Types of Pipelines in the Oil & Gas Industry
In the pipeline industry, various names are provided for the lines depending on the function and location of the pipelines. They are
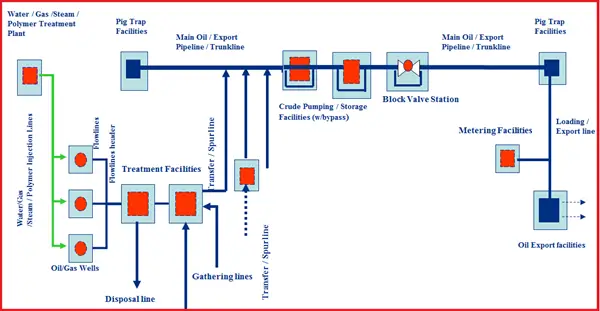
- Injection lines: Pipelines injecting water/steam/polymer/gas into the wells to improve the lift.
- Flow lines: Pipelines from the wellhead to the nearest processing facility.
- Trunk lines / Inter field lines: Pipelines between two processing facilities or from pig trap to pig trap or from block valve station to block valve station.
- Export lines / Loading lines: From the processing facility to the loading or export point.
- Transfer lines / Spur lines: Branch line exiting into trunk line or export line.
- Gathering lines: One or more segments of pipelines forming networks and connected from the wells to processing facilities.
- Disposal lines: Pipeline which disposes of normally produced water into disposal wells (shallow/deep).
- Subsea pipelines: Pipelines connecting the offshore production platforms to onshore processing facilities.
Pipeline Typical Flow Scheme – Export Crude (Fig. 1)
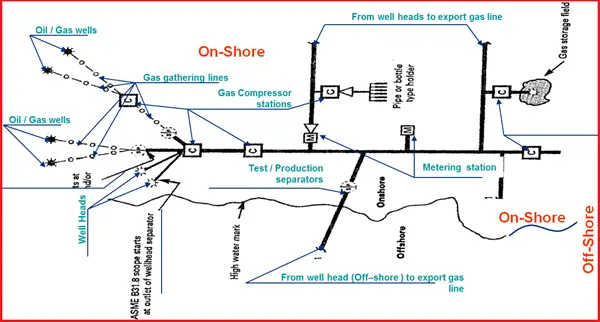
Pipeline Typical Flow Scheme – Export Gas (Fig. 2)
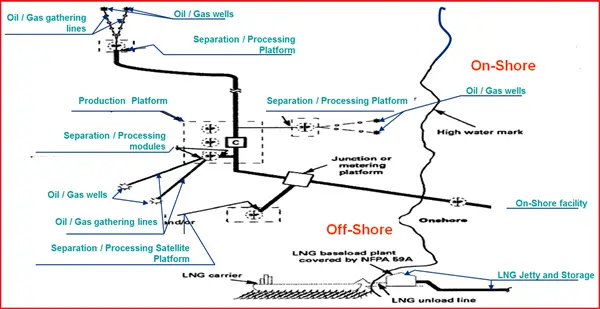
Pipeline Typical flow scheme – Offshore (Fig. 3)
Codes used in the Oil & Gas Industries
Design and Construction
Different codes and standards used for the design and construction of pipelines are
- ASME B31.4 – Pipeline Transportation Systems for liquid hydrocarbons and other liquids
- ASME B31.8 – Gas Transmission and distribution piping systems
- ISO – 13623 – Petroleum and Natural gas industries Pipeline transportation systems
- DNV –F-101 – Offshore Standard for submarine pipeline systems
Sour Applications
The pipeline codes and standards used for sour service applications are
- NACE MR-01-75 – Sulphide stress cracking resistant materials for oilfield equipment
- ISO 15156 – Materials for use in H2S-containing environments in oil and gas production
Materials
Pipeline codes and standards that define the material requirements are
- API 5L – Specification for line pipe
- API 5LC – Specification for CRA line pipe
- API 5LD – Specification for CRA clad or lined pipe
- API 5LE – Specification for Polyethylene line pipe
- ISO 3183 – Petroleum & Natural gas industries – Steel Pipe
- ISO 14692 – Petroleum and Natural gas industries – Glass Reinforced plastic piping
- AWWA M – 45 Fiberglass pipe design
Pipeline Fittings
- ISO – 15590 – 1 Pipeline Induction bends
- ISO – 15590 – 2 Pipeline Fittings
- ISO – 15590 – 3 Pipeline Flanges
- MSS – SP 75 – Specification for High Test Wrought Butt welding fittings
- MSS – SP 44 – Steel Pipeline Flanges
- ASTM A 694 – Steel forgings for high-pressure transmission service
Valves
- API 6D – Pipeline valves
- API 594 – Check valves
- API 608 – Metal Ball Valves
- API 609 – Butterfly valves
- ISO 14313 – Petroleum & Natural gas industries – Pipeline valves
Other Pipeline Components
- Pig launcher / Pig receivers
- Barred Tees
- Isolation Joints
- Pig signallers
- Corrosion monitoring fittings
- Shrink sleeves / External coatings / Cathodic protection for buried lines
Corrosion Threats in Oil & Gas
- CO2 Corrosion (Sweet Corrosion) – General metal loss due to the presence of CO2 in the process fluid.
- H2S Corrosion (Sour Corrosion) – Localized metal cracking and corrosion due to the presence of H2S in the process fluid.
- Chlorides and Bicarbonates – Cracking in the metal due to the presence of stress and chlorides in the process fluid.
