In the world of piping and pipeline systems, efficiency, reliability, and safety are paramount. When designing or modifying piping systems, various components, and fittings come into play to ensure the smooth flow of fluids or gases. One such crucial component is the Weldolet. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of Weldolets, understanding what they are, how they work, their advantages, and their applications.
What is a Weldolet?
A Weldolet is a type of branch connection fitting used in piping systems to create a branch connection from a larger main pipe to a smaller pipe or pipeline component. It is designed to provide a smooth transition from the main pipe to the branch pipe, thus facilitating efficient fluid or gas flow while minimizing turbulence.
Weldolet connections replace the traditional piping tee connections. Even they are used when standard piping tee connection fittings are not available. Let’s take an example, For a parent pipe size of 16 inches, the standard piping reducing-tee connection is available up to a branch size of 6 inches. So, if we need to use lower branch sizes, then standardized reducing pipe tees are not an option. In such situations, the weldolet piping connections come as a savior. For 16 inches main pipe, weldolets are available up to 1/2 inches branch size. Fig. 1 below shows a weldolet connection.
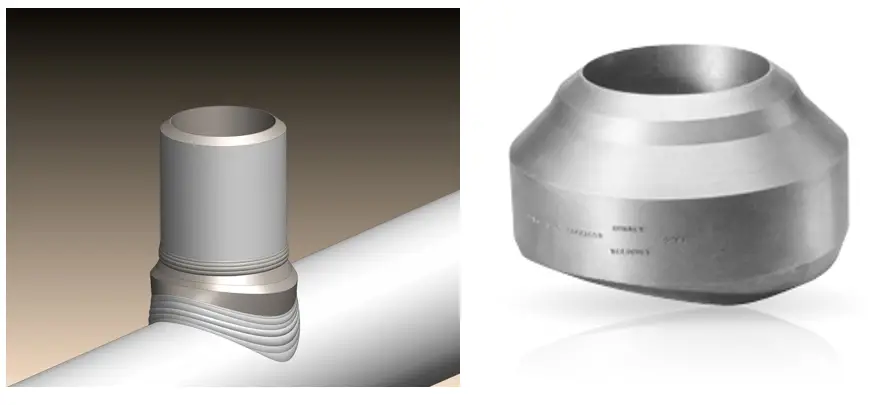

Characteristics of Weldolet Connection
The main characteristics of a weldolet connection are:
- They are smaller in size than traditional tee fittings and hence they take up less space in the system.
- They are forged components.
- they can be made of various compatible pipe materials like A105 carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, nickel alloys, etc
- They are easy to weld (Butt-welding) to the main pipe to create a strong branch connection.
- The thickness of weldolet connection is always higher than the tee fitting thickness.
- Weldolets provide integral reinforcement or self-reinforcement.
- Weldolet connections are produced by a company called Bonney Forge
How Does a Weldolet Work?
Weldolets are installed through welding, hence the name. The fitting has a welding outlet on one end, which is welded onto the main pipe, and a threaded or socket weld connection on the other end to accommodate the smaller branch pipe or component. This welding process ensures a strong and leak-resistant connection between the main pipe and the branch pipe.
Weldolet Standard
The Manufacturers Standardization Society (MSS) publishes the SP-97 standard, which specifically addresses integrally reinforced forged branch outlet fittings, including Weldolets. This standard provides guidelines for the design, manufacturing, dimensions, testing, and marking of these fittings.
Advantages of Using Weldolets
Using a weldolet connection provides various benefits including
- Reduced Welding and Fabrication Time: Weldolet fittings streamline the process of creating branch connections, saving time and labor costs compared to traditional methods that involve cutting the main pipe and welding a separate branch pipe.
- Minimized Stress Concentration: The design of a Weldolet helps distribute stress evenly across the fitting, reducing the risk of stress concentration that can lead to fatigue and failure in the pipeline system.
- Improved Fluid Flow: Weldolet fittings create a smooth transition from the main pipe to the branch pipe, minimizing turbulence and pressure drop, which results in improved fluid flow efficiency.
