Many times, you will find the piping geometry to run in the vertical direction. A typical example could be the Column or Tower piping (Refer to Fig. 1). From the overhead nozzle, the pipe runs vertically downward for a certain stretch until it reaches the pipe rack location. In such cases, the supporting of vertical piping runs may seem to be very difficult. For the specific example, the pipe is usually supported using cleat or clip supports from the equipment itself. Similar types of vertical runs of pipe can occur in many different locations. In this article, we will describe some of the vertical pipe supports to understand the supporting philosophy for such pipes.
What is a Vertical Pipe Support?
In the complex world of piping systems, support mechanisms play a pivotal role in ensuring structural integrity, operational efficiency, and safety. Vertical pipe supports are crucial in maintaining the stability and alignment of piping that runs vertically, either within industrial facilities.
Vertical pipe support refers to the system or method used to stabilize and hold vertical piping in place within a structure. These supports are essential for preventing the pipe from buckling, swaying, or experiencing undue stress due to the weight of the fluid or gases they transport, as well as external forces like wind or seismic activity. They are particularly critical in high-rise equipment like reactors, distillation columns, towers, and other structures where extensive vertical piping systems are present.
The primary goal of vertical pipe support is to ensure that the piping remains in its designated position without shifting, bending, or being subject to excessive loads. This, in turn, helps to prevent leaks, breaks, or other failures that could lead to operational downtime, costly repairs, or even catastrophic events.
Types of Vertical Pipe Supports
Vertical pipe supports used in the oil and gas industries can be classified into the following groups:
- Load Carrying Supports to Carry the Pipe and Content Weight
- Guide supports to restrict the pipe’s sideway movement, and
- Axial Stop supports for restricting the pipe movement in the axial direction.
Let’s understand the types of vertical pipe supports with some examples.
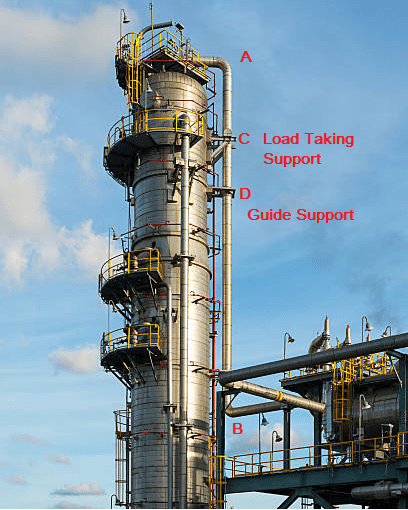
In Fig. 1, the supporting of a typical distillation column piping is shown. The Stretch A to B is a vertical run of the pipe. We can not support the pipe run near point B as that will cause uneven thermal movement at the nozzle due to the piping side and equipment side thermal growth. At the same time, the weight of the vertical run of the pipe must be transferred from the nozzle by providing load-carrying support. It is, therefore, supported at point C using trunnions (dummy) from the vertical pipe and resting those at the equipment cleats. Again at point D the pipe is supported using Guide Supports from the equipment clips.
Load-Taking Vertical Pipe Supports
Load-carrying vertical pipe supports can be installed by welding Lugs or Trunnions on the vertical Pipe as shown in Fig. 2 below.
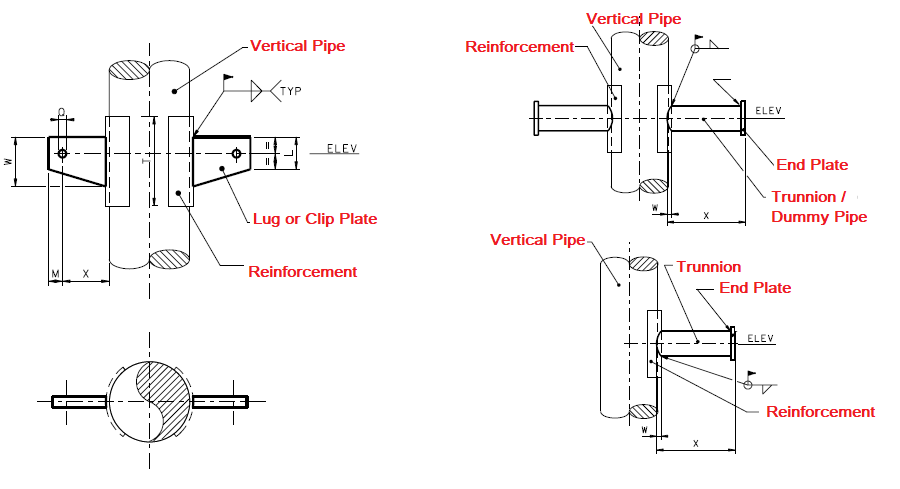
This type of support is known as Rest support for vertical pipes.
Guide Support on Vertical Pipes
The guide supports on vertical pipe restrict sideway movements. Refer to Fig. 3 below which shows a typical example of vertical pipe guide support. This type of support is known as all-around guide support.
