Pressure vessels are widely used in various industries to store and transport substances under high pressure. These vessels consist of several crucial components, and one of the most important parts is the pressure vessel head. The head of a pressure vessel is responsible for sealing the contents and ensuring structural integrity. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the different types of pressure vessel heads, their features, and their applications.
What is a Pressure Vessel Head?
Pressure vessels are containers that are designed to hold gases or liquids at high pressure. They are used in a variety of industries, including chemical, oil and gas, and power generation. The head of a pressure vessel is the end cap that closes the vessel and prevents the contents from escaping.
Different Types of Pressure Vessel Heads
Depending on the shape of the pressure vessel heads, there are different types of pressure vessel heads that are found in industrial applications. The most common types of pressure vessel heads (Fig. 1) are discussed here:
Flat Heads:
Flat heads, also known as flat plates or blind plates, are the simplest type of pressure vessel heads. They are flat and provide a straightforward sealing solution for pressure vessels. Flat heads are commonly used in small vessels or as temporary covers during maintenance and inspection procedures. They are easy to manufacture and install, making them cost-effective for certain applications. Flat heads are not very strong, and they are only used for low-pressure applications.
Hemispherical Heads:
Hemispherical heads are semi-spherical in shape and provide excellent structural strength. They distribute pressure evenly, making them suitable for high-pressure applications. Hemispherical heads are often used in storage tanks, boilers, and other vessels that require resistance against internal pressure. Their curved shape allows for efficient distribution of stress, reducing the risk of deformation or failure. It is the strongest type of pressure vessel head. Hemispherical heads are more expensive than other types of heads, but they are worth the cost in high-pressure applications.
Ellipsoidal Heads:
Ellipsoidal heads, also known as elliptical heads or semi-elliptical heads, have a more elongated shape compared to hemispherical heads. They offer good pressure distribution and structural integrity, making them a popular choice for pressure vessels. The elliptical shape of these heads allows for increased internal volume while maintaining adequate strength. Ellipsoidal heads are widely used in tanks, reactors, and pressure vessels where space and weight considerations are important. It is stronger than a flat head, but not as strong as a torispherical head. Ellipsoidal pressure vessel heads are used for a variety of pressure applications, but they are most common in moderate-pressure applications. The common width-to-depth ratio for semi-elliptical heads is 2:1
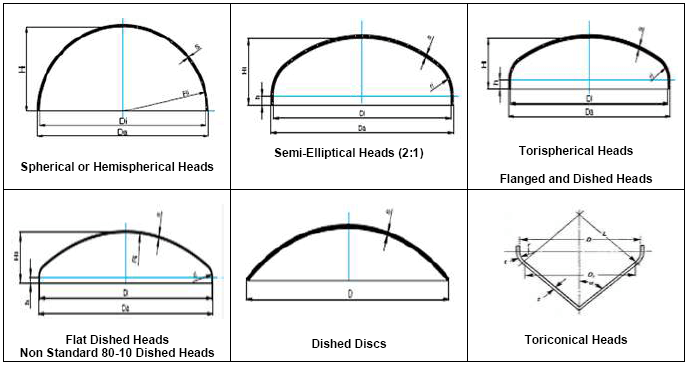
Torispherical Heads:
Torispherical heads, also referred to as flanged and dished heads, are a common choice for a wide range of pressure vessel applications. These heads have a dish shape with a flanged edge for connecting to the vessel body. Torispherical heads provide excellent pressure resistance, uniform stress distribution, and increased volume capacity compared to ellipsoidal heads. They are versatile and can be fabricated with different knuckle and crown radius ratios to meet specific design requirements. Torispherical heads are used for a variety of pressure applications, but they are most common in high-pressure applications. The flanged and dished head usually requires more thickness than the matching cylinder.