- Space and Weight Savings: Weldolets eliminate the need for bulky fittings or flanges to create branch connections, leading to a more compact and lightweight piping system.
- Versatility: Weldolet connections are available in various materials, sizes, and configurations, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from high-pressure pipelines to low-pressure systems.
Applications of Weldolets
Weldolets find applications in a multitude of industries, including:
- Oil and Gas: They are commonly used in oil refineries, petrochemical plants, and offshore platforms for creating branch connections in pipelines carrying hydrocarbons and other fluids.
- Power Generation: Weldolets are employed in power plants to create connections in steam and water pipelines.
- Chemical Processing: They play a crucial role in connecting pipes that transport corrosive or hazardous chemicals.
- Water Treatment: In water treatment facilities, Weldolets are utilized to create branch connections for distribution and collection pipelines.
- Food and Beverage: These fittings are used in the food and beverage industry for creating connections in pipelines carrying various liquids and gases.
Sockolet vs Weldolet
Here’s a comparison table between Sockolets and Weldolets, two common types of branch connection fittings used in piping systems:
| Aspect | Sockolet | Weldolet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sockolet is a socket weld branch connection fitting. | Weldolet is a butt-weld branch connection fitting. |
| Installation Method | Socket welding onto the run pipe. | Butt welding onto the run pipe. |
| Connection Type | Socket weld connection for the branch pipe. | Butt weld connection for the branch pipe. |
| Fitting Type | Forged fitting | Forged fitting or wrought fitting. |
| Stress Concentration | Generally higher due to the abrupt transition. | Generally lower due to smoother transition. |
| Fluid Flow | May cause slight turbulence and pressure drop. | Smooth transition reduces turbulence and pressure drop. |
| Applications | Suitable for small-sized branches and lower-pressure applications. | Suitable for a wide range of sizes and pressure applications. |
| Standards | Usually follow ASME B16.11 standard. | Usually follow ASME B16.9 or MSS SP-97 standard. |
| Availability | Limited to socket welding processes. | Available for both butt welding and socket welding processes. |
| Common Materials | Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. | Same as Sockolets: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. |
| Usage Preference | Used when socket welding is preferred or required. | Used when butt welding is preferred or required. |
Weldolet vs Threadolet
here’s a comparison table between Weldolets and Threadolets, two types of branch connection fittings used in piping systems:
| Aspect | Weldolet | Threadolet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Weldolet is a butt-weld branch connection fitting. | Threadolet is a threaded branch connection fitting. |
| Installation Method | Butt welding onto the run pipe. | Threaded connection onto the run pipe. |
| Connection Type | Butt weld connection for the branch pipe. | Threaded connection for the branch pipe. |
| Fitting Type | Forged fitting or wrought fitting. | Forged fitting. |
| Stress Concentration | Generally lower due to smoother transition. | Generally higher due to the abrupt transition. |
| Fluid Flow | Smooth transition reduces turbulence and pressure drop. | May cause slight turbulence and pressure drop. |
| Applications | Suitable for a wide range of sizes and pressure applications. | Suitable for smaller-sized branches and lower-pressure applications. |
| Standards | Usually follow ASME B16.9 or MSS SP-97 standard. | Usually follow ASME B16.11 standard. |
| Availability | Available for both butt welding and socket welding processes. | Primarily used with threaded connections. |
| Common Materials | Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. | Same as Weldolets: carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. |
| Usage Preference | Used when butt welding is preferred or required. | Used when threaded connections are preferred or required. |
Weldolet Dimensions
The dimensions of the weldolet vary depending on the thickness. Weldolats are available with four schedules as mentioned below:
- Schedule STD Weldolet
- Schedule XS Weldolet
- Schedule 160 Weldolet, and
- Schedule XXS Weldolet
The weldolet dimensions are provided in a tabular format below. All the tables need to be referred to in conjunction with the Image in Fig. 2.