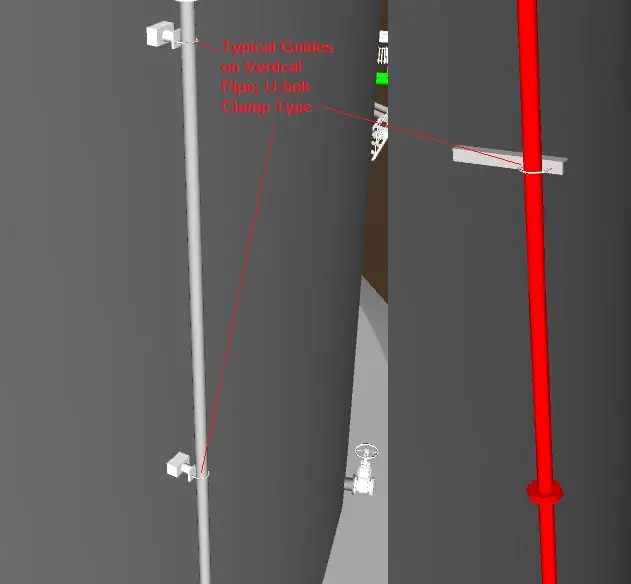
Hold-down supports with pipe shoes, if installed in the vertical pipe will also act as all-around guide support.
Axial Stops on Vertical Pipes
Axial Stops or Limit Stops on vertical pipe restrict the axial movement of the vertical pipe. As the pipe run is in the vertical direction so here the axial stop will restrict the movement in vertical direction. Also, it carries the piping load. If the same trunnion support as shown in Fig. 2 is clamped on the structure, it will act as an axial stop support. By default, due to the trunnion over structure, the pipe is not able to move in the downward direction. Again, when clamped it will not be able to move in the vertically upward direction. So, in both directions, upward and downward movement is locked at the support location which is the characteristic of axial stop support.
Vertical Pipe Support Bracket
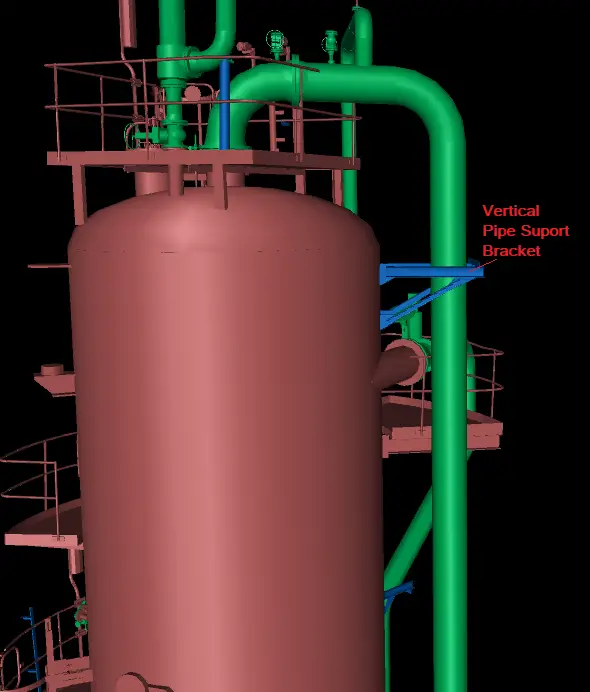
A vertical pipe support bracket is a structural element designed to hold, guide, and support vertical piping. These brackets are typically attached to walls, ceilings, or other structural elements, providing a secure point of support that prevents pipes from shifting, sagging, or becoming misaligned due to gravity, thermal expansion, or external forces. Fig. 4 shows a typical vertical pipe support bracket.
Types of Vertical Pipe Support Brackets
There are various types of vertical pipe support brackets, each designed for specific applications and requirements:
a) Wall-Mounted Brackets
Wall-mounted brackets are commonly used in scenarios where vertical pipes run along or are close to a wall. These brackets can be made from different materials such as steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, and are typically bolted or welded to the wall.
Applications: Ideal for indoor installations in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
b) Ceiling-Mounted Brackets
These brackets are used when pipes are suspended from the ceiling. They typically feature a clamp or cradle that secures the pipe while being attached to a ceiling-mounted anchor point.
Applications: Commonly used in commercial buildings, factories, and facilities where pipes need to be kept off the floor or away from walls.
c) Floor-Mounted Brackets
Floor-mounted brackets, or pipe stands, are used to support vertical pipes that extend from the floor. These brackets are often adjustable and can handle a significant amount of weight.
Applications: Suitable for industrial settings where pipes are required to rise vertically from machinery, tanks, or other ground-level equipment.
d) Adjustable Brackets
Adjustable brackets provide installation flexibility. They allow for fine-tuning the pipe’s position during or after installation, which is particularly useful in systems where precision alignment is crucial.
Applications: Used in custom installations or where piping may need to be adjusted after the initial installation due to settling or realignment.
e) Anchor Brackets
Anchor brackets are designed to hold the pipe rigidly in place, preventing any movement. These are critical in sections of the piping system where movement could lead to misalignment or damage.
Applications: Often used in seismic zones or where the pipe is subject to dynamic forces, such as in high-pressure systems.

Hi I am a researcher of underground piping. Can you help me understand what equations can be used to calculate weight of vertical pipes and how to determine where to add supports to prevent pipe from buckling. can you help guide me on these subjects?