The objective of the commissioning
- To bring the constructed/installed system to deliver the desired function.
- Pipeline commissioning means introducing crude/ product/Gas in the pipeline from originating station, filling the entire length, and then start delivering to the receipt system.
What do we need prior to commissioning?
- The pipeline and associated facilities are completed in all respect
- All Fire and Safety equipment/facilities are tested and commissioned
- Availability of dedicated communication
- Statutory Clearances obtained
- Availability of Product (HSD)/ Crude oil – Not less line-fill
- Required Manpower is placed at all locations
- Availability of water and its disposal plan
- Availability of a dedicated commissioning team
Critical issues in commissioning a Petroleum Pipeline
- The movement of hydrocarbon in an empty pipeline can generate static current.
- Hydrocarbon Vapor mixed with oxygen may lead to an explosion.
- There may be the formation of an Air / Vapor pocket that may get compressed leading to a rise in pressure.
- Air/vapor pocket may explode in the receiving tank leading to damage to the tank roof seal.
- Leakage of any hydrocarbon may lead to fire or damage to the environment.
Properties of Hydrocarbons
Flash Point:-The flash point of a volatile liquid is the lowest temperature at which it can vaporize to form an ignitable mixture in air.
Vapor Pressure:-The vapor pressure of a liquid is the pressure exerted by its vapor when the liquid and vapor are in dynamic equilibrium. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with lower vapor pressure.
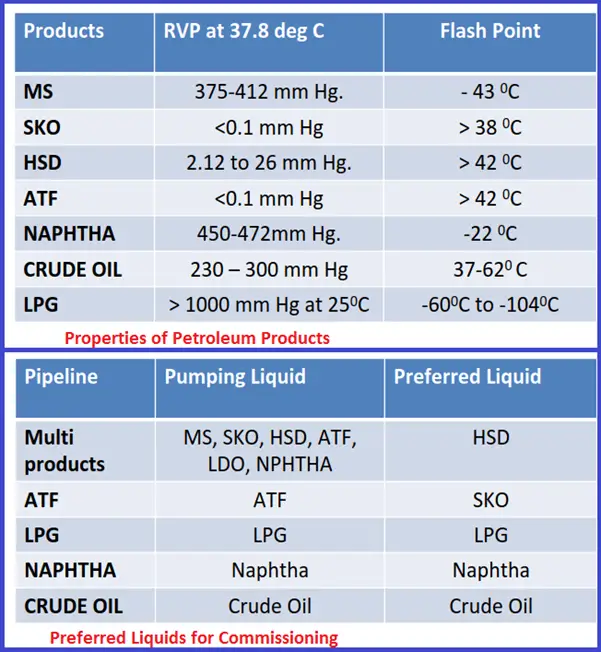
Properties of Petroleum Products and Preferred Liquid for Commissioning:
What is a PIG?
A device that moves through the inside of a pipeline for the purpose of cleaning, dimensioning, sealing, and inspecting.
The objective of Pigging
Pigging for New Pipeline-
- Remove debris
- Verify ovality, dent, etc
- Water filling & dewatering after hydro‐testing
- Sealing of product or water during commissioning
Pigging for In-Service Pipeline-
- Maintain line efficiency
- Corrosion control
- Check dents, buckles, and any other internal abnormalities
- To minimize interface generation between two dissimilar products
- To avoid cross‐contamination
- To evacuate the pipeline
Conventional / Utility Pigs – Different types
- Various components are fitted on a mandrel.