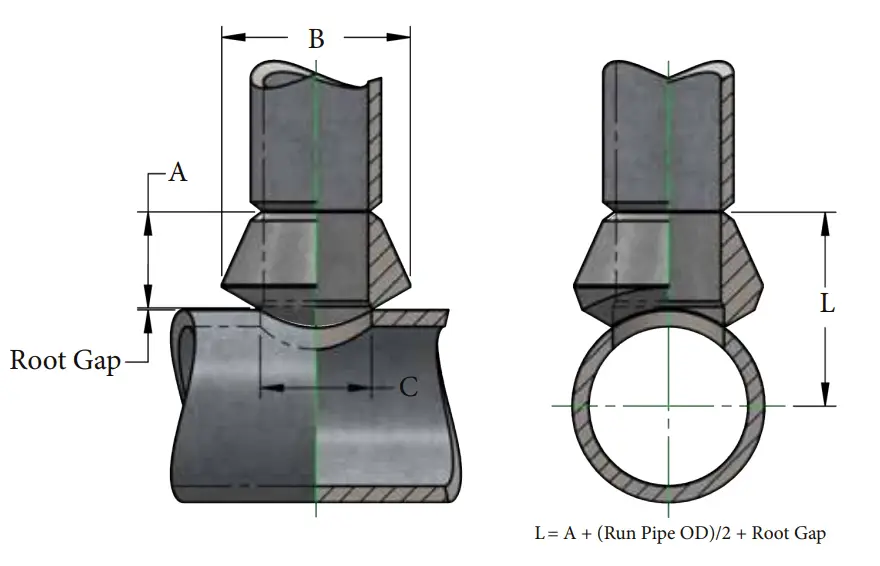
Schedule STD Weldolet Dimensions
| Outlet Size(NPS) | Height A (mm) | OD -B (in) | Hole Dia C (in) | Weight in LB | Outlet Size in mm | Height A (mm) | OD -B (mm) | Hole Dia C (mm) | Weight in KG |
| 1/8 | 5/8 | 1 | 5/8 | 0.1 | 8 | 14.3 | 25.4 | 15.9 | 0.04 |
| 1/4 | 5/8 | 1 | 5/8 | 0.1 | 8 | 14.3 | 25.4 | 15.9 | 0.04 |
| 3/8 | 3/4 | 1-1/4 | 3/4 | 0.15 | 10 | 19.05 | 31.75 | 19.05 | 0.07 |
| 1/2 | 3/4 | 1-3/8 | 15/16 | 0.2 | 15 | 19.05 | 34.93 | 23.81 | 0.08 |
| 3/4 | 7/8 | 1 3/4 | 1 3/16 | 0.250 | 20 | 22.23 | 44.45 | 30.16 | 0.11 |
| 1 | 1 1/16 | 2 1/8 | 1 7/16 | 0.500 | 25 | 26.99 | 53.98 | 36.51 | 0.23 |
| 1 1/4 | 1 1/4 | 2 9/16 | 1 3/4 | 0.800 | 32 | 31.75 | 65.09 | 44.45 | 0.36 |
| 1 1/2 | 1 5/16 | 2 7/8 | 2 | 1.000 | 40 | 33.34 | 73.03 | 50.8 | 0.45 |
| 2 | 1 1/2 | 3 1/2 | 2 9/16 | 1.750 | 50 | 38.1 | 88.9 | 65.09 | 0.79 |
| 2 1/2 | 1 5/8 | 4 1/16 | 3 | 2.500 | 65 | 41.28 | 103.19 | 76.2 | 1.13 |
| 3 | 1 3/4 | 4- 13/16 | 3 11/16 | 4.000 | 80 | 44.45 | 122.24 | 93.66 | 1.81 |
| 3 1/2 | 1 7/8 | 5- 1/4 | 4 | 5.500 | 90 | 47.63 | 142.88 | 112.71 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 2 | 6 | 4 3/4 | 6.300 | 100 | 50.8 | 152.4 | 120.65 | 2.86 |
| 5 | 2 1/4 | 7- 1/16 | 5 9/16 | 10.250 | 130 | 57.15 | 179.3 | 141.29 | 4.65 |
| 6 | 2 3/8 | 8- 3/16 | 6 11/16 | 12.000 | 150 | 60.33 | 215.9 | 169.86 | 6.44 |
| 8 | 2 3/4 | 10 1/4 | 8 11/16 | 23.000 | 200 | 69.85 | 263.53 | 220.66 | 10.66 |
| 10 | 3 1/16 | 12 11/16 | 10 13/16 | 36.000 | 250 | 77.79 | 322.26 | 274.64 | 17.69 |
| 12 | 3 3/8 | 14 7/8 | 12 13/16 | 59.000 | 300 | 85.73 | 377.83 | 325.44 | 26.76 |
| 14 | 3 1/2 | 16 9/16 | 14 1/16 | 66.000 | 350 | 88.9 | 409.58 | 357.19 | 29.94 |
| 16 | 3 11/16 | 18 1/4 | 16 1/16 | 75.000 | 400 | 93.6 | 463.55 | 407.99 | 34.02 |
| 18 | 3 13/16 | 21 1/16 | 18 1/16 | 97.000 | 450 | 96.84 | 520.7 | 458.79 | 44 |
| 20 | 4 | 23 3/16 | 20 | 118.000 | 500 | 101.6 | 571.5 | 508 | 53.52 |