- Corrosion due to Oxygen – Oxidation and metal loss due to the contact of metal with oxygen in the process fluid.
- Microbiologically induced corrosion – Bacteria that induces corrosion, particularly within H2S
- Erosion (Abrasion) corrosion – Corrosion due to the fluid flow and velocity within the pipe environments.
- Corrosion (External) Threats in the facilities – External atmospheric corrosion on above-ground lines and corrosion due to soil for buried lines.
- Corrosion Under Insulation – External corrosion due to water ingress under the insulating materials.
Material Selection Process
- Identify corrosion threats
- Define the corrosion circuits
- Calculate the corrosion rate per year
- Calculate the Service Life Corrosion (SLC) based on design life
- Consider the materials options
- Carry out the Life Cycle Costing (LCC) – Capex / Opex / Install
- Review the selection of the material with respect to the design/operating/constructability
- Finally, select the chosen materials
Corrosion Agents in Oil & Gas
- Carbon Dioxide – CO2
- Hydrogen Sulphide – H2S
- Oxygen – O2
- Chlorides – Cl-
- Water – H2O
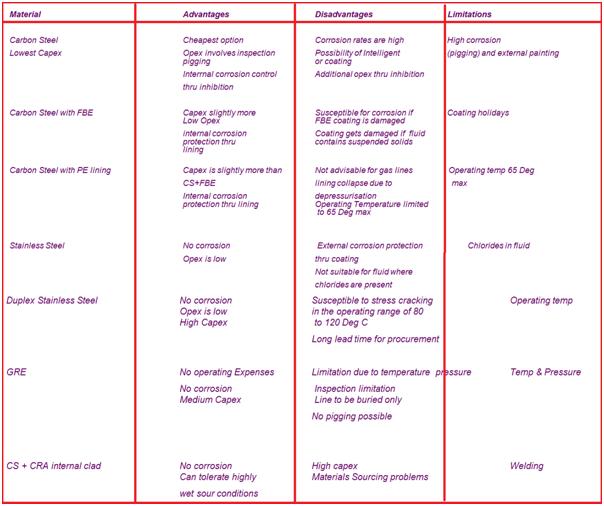
Material Options
Metals:
- CS with a corrosion allowance
- Stainless Steel
- Duplex Stainless Steel
- Super Duplex Stainless Steel
Metals + Lining:
- CS with internally coated FBE
- CS with internal PE lining
- CRA clad/lined materials
Non Metals:
- Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE)
- Polyethylene (HDPE)
Advantages & Disadvantages of Material Options (Fig. 4)
Corrosion Control in Oil & Gas Pipeline Chemical Injections
Corrosion inhibitor: Basically meant for CS pipelines, forms a layer of film on the surface and protects the core pipe from corrosion attack. Batch injection or continuous
Scale Inhibitor: Prevents scale formation in the pipelines by dissolving scale-forming salts
Wax inhibitor: Dissolves the wax within the crude
Oxygen Scavenger: Reacts and removes oxygen in the fluid
Biocide: Destroys the bacteria, algae, and fungi in the process fluid.
Coagulant / Antifoam: Normally mixed in the separators to improve mixing and reducing the foam
Demulsifier: Prevents emulsion in the multiphase system
Dehydration agents: Removes moisture in the gas normally Glycol injection
Odorant: Added to the fluid to add smell and detect the leakage
Online Video Courses related to Pipeline Engineering
If you wish to explore more about pipeline engineering, you can opt for the following video courses
- Pipeline Stress Analysis using Caesar II
- Design of Underground Pipeline Supports
- Hot Tapping in Piping and Pipeline Industry
- Buried or Underground Pipeline Stress Analysis using Caesar II
Few more Pipeline related useful Resources for You..
Underground Piping Stress Analysis Procedure using Caesar II
Comparison between Piping and Pipeline Engineering
A Presentation on Pipelines – Material Selection in Oil & Gas Industry
Corrosion Protection for Offshore Pipelines
Start up and Commissioning of the Pipeline: An Article
DESIGN OF CATHODIC PROTECTION FOR DUPLEX STAINLESS STEEL (DSS) PIPELINE
AN ARTICLE ON MICRO TUNNELING FOR PIPELINE INSTALLATION
A short presentation on: OFFSHORE PIPELINE SYSTEMS: Part 1
Factors Affecting Line Sizing of Piping or Pipeline Systems

I am not able to get the figures. Try to open , saying page not found.
Kindly mail me the figures.
A Great Presentation on different types of Pipelines and there importance.
Amazing article I have ever read.Thanks for posting this wonderful, informative article. I’m happy that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this.
Great article, Thanks for posting this wonderful, informative article.
I think it would be perfect if you’ll continue with stress calculation for Pipelines system.
While waiting for the continuity, I mean “Stress calculation for Pipelines”
Thanks again and have a wonderful day
It is a pleasure worth reading this article which is stating about the pipelines material.This article is very helpful and knowledgeable for everyone. It makes the work straight and easy for us. I am sure many people will come to read this in future.I never thought will get to visit this site which has some nice content for everyone.
Thank you very much for presenting this data about pipelines material, it’s known how to get approved but what are the next steps after getting the approval… Wonderful information, thanks a lot for sharing kind of content with us… great post!
Hi
Thanks for sharing the knowledge about pipelines through the presentation. very well defining.
It’s very helpful and informative. It will definitely helpful for us. well done. keep sharing.
Hi..
Keep up the good works