API 5L is a seamless and welded carbon steel pipe material specification. API 5L pipes are widely used to transport oil, water, and gases in the pipeline industry. Depending on the strength, schedule, and service requirements API 5L pipes are manufactured in various grades and are suitable for both onshore and offshore applications. In this article, we will learn about the various grades, specifications, and schedule charts of API 5L pipes.
API 5L pipes in the oil and gas, water, and petrochemical industries are available in two Product Specification Levels (PSL) depending on quality levels. The first one is PSL1 which provides a standard quality level. The other one PSL2 provides additional mandatory requirements in strength, chemical composition, NDT, or notch toughness.
Grades of API 5L Pipes
API 5L pipes are produced in various grades. Each API 5L grade varies in its strength capabilities. A unique alpha or alphanumeric designation is assigned to each grade of API 5l pipes. Leaving Grade A and Grade B, all other API 5l grades mention the specified minimum yield strength in their numerical portion of the designation. These yield strength values are expressed in KSI (kilopound per square inch) for the USC unit and in MPa (Mega Pascal) for the SI unit system.
The common grades of API 5L pipes that are widely used are:
- API 5L Grade B (USC unit system) or L245 (SI unit system)
- API 5L Grade X42 or L290
- API 5L Grade X52 or L360
- API 5L Grade X60 or L415
Other API 5L grades that are also manufactured for various applications are:
- API 5L Grade A25 or L175
- API 5L Grade A25P or L175P
- API 5L Grade A or L210
- API 5L Grade X46 or L320
- API 5L Grade X56 or L390
- API 5L Grade X65 or L450
- API 5L Grade X75 or L485
Various letters have suffixed these grades to indicate special requirements like N denotes normalized, Q denotes quenched and tempered, and M denotes thermomechanical rolled or formed.
As informed earlier the numerical value denotes the specified minimum yield strength in USC or SI unit. For example, for API 5L X42 material the term 42 denoted 42KSI as the specified minimum yield strength of the material. Similarly, API 5L L360 denotes the specified minimum yield strength for the material is 360 MPa.
Purchasing Information
While purchasing the API 5L material the following details must be specified in the purchase order or material data sheet.
- PSL levels (PSL1 or PSL2).
- Grade of the Pipe required (Proper pipe designation).
- Pipe Size, Outer diameter, and thickness.
- Random or Approximate length.
- Seamless or Welded.
- Quantity of pipe required (Total length or Total mass).
- Pipe end connection.
- Coating and lining requirements.
- Fluid service sour or sweet.
- Any marking requirements.
- Any special requirements, etc
Specification of API 5L Pipe
API 5L Pipe specification is prepared with respect to various aspects as listed below:
Standard Scope: The scope of API 5L pipe mainly includes the application of the pipe for water and oil and gas pipeline transmission.
Manufacturing types: The specification includes the manufacturing types as welded and seamless. Cast pipes are not covered in the specification.
Pipes under 24″ are usually seamless or ERW, whereas large diameter pipes are SAW/DSAW. LSAW is used up to 48″ in size whereas SSAW/HSAW can be used up to 100″ in size.
Different Grades: API 5L line pipe specification covers Gr. A, B, X42, X46, X52, X56, X60, X65, X70, X80, etc. There are various delivery conditions as required for different applications.
Material specifications (Chemical and Mechanical): The material datasheet specifies the chemical composition and mechanical properties of each grade of API 5L pipe material.
Test Methods: Hydrostatic test is the most common testing method applied for the API 5L line pipe to investigate joint leakage. Other tests include the bend test, flattening test, etc. The line pipe must be free from cracks, sweat, leaks, or any other defects.