| 24 | 4 9/16 | 27 3/4 | 24 3/16 | 220.000 | 600 | 144.5 | 717.5 | 609.6 | 101 |
| 26 | 4 11/16 | 29 7/8 | 26 1/4 | 265.000 | 650 | 155.6 | 778 | 660.4 | 120 |
| 30 | 5 3/8 | 34 1/2 | 30 7/16 | 430.000 | 750 | 174.6 | 893.6 | 762 | 190 |
| 36 | 5 3/8 | 40 1/2 | 26 1/2 | 900.000 | 900 | 206.4 | 1070 | 914.4 | 310 |
Schedule XS Weldolet Dimensions
| Outlet Size(NPS) | Height A (mm) | OD -B (in) | Hole Dia C (in) | Weight in LB | Outlet Size in mm | Height A (mm) | OD -B (mm) | Hole Dia C (mm) | Weight in KG |
| 1/8 | 5/8 | 1 | 5/8 | 0.100 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1/4 | 5/8 | 1 | 5/8 | 0.100 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 3/8 | 3/4 | 1 1/4 | 3/4 | 0.150 | – | – | – | – | – |
| 1/2 | 3/4 | 1 3/8 | 15/16 | 0.200 | 15 | 19.05 | 34.93 | 23.81 | 0.09 |
| 3/4 | 7/8 | 1 3/4 | 1 3/16 | 0.300 | 20 | 22.23 | 44.45 | 30.16 | 0.14 |
| 1 | 1 1/16 | 2 1/8 | 1 7/16 | 0.500 | 25 | 26.99 | 53.98 | 36.51 | 0.21 |
| 1 1/4 | 1 1/4 | 2 9/16 | 1 3/4 | 0.900 | 32 | 31.75 | 65.09 | 44.45 | 0.41 |
| 1 1/2 | 1 5/16 | 2 7/8 | 2 1 | 1.100 | 40 | 33.34 | 73.03 | 50.8 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 1 1/2 | 3 1/2 | 2 9/16 | 1.750 | 50 | 38.1 | 88.9 | 65.09 | 0.79 |
| 2 1/2 | 1 5/8 | 4 1/16 | 3 | 2.600 | 65 | 41.28 | 103.19 | 76.2 | 1.18 |
| 3 | 1 3/4 | 4 13/16 | 3 11/16 | 4.100 | 80 | 44.45 | 122.24 | 93.66 | 1.86 |
| 3 1/2 | 1 7/8 | 5 1/4 | 4 | 5.600 | 90 | 47.63 | 136.53 | 112.71 | 2.54 |
| 4 | 2 | 6 | 4 3/4 | 6.400 | 100 | 50.8 | 152.4 | 120.65 | 2.9 |
| 6 | 3 1/16 | 8 5/16 | 6 11/16 | 23.000 | 150 | 77.79 | 225.43 | 169.86 | 10.43 |
| 8 | 3 7/8 | 11 1/2 | 8 11/16 | 37.000 | 200 | 98.43 | 292.1 | 220.66 | 16.78 |
| 10 | 3 11/16 | 13 3/16 | 10 7/16 | 46.000 | 250 | 93.66 | 323.85 | 265.11 | 20.87 |
| 12 | 4 1/16 | 15 5/8 | 12 1/2 | 61.000 | 300 | 103.1 | 379.41 | 317.5 | 27.67 |
| 14 | 3 15/16 | 16 | 13 | 70.000 | 350 | 100.01 | 431.8 | 350.84 | 31.75 |
