Vibration Sensors are vibration monitoring equipment used widely by plant maintenance teams to find insight regarding equipment or piping performance. Using vibration sensors and studying the data from these devices, engineers can predict possibilities of equipment failure and they can safeguard major equipment from breakdown by taking proper action. Vibration Sensors are also known as vibration transducers. In this article, we will explore the importance of vibration sensors, their types, working, and selection procedures. Let’s dive into the subject starting with the definition of vibration sensors.
What are Vibration Sensors?
A vibration sensor is a measuring device. As the name implies it senses the vibration or to-and-fro movement of any equipment or system at the location where it is applied. It measures the amplitude and frequency of vibration of the system under study. The most widespread application of vibration sensors is found to measure the vibration of rotating equipment and machines like pumps, compressors, steam turbines, and connected lines. These measured outputs are then studied to detect any imbalance or issues in the asset or equipment under investigation to predict the condition of the system. Vibration sensors are very important components of a vibration-measuring tool.
As vibration impacts the reliability and durability of the system in working conditions it must be measured. Industrial vibration sensors can help in monitoring the vibration issues of systems. Monitoring and measuring the vibration of equipment or systems provide several benefits like:
- Root cause analysis of any problem.
- Deciding repairing needs.
- Checking the overall plant or equipment condition.
- Overall it reduces plant operating costs by avoiding costly shut-downs in advance.
Applications of Vibration Sensors
Vibration sensors are very useful in all industries wherever there is a possibility of vibration and need to monitor the same for improved asset performance. In general, the following industries find a wide application of vibration sensors:
- Oil and gas
- Mining
- Aerospace
- Food and beverage
- Pulp and paper
- Refining, chemical, petrochemical, and other processing industry.
- Metalworking
- Automotive & Transportation
- Power generation
- Certain manufacturing industries
- Wind power and other renewable power
- Cement
- Research and Development
There are several industry standards that govern vibration measurement for industries. Some of those are:
- ISO 4866
- ISO 20816
- AS 2625.1
Working of Vibration Sensors
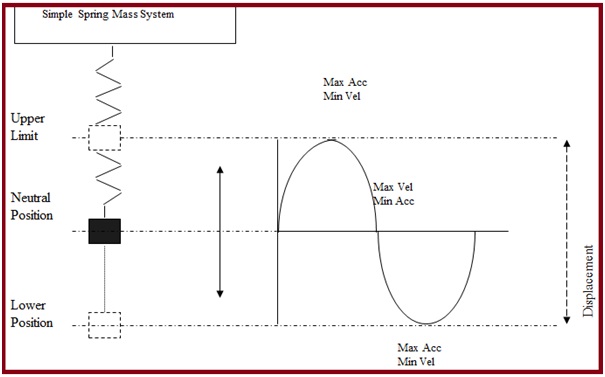
Vibration sensors or vibration transducers can be used either directly mounted on the equipment or used wirelessly to monitor the system. When it is placed in service, the sensors will start working and measure the displacement, velocity, or acceleration of vibration depending on the types of vibration sensors used.
Vibration sensors operate based on mechanical, electromagnetic, or optical principles to detect equipment vibration. Depending on the application requirement, the sensitivity of these vibration sensors may vary, the usual range is from 10 mV/g to 100 mV/g.
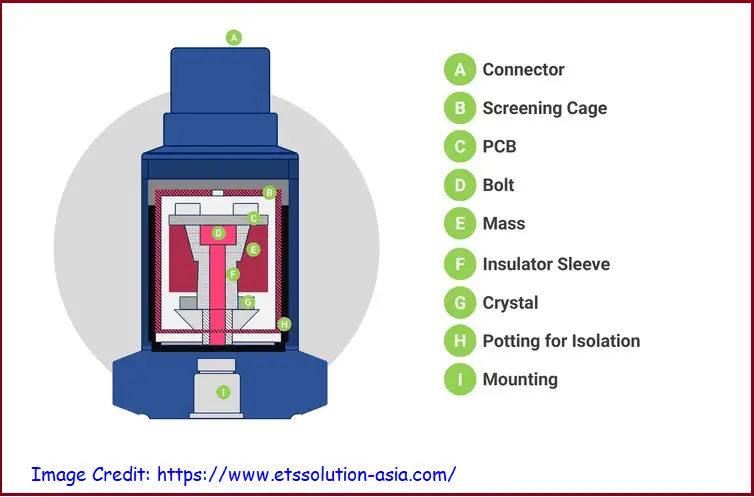
Vibration sensors consist of a crystal of piezoelectric material to which is attached a seismic mass. When the crystal is stressed, an electric signal is produced which is measured as output data. They are robust in construction and provide high reliability and long-term stability. Fig. 1 below provides the major components of a typical vibration sensor.
If the vibration sensors are placed for a longer duration of time, it will provide the following information:
- How frequently vibration occurs and
- The intensity of vibration.
These data then can be compared with standard acceptable data as specified by equipment manufacturers or various codes and standards to find out if that vibration needs attention or not.
Types of Vibration Sensors
The vibration sensors used in industries can be grouped into the following three primary types:
- Accelerometers or Acceleration Transducers
- Velocity sensors, and
- Displacement sensors or Displacement transducers
Accelerometers:
Accelerometers measure the acceleration of motion of a system. This type of vibration sensor converts the mechanical forces of vibration into an electrical signal using the piezoelectric effect. Accelerators are of two types; High impedance accelerometers and Low impedance accelerometers.
Accelerometers as industrial vibration sensors have a more extended high-frequency capability as compared to other types of vibration transducers. Accelerometers are used specifically for rolling element bearing and gear fault detection, detecting unbalance, misalignment, bent shaft, loose or broken parts, component resonances, etc, and are available in various sizes with an extended temperature range of applications.
Velocity Sensors:
Velocity sensors are good for monitoring rotating and reciprocating equipment and for general vibration measurement. This type of vibration sensor is used for medium-frequency measurements. The main advantage of velocity sensors is that they are electrodynamic and do not require external power.
Displacement Sensors:
Displacement Transducers are also known as proximity sensors, eddy current sensors, or proximity transducers and measure displacements. Displacement sensors are suitable for measuring radial vibration, axial movement, eccentricity, internal clearances, differential expansion, etc. This type of vibration sensor is suitable for low-frequency ranges.
Selecting a Vibration Sensor
The selection of a specific type of vibration sensor or vibration transducer is dictated by the application. The main factors that contribute to the selection of vibration sensors are:
- Range and accuracy of the vibration transducer
- Environmental conditions where it will be mounted
- The shape of the measuring surface
In general, displacement sensors are suitable for vibration frequency ranges of 0 to 10 Hz, velocity sensors are suitable for 10 to 100 Hz, and accelerometers are suitable for greater than 100 Hz. The following table provides the selection of vibration transducers based on the frequency of vibration.
| Frequency Range | Type of Vibration Sensor |
| 0 to 10 Hz | Displacement Sensors |
| 10 to 100 Hz | Displacement or Velocity Sensors |
| 100 to 1000 Hz | Displacement, Velocity, or Acceleration sensors |
| 1000 to 2000 Hz | Velocity or Acceleration sensors |
| Greater than 2000 Hz | Accelerometers. |
Will you be interested to learn more about sensors, their working, and fundamentals in more detail? Then the following two online video courses are just for you: