे आहे.
What does IBR code says about stress analysis of steam piping
Could someone clarify the IBR regulations concerning isolation valves for Pressure transmitters —particularly in terms of placement and compliance?
At what pressure and temperature thresholds is a double isolation valve arrangement typically recommended or adopted?
Also, is double isolation applicable only at main inlets and outlets, or should it be considered for drain lines as well?
If possible, please share the relevant clause or section from the IBR Regulation.
if we working on a boiler drain line, then we have to taken approval from boiler inspector or not