Ductile iron pipes are are mode of ductile cast iron and hence the name. They find extensive applications for potable water transmission and distribution. Ductile iron pipes are produced by the centrifugal casting method. Internal linings and external coatings are applied to prevent the corrosion of ductile iron pipes.
Nominal Diameter or DN, a dimensionless term is used to specify ductile iron pipe dimensions. Similar to steel pipes, the outside diameter of ductile iron pipes is kept constant, and depending on the pipe thickness the inner diameter varies. Ductile iron pipe dimensions vary from region to region. The dimension also varies according to the design code used. In the following paragraphs, the dimensions of ductile iron pipes are provided according to the design codes and regions.
Ductile Iron Pipe Dimensions in North America
AWWA C-151 governs the dimensions of ductile iron pipes in North America. Typical dimensions of centrifugally cast ductile-iron pipes according to AWWA C151/A.21.51 is provided below in a chart format:
| Nominal Size | Outside Diameter | Pressure Class | Outside Diameter | Pressure Class | ||||||||
| (inches) | (inches) | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | (mm) | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 |
| Wall Thickness (inches) | Wall Thickness (mm) | |||||||||||
| 3 | 3.96 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 101 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 6.35 |
| 4 | 4.8 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 0.26 | 122 | 6.6 | 6.6 | 6.6 | 6.6 | 6.6 |
| 6 | 6.9 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 175 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 6.35 | 6.35 |
| 8 | 9.05 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 230 | 6.86 | 6.86 | 6.86 | 6.86 | 6.86 |
| 10 | 11.1 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 282 | 7.37 | 7.37 | 7.37 | 7.37 | 7.37 |
| 12 | 13.2 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 335 | 7.87 | 7.87 | 7.87 | 7.87 | 7.87 |
| 14 | 15.3 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 389 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 | 8.38 |
| 16 | 17.4 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 442 | 8.64 | 8.64 | 8.64 | 8.64 | 8.64 |
| 18 | 19.5 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 495 | 8.89 | 8.89 | 8.89 | 8.89 | 8.89 |
| 20 | 21.6 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 549 | 9.14 | 9.14 | 9.14 | 9.14 | 9.14 |
| 24 | 25.8 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.44 | 655 | 9.65 | 9.65 | 9.65 | 10.4 | 11.2 |
| 30 | 32 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.51 | 813 | 9.91 | 9.91 | 10.9 | 11.9 | 13 |
| 36 | 38.3 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 973 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 12.2 | 13.5 | 14.7 |
| 42 | 44.5 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.59 | 0.65 | 1130 | 11.9 | 11.9 | 13.5 | 15 | 16.5 |
| 48 | 50.8 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.58 | 0.65 | 0.72 | 1290 | 13 | 13 | 14.7 | 16.5 | 18.3 |
| 54 | 57.56 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.65 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 1462 | 14.5 | 14.5 | 16.5 | 18.5 | 20.6 |
| 60 | 61.61 | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.83 | 1565 | 13.7 | 15.5 | 17.3 | 19.3 | 21.1 |
| 64 | 65.67 | 0.56 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 1668 | 14.2 | 16.3 | 18.3 | 20.3 | 22.1 |
The pressure class in the above table for ductile iron pipe dimension is the rated water pressure that the pipe can withstand in psi. The pipe thicknesses shown in the above table are adequate for the rated water working pressure plus a surge allowance of 100 psi. Thickness calculations are based on the minimum yield strength of 42,000 psi and a safety factor of 2.0 times the sum of the working pressure and 100 psi surge allowance.
