Pipelines handling multiphase flows of gas and liquid, slug flow can pose significant operational challenges. To mitigate these challenges, slug catchers serve as critical components in pipeline systems. In this article, we will explore what slug catchers are, how they work, their types, and their benefits.
What is a Slug Catcher?
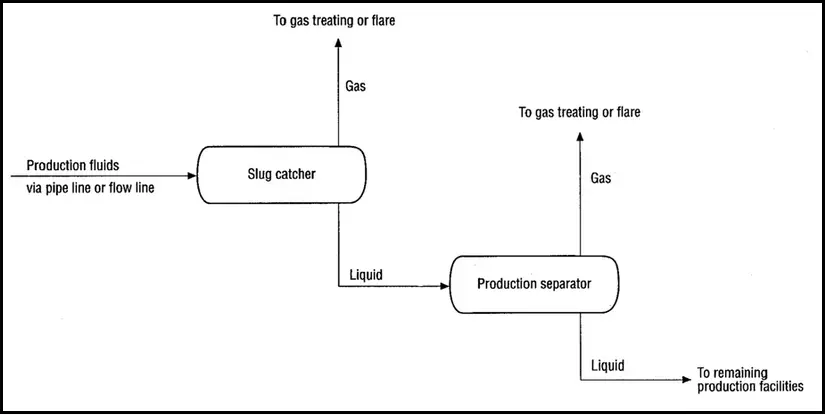
A slug catcher is a piece of static equipment in the form of a vessel or piping network. It contains sufficient buffer volume to handle the largest expected slug from the oil & gas pipeline systems or flowlines. Flowlines carrying multiphase fluids (Crude Oil, Gas, Water, mixtures) often form damaging slugs. Slug catchers protect the equipment and support from abrupt failure due to forces generated because of slug flow. They are normally located (Fig. 1) before transferring the fluid into the processing equipment.
Benefits of Slug Catchers
Slug catchers are widely used in multiphase flow lines to serve the following functions:
- To protect the downstream system and equipment from the damaging effects of slug flow.
- To efficiently manage high volumes of liquids (slugs) generated.
- To separate part of the liquid from gases in multiphase gas processing plants (Product Separation). The preliminary separation of liquid and gas phases occurs due to the density difference inside the slug catcher.
- To reduce the probability of further slug formation in the downstream processes.
- To allow the liquid to follow into downstream facilities and equipment at a lower rate which can be properly handled.
- Slug catchers can also work as temporary storage devices.
- To stabilize the flow by capturing the generated slug.
- To increase efficiency by preventing slugs from disrupting flows.
Depending on the type and frequency of slug generation, slug catchers can be used permanently or intermittently. When slugging behavior is difficult to predict, they are used continuously. However, for purposely generated slugs like during pipeline pigging operations, slug catchers are used during requirement only.
Types of Slug Catchers
Based on their design construction, four types of slug catchers are found in industrial use. They are:
- Vessel Type Slug Catcher
- Finger Type Slug Catcher
- Stored loop type/ Parking Loop type Slug catcher and
- Hybrid Slug Catcher
1. Vessel Type Slug Catcher:
As the name suggests, vessel-type slug catchers are basically two-phase separation vessels. The main design consideration is the vessel volume to contain the largest expected slug from the pipelines. However, the vessel-type slug catchers must be strong enough to sustain the high pipeline pressures. The vessel can be horizontal or vertical. Vertical vessels have more efficiency as compared to horizontal vessel slug catchers. They are simple for design and maintenance but with an increase in volume requirement and pressure, this equipment becomes too costly.
2. Finger Slug Catcher or Harp Slug Catcher:
A number of large-diameter pipes are used to construct a Finger type or Harp slug catcher. As piping design to withstand high pressure is easier, finger-type slug catchers are widely used due to their economic reasons. Fig. 2 below shows a typical example of a Harp Slug catcher.
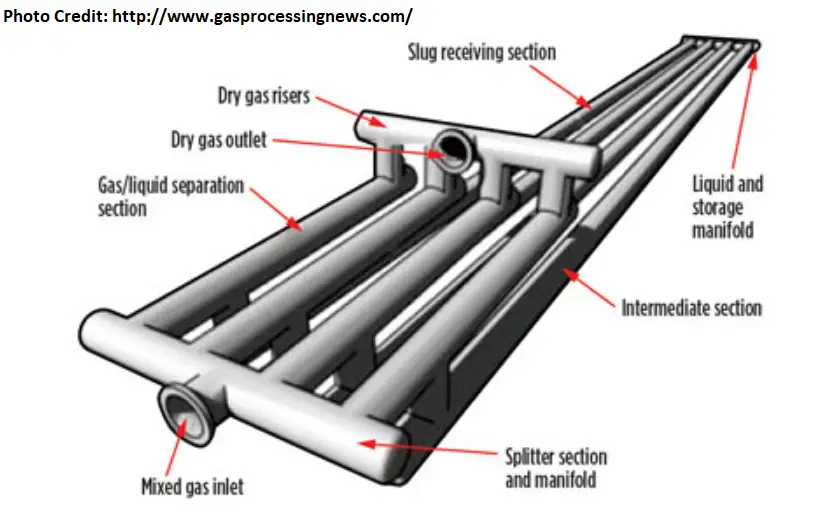
Finger-type slug catchers consist of
- Fingers have three distinct sections
- Gas/Liquid Separation Section
- Intermediate Section, and
- Storage Section
- Gas Risers that are connected to each finger at the transition zone between separation and intermediate sections.