Conical Heads:
Conical heads, as the name suggests, have a conical shape. They are often used in vessels that require a smooth transition between cylindrical sections and a smaller opening. Conical heads provide strength and structural stability, particularly in applications where the flow of contents needs to be directed or channeled. These heads are commonly found in separators, cone-bottom tanks, and hoppers.
Custom Heads:
In addition to the standard types mentioned above, pressure vessel heads can also be custom-designed to meet specific requirements. Custom heads are often used when the vessel has unique dimensions, unusual geometries, or specific process requirements. They are fabricated to fit the vessel precisely and can incorporate features such as nozzles, manways, or special connections.
What is Toriconical Pressure Vessel Head?
A toriconical head is a type of pressure vessel head that is a combination of a torispherical head and a conical head. It is shaped like a dome with a cone-shaped bottom. Toriconical heads are used for a variety of pressure applications, but they are most common in high-pressure applications.
The toriconical head is a stronger and more efficient design than the torispherical head. This is because the conical bottom helps to distribute the pressure more evenly across the head. Toriconically shaped heads are more efficient than the traditional torispherical head because the conical section helps to direct the flow of fluid around the head, reducing turbulence and pressure losses. This makes them a good choice for applications where efficiency is important, such as in the oil and gas industry.
The toriconical head is also a more versatile design than the torispherical head. This is because the conical bottom can be made to fit a variety of vessel geometries. This makes them a good choice for applications where the vessel geometry is not well-defined, such as in the chemical industry.
Selection of a Pressure Vessel Head
The head of a pressure vessel is an important component of the vessel, and it must be designed and manufactured to meet the specific requirements of the application. The type of head that is used will depend on the pressure, temperature, and contents of the vessel.
Here are some of the factors that should be considered when selecting a pressure vessel head:
- Pressure: The pressure of the contents of the vessel will determine the strength of the head that is needed.
- Temperature: The temperature of the contents of the vessel will also affect the strength of the head that is needed.
- Contents: The type of contents of the vessel will also affect the type of head that is needed. For example, if the contents of the vessel are corrosive, then a head that is made of a corrosion-resistant material will be needed.
- Application: The application of the vessel will also affect the type of head that is needed. For example, if the vessel is used in a mobile application, then a head that is lightweight and easy to transport will be needed.
By considering these factors, the right type of pressure vessel head can be selected for the specific application.
Differences between the Flat Heads, Hemispherical Heads, Ellipsoidal Heads, and Torispherical Heads
The main differences between various types of pressure vessel heads are provided in Table 1 below:
| Head Type | Shape | Pressure Distribution | Volume Capacity | Strength | Cost | Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Heads | Flat plates | Uneven | Low | Weakest | Lowest | Simple to manufacture, lightweight | Temporary covers, small vessels |
| Hemispherical Heads | Semi-spherical | Even | Moderate | Strongest | Highest | Strongest, most efficient | Storage tanks, boilers |
| Ellipsoidal Heads | Elliptical | Even | Moderate | Strong | Moderate | Moderate strength, versatile | Tanks, reactors, pressure vessels |
| Torispherical Heads | Dish-shaped with flange | Even | High | Moderate | Moderate | Good balance of strength and cost | Pressure vessels, boilers, separators |
| Conical Heads | Conical | Even | Variable | Moderate | High | Moderate strength | Separators, cone-bottom tanks, hoppers |
Conclusion
Pressure vessel heads are critical components that ensure the safe and efficient operation of pressure vessels. Understanding the different types of pressure vessel heads is essential for selecting the appropriate design based on the specific application and pressure requirements. Whether it’s the simplicity of flat heads, the strength of hemispherical or ellipsoidal heads, the versatility of torispherical heads, or the functionality of conical heads, each type has its advantages and applications. By considering the specific needs of the pressure vessel, proper head selection can contribute to the vessel’s overall performance, reliability, and safety.
Online Course on Pressure Vessels
If you wish to learn more about Pressure Vessels, their design, fabrication, installation, etc in depth, then the following online courses will surely help you:

Thanks for sharing
It’s very useful post