- It can be uni‐directional or bi‐directional
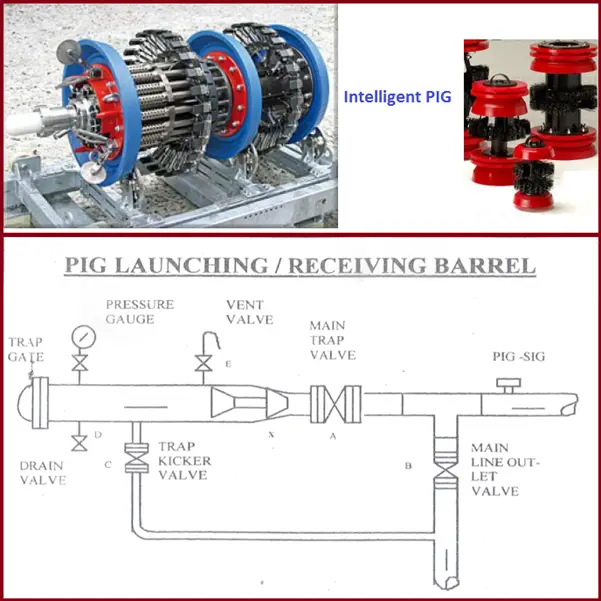
Intelligent Pig (Fig. 2)
- To record bends, dents, ovality, bend radius & angle.
PIG Launching / Receiving Barrel: Refer to Fig. 2
Commissioning of a Gas Pipeline
A gas pipeline is treated as Tank. However, before taking gas in the Pipeline, it is to be made moisture and oxygen-free.
Commissioning Steps
Drying – Purging of super dry air: Compressed Super dry air is purged using air compressors with accessories viz. Moisture Separator, Oil Separator, and Dryer. The air shall be supplied in the pipeline at (-) 20 deg. C dew point. Super dry air with dew point (-) 20 deg. C will have sufficient capacity to absorb water vapor to the extent of 30 % of the desired capacity.
Vacuum Drying: The process utilizes a high-capacity vacuum to reduce pressure within the Pipeline to a level from 760 Torr to 40 Torr. At this pressure (40 Torr), any water within the pipeline will start boiling and vaporizing. Air left inside the Pipeline is subjected to a vacuum of 40 Torr, and the water vapor will expand approx. 18.8 times, which will be displaced using high-capacity vacuum booster pumps (rated capacity 5000 CuM/Hr)When the vacuum of 7.6-10 Torr is achieved, it is confirmed that the whole pipeline system has been dried to the required level.
Nitrogen Purging: At vacuum level 7.6 Torr and dew point (-) 20 deg.C, the oxygen content inside the Pipeline is 0.20%. To further dilute the oxygen content, nitrogen purging is done almost 13 times more than pipeline volume. This will reduce the oxygen content to 0.015%, which is considered negligible.
Now the Pipeline system is ready to receive Gas.
Online Video Courses related to Pipeline Engineering
If you wish to explore more about pipeline engineering, you can opt for the following video courses
- Pipeline Stress Analysis using Caesar II
- Design of Underground Pipeline Supports
- Hot Tapping in Piping and Pipeline Industry
- Buried or Underground Pipeline Stress Analysis using Caesar II
Few more Pipeline related useful Resources for You..
Underground Piping Stress Analysis Procedure using Caesar II
Comparison between Piping and Pipeline Engineering
A Presentation on Pipelines – Material Selection in Oil & Gas Industry
Corrosion Protection for Offshore Pipelines
Factors Affecting Line Sizing of Piping or Pipeline Systems

Hello,
I’d like to have your opinion on the following case.
We need to clear a 10″ multi-product pipeline to make repair cuts. The pipe is filled with diesel oil of density 0.8 at a pressure starting at 14 bar.
We are going to use the procedure of using a first foam piston to push a 500 meter water batch and then a second foam piston to push the water with an air compressor.
We can’t put more water because of pollution.
Thank you for responding,
sir make article on MTO
I AM HAPPY TO RUN INTO YOUR BLOG HOPE TO INITIATE A BUSINESS RELATIONSHIP WITH YOUR GOODSELF. I AM I GAGED IN PIPELINE TESTING NEED SOMEHELP
I am a mechanical engineer in gas production/ filtration , i repair/ service regulator of 10″,20″ or even 8,6,4 and 2″ gas regulator, Itron and other turbine meter for measuring and also supply some gas equipment for measuring of gas before selling it to your customer