What is a Seamless pipe?
Seamless pipe is made from a round steel billet (solid cylindrical hunk of steel that is cast from raw steel). This billet is then heated, stretched out, and pushed or pulled over a form. It is then pierced through the center with a die and mandrel which increases the inside diameter and reduces the outside diameter. Even though seamless pipes are manufactured in a variety of sizes, with an increase in pipe diameter the production cost increases. The name seamless comes from its absence of a seam. Seamless pipes are widely used in process piping, power piping, shipbuilding, pressure vessel, construction, and chemical industries.
What is a Welded Pipe?
Welded pipe is made by cold forming flat strips, sheets, or plates into a round or circular shape by a roller or plate bending machine. The pipe is then welded with or without filler material using a high-energy source. Welded pipes can be produced in large sizes without any size restriction. Welded pipes are normally used for the transportation of water, oil, or gases in large quantities.
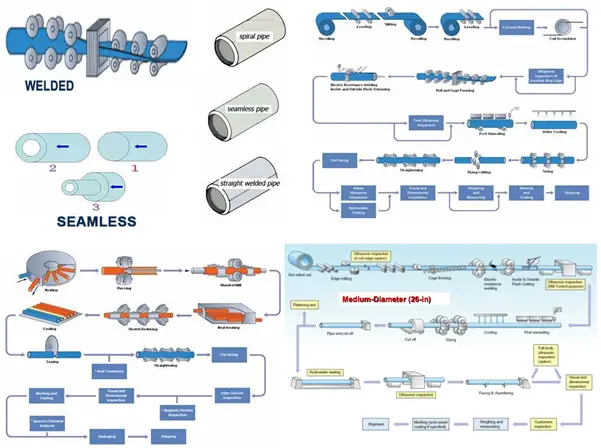
Seamless vs Welded Pipe
From the above paragraphs, it is obvious that seamless and welded pipes differ in their manufacturing process. The other differences are listed in the below-attached table.
| Sr. No | Parameter | Seamless Pipe | Welded Pipe |
| 1 | Strength | Seamless pipes are able to withstand more pressure and load as there is no weak seam. | Due to welding, welded pipes are believed to withstand 20% less pressure and load as compared to seamless pipes. |
| 2 | Length | Seamless pipes are relatively shorter in length due to manufacturing difficulties. | Welded pipes can be manufactured in long continuous lengths. |
| 3 | Size | Seamless pipes are usually manufactured for a nominal size of 24 inches or less. | There is no such size restriction on welded pipe production. |
| 4 | Corrosion Resistance | Sealless pipes are less prone to corrosion means more corrosion-resistant. | The weld areas of the welded pipes are more prone to corrosion attacks, which means less corrosion resistance. |
| 5 | Surface Quality | The surface quality of seamless pipes is rough due to the extrusion process | Welded pipes have a smooth high-quality surface as compared to seamless pipes. |
| 6 | Economy | Costlier | More economic |
| 7 | Production Process | The production process of seamless pipe is quite complex with a long procurement lead time | The welded pipe production process is comparatively simpler with a short procurement lead time. |
| 8 | Tests | Seamless pipes do not require testing for weld integrity. | Welded pipes must be tested before use. |
| 9 | Application | Seamless pipes are widely suitable for high pressure, temperature, and corrosive environment | Welded pipes are normally used for less corrosive and low-pressure environments. |
| 10 | Availability | Less availability, limited material types, longer delivery time. | Readily available for various different materials; shorter delivery time. |
| 11 | Wall Thickness | Seamless pipes have inconsistent wall thickness across the length, thicker so heavier | Wall thickness for welded pipes is more consistent than seamless ones, thinner |
| 12 | Ovality | Seamless pipes provide better ovality, roundness | Welded pipes provide poor ovality and roundness as compared to their seamless counterpart. |
| 13 | Internal surface check | Checking not possible | The internal surface for welded pipes can be checked before manufacturing |
Pipe Selection, Welded or Seamless?
Even though improved manufacturing methods of recent times can produce welded pipes comparable to seamless pipes, still seamless pipes are preferred in a maximum of cases. However, for large-size piping applications, (> 24-inch NPS) welded pipes are mostly preferred due to less cost. Along with cost, various other parameters like diameter-to-thickness ratio, availability, corrosion resistance, etc. are considered for pipe selection.
Few more useful resources for you..
Other differences between piping terms or items
Piping Design and Layout Basics
Piping Stress Analysis
Mechanical Design Basics
Process Design Basics
Instrumentation Design Basics
Civil Design Basics
Pipeline Design Basics
Piping Material Basics

Thanks for sharing your knowledge
Nice information
Hi
We r propeller shafts mfr
Can you send me an article on various piping supports and their functions / selection.? Include photographs or sketches where possible.!
Thanks for sharing
Great
please let me know whether is welding desirable to make long seamless pipe?
Is it possible to bend a seamless pipe of 76mm(ID) with a pipe bending machine?
I see your blog it’s attractive…
Very Nicely explained