Note that the above ductile iron pipe dimensions chart is based on standard pressure classes as specified in AWWA C151. However, there are special thickness classes as well based on AWWA C150 for which the dimensions for ductile iron pipes are provided in Fig. 1:
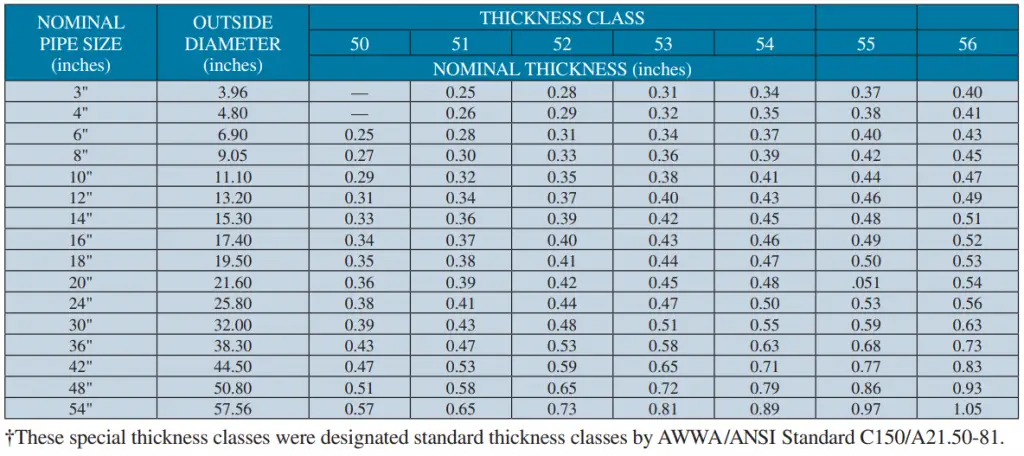
Ductile Iron Pipe Dimensions in Europe
European ductile iron pipe industry follows ISO 2531-Ductile iron pipes, fittings, accessories, and their joints for water applications. Accordingly, the dimensions of ductile iron pipes in Europe are governed by ISO 2531. Typical Dimensions are provided below:
| Pipe Size (DN) | Outside Diameter | Wall thickness | Outside Diameter | Wall thickness | ||||
| inches | inches | mm | mm | |||||
| Class 40 | K9 | K10 | Class 40 | K9 | K10 | |||
| 40 | 2.205 | 0.189 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 56 | 4.8 | 6 | 6 |
| 50 | 2.598 | 0.189 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 66 | 4.8 | 6 | 6 |
| 60 | 3.031 | 0.189 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 77 | 4.8 | 6 | 6 |
| 65 | 3.228 | 0.189 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 82 | 4.8 | 6 | 6 |
| 80 | 3.858 | 0.189 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 98 | 4.8 | 6 | 6 |
| 100 | 4.646 | 0.189 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 118 | 4.8 | 6 | 6 |
| 125 | 5.669 | 0.189 | 0.236 | 0.236 | 144 | 4.8 | 6 | 6 |
| 150 | 6.693 | 0.197 | 0.236 | 0.256 | 170 | 5 | 6 | 6.5 |
| 200 | 8.74 | 0.213 | 0.248 | 0.276 | 222 | 5.4 | 6.3 | 7 |
| 250 | 10.787 | 0.228 | 0.268 | 0.295 | 274 | 5.8 | 6.8 | 7.5 |
| 300 | 12.835 | 0.244 | 0.283 | 0.315 | 326 | 6.2 | 7.2 | 8 |
| 350 | 14.882 | 0.276 | 0.303 | 0.335 | 378 | 7 | 7.7 | 8.5 |
| 400 | 16.89 | 0.307 | 0.319 | 0.354 | 429 | 7.8 | 8.1 | 9 |
| 450 | 18.898 | – | 0.339 | 0.374 | 480 | – | 8.6 | 9.5 |
| 500 | 20.945 | – | 0.354 | 0.394 | 532 | – | 9 | 10 |
| 600 | 25 | – | 0.39 | 0.437 | 635 | – | 9.9 | 11.1 |
| 700 | 29.055 | – | 0.429 | 0.472 | 738 | – | 10.9 | 12 |
| 800 | 33.15 | – | 0.461 | 0.512 | 842 | – | 11.7 | 13 |
| 900 | 37.205 | – | 0.508 | 0.555 | 945 | – | 12.9 | 14.1 |
| 1000 | 41.26 | – | 0.531 | 0.591 | 1,048 | – | 13.5 | 15 |
| 1100 | 45.354 | – | 0.567 | 0.63 | 1,152 | – | 14.4 | 16 |
| 1200 | 49.409 | – | 0.602 | 0.669 | 1,255 | – | 15.3 | 17 |
| 1400 | 57.559 | – | 0.673 | 0.748 | 1,462 | – | 17.1 | 19 |
| 1500 | 61.614 | – | 0.709 | 0.787 | 1,565 | – | 18 | 20 |
| 1600 | 65.669 | – | 0.744 | 2.008 | 1,668 | – | 18.9 | 51 |
| 1800 | 73.819 | – | 0.815 | 0.906 | 1,875 | – | 20.7 | 23 |
| 2000 | 81.969 | – | 0.886 | 0.984 | 2,082 | – | 22.5 | 25 |
There are other European Standards that are dedicated to a specific type of ductile iron piping as follows EN 15655, EN 877, EN 598, EN 12842, EN 14628, EN 15189, EN 14901, EN 969, EN 15542, EN 545, EN 14525, etc.
Ductile Iron Pipe Dimensions in Australia and New Zealand
The ductile iron piping industry in Australia and New Zealand follows an independent specification AS/NZS 2280- Ductile iron pipes and fittings. Typical dimensions for ductile iron pipes