- Gas equalization lines are located on each finger within the slug storage section.
- Liquid header configured perpendicular to the fingers.
3. Stored loop type / Parking Loop type Slug catcher:
The features of both the vessel and finger types are combined into a Parking Loop slug catcher. The Separation of the gas and liquid phases occurs in the Vessel, while the parking loop-shaped fingers provide the buffer volume for storing the liquid.
4. Hybrid Slug Catcher:
The high efficiency of a vessel separator and the large storage volume of a harp slug catcher combines in a hybrid slug catcher.
Slug Catcher Type Selection
The basic selection between the “Vessel Type” and “Finger Type” is done considering
- Economical aspects (Slug Catcher Design and Installation costs)
- Equipment characteristics
- Volume Requirement (Thumb rule is to use Vessel type for volumes less than 100 m3. For high steady-state gas flow: vertical type and for low steady-state gas flow: horizontal type)
- Site Conditions like Space Requirements. Finger-type slug catchers occupy huge plot space.
- Design Pressure (Low Design Pressure-Vessel Type; High Design Pressure-Finger Type)
- Transportation feasibility, etc.
Slug Catcher Design Steps
As Slug catchers are used in both oil/gas multiphase production systems and in gas/condensate systems to handle the dangerous effects of slugs, they must be properly sized to dampen the slugs to a level that the downstream processing equipment can easily process. Information on liquid handling rate, pigging frequency, slugging possibility, slug duration, ramp-up rates, etc is required to estimate the required size of a slug catcher. To determine the slug arrival duration, volume, and other relevant information, a transient simulation of the arrival scenarios like pigging, flow ramp-up, etc. is normally performed. The main slug catcher design steps consist of the following:
- Determination of Slug Catcher function and location.
- Based on Design criteria and data, estimating slug catcher volume (Dimensions)
- Selecting Slug catcher types or configurations considering the design and economic consideration
- Feasibility study
Slug Catcher Working Principle
The basic workings of a slug catcher is explained nicely in the following animated video:
To conclude, slug catchers are indispensable devices for managing slug flow in pipelines, contributing to flow stability, equipment protection, and overall operational efficiency.
Some Handpicked Articles for you..
How to Model Slug Flow Loads
Slug Flow and Slug Flow Analysis
Introduction to Pressure Surge Analysis
Pressure Transient Analysis for Liquid HC Pipelines

Hi Anup,
Thanks for this article.
Could you tell me please what are stress considerations for Finger type slug catchers desifn?
Is there any specific phenomenon to consider for stress analysis?
Thank you.
Regards,
A complete stress analysis is required based on where the slug catcher is physically located. We use HYSYS for this work. The 44,000 bbl unit we designed and engineered for CNOOC in S. China is subjected to wind and earthquake forces as well as high temperatures. This study is essential for the design of the foundations and the pipe supports.
Thanks for the explanation. I have some questions regarding the finger-type slug catcher:
1- Could you please explain what type of pipe supports should be used for figer-type slug catchers?
2- In which locations the line stop supports should be placed in this type of slug catchers?
3- Should the base plate of the pipe support and structural support(secondary support) under the slug catcher have the same slope as the slug catcher?
TECorp slug catchers all have a 1% slope from the inlet header to the outlet and the pipe supports are fabricated with this slope and are marked so they’re orientated correctly. The supports themselves include fixed supports at the inlet header and sliding supports to the outlet. These have a base plate that is anchored and grouted to the foundation supports with an upper support that has PTFE, or similar material that slides on the highly polished base plate. Absolutely essential for thermal expansion
What type of dished head can you use for a pressure vessel slug catcher?
TECorp International in Houston, TX – who produced the video with shows how the slug catcher operates in the Liwan Offshore Receiving station – is an industry recognized expert in slug catcher design, engineering and fabrication.. At 44,000 bbls/d, it is the largest harp-style slug catcher in the world and has been in operation since 2013 and was the subject of a technical paper at the 2013 Offshore Technology Conference.
Can you please provide us with the calculation steps of how to design vessel type slug catcher?