| 16 | 4 3/16 | 18 3/8 | 15 | 102.000 | 400 | 106.36 | 466.73 | 403.23 | 46.27 |
| 18 | 4 3/8 | 20 3/8 | 17 | 130.000 | 450 | 111.13 | 523.88 | 455.61 | 58.97 |
| 20 | 4 11/16 | 22 15/16 | 19 | 158.000 | 500 | 119.06 | 582.61 | 509.59 | 71.67 |
| 24 | 5 1/2 | 28 1/2 | 24 3/16 | 290.000 | 600 | 152.4 | 722.2 | 609.6 | 142 |
| 26 | 5 3/4 | 30 1/8 | 27 1/4 | 350.000 | 650 | 165.1 | 782.6 | 660.4 | 168 |
Schedule XXS and Sch 160 Weldolet Dimensions
| Outlet Size(NPS) | Height A (mm) | OD -B (in) | Hole Dia C (in) | Weight in LB | Outlet Size in mm | Height A (mm) | OD -B (mm) | Hole Dia C (mm) | Weight in KG |
| 1/2 | 1 1/8 | 1 3/8 | 9/16 | 0.25 | 15 | 28.58 | 34.93 | 14.29 | 0.11 |
| 3/4 | 1 1/4 | 1 3/4 | 3/4 | 0.7 | 20 | 31.75 | 44.45 | 19.05 | 0.32 |
| 1 | 1 1/2 | 2 | 1 | 0.85 | 25 | 38.1 | 50.8 | 25.4 | 0.38 |
| 1 1/4 | 1 3/4 | 2 7/16 | 1 5/16 | 1 1/4 | 32 | 44.45 | 61.91 | 33.34 | 0.57 |
| 1 1/2 | 2 | 2 3/4 | 1 1/2 | 1 3/4 | 40 | 50.8 | 69.85 | 38.1 | 0.79 |
| 2 | 2 3/16 | 3 3/16 | 1 11/16 | 2.15 | 50 | 55.56 | 80.96 | 42.86 | 0.97 |
| 2 1/2 | 2 7/16 | 3 13/16 | 2 1/8 | 3 2/5 | 65 | 61.91 | 96.84 | 53.98 | 1.53 |
| 3 | 2 7/8 | 4 3/4 | 2 7/8 | 6.3 | 80 | 73.03 | 120.7 | 73.03 | 2.87 |
| 4 | 3 5/16 | 6 | 3 7/8 | 10.5 | 100 | 84.14 | 152.4 | 98.43 | 4.76 |
| 5 | 3 11/16 | 7 3/8 | 4 13/16 | 14.25 | 130 | 93.66 | 187.3 | 122.24 | 6.46 |
| 6 | 4 1/8 | 9 5/16 | 5 3/4 | 28 | 150 | 104.78 | 220.7 | 146.05 | 12.7 |
Conclusion
Weldolets are indispensable components in the world of piping and pipeline systems. Their efficiency, ease of installation, and ability to create smooth branch connections make them a preferred choice across industries. By understanding the working principles, advantages, and applications of Weldolets, engineers, and professionals can make informed decisions when designing and implementing complex piping systems. Whether it’s optimizing fluid flow or ensuring the safety of operations, Weldolets prove their worth time and time again.