Other important considerations are:
- Tolerances on pipe diameters, wall thickness, out-of-roundness
- Common defects
- Line pipe history and milestones
- Applications
- Pipe designation
- Carbon equivalent limits
- Jointer welds
- Ends type: plain, beveled, threaded ends
- Repairs Requirements
- Pipe markings and end colors
- CVN impact test
- DWT test
- Hardness test
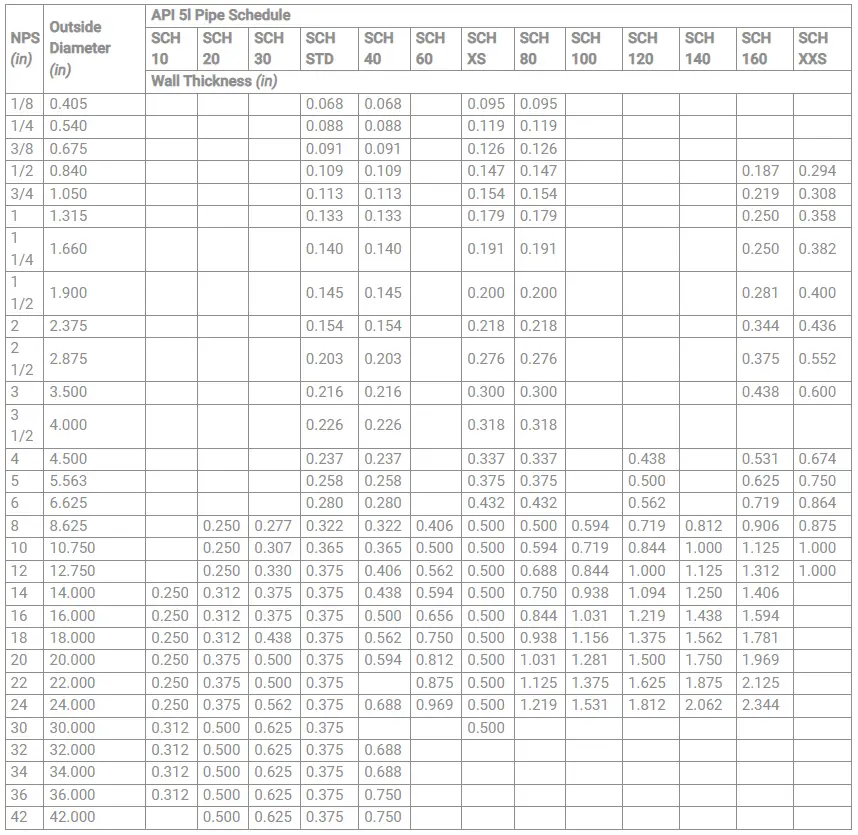
API 5L Schedule Chart
Similar to other carbon steel pipes, the pipe thicknesses are not standardized for all API 5L pipe grades. The OD of pipes matches the OD of other carbon steel pipes. However, the thickness varies. Depending on high strength the thickness used for specific applications is usually reduced. High-strength and low-thickness pipelines are widely used in the pipeline industry.
Manufacturers of API 5L pipes provide their schedule chart mentioning the available pipe thicknesses with respect to pipe size. The weights and prices per unit length are also usually provided in the API 5L pipe schedule chart. Some grades of pipe schedules like API 5L grade pipes have standardized pipe schedules similar to as provided in ASME B36.10. But for high-strength line pipes, for example, X60, X52, X42, etc have standardized as well as non-standardized pipe schedules.
A typical API 5L standardized pipe schedule chart is provided in Fig. 1 below.







Hello!
what is the relation between the API 5l grades (X42, X46, X52, etc..) and the pipe schedule (Sch 20, 40, 80…)?
additional question, is the provided figure (Fig. 1: API 5L Standardized Pipe Schedule Chart) is standardize for all grades (X42, X46, X52, etc…) or it is specific for one grade only…
last one, can i use these thickness directly or i have to do a recheck calculations (using the equations) to ensure that the required thickness can handle the internal pressure, temperature, etc..
thanks!
Pipe grade is the tensile strength of the steel.
Pipe schedule is the dimensions of the pipe, specifically the pipe wall thickness; the OD of the pipe for a given size is the same regardless of pipe schedule.
It is ultimately the Engineer’s responsibility to ensure the specified pipe will withstand the service pressures, temperatures and corrosion service conditions. In temperatures up to 300-400 deg F and pressures up to 150 psi, ‘Standard’ wall thickness will usually suffice. ASME B31.1 or B31.3 are standards frequently used for piping design for process piping and power plant piping.
Very informative site. But I would like to know whether seamless pipe conforming to Sch 40, B 36.10, ASTM A106 Gr B is equivalent or superior to API 5L Grade A/B pipe of same dia and thickness?
No there is different table for each type of pipe but the question 🤔 can we use seamless pipe API 5l in applications which usually use ASTM A106 seamless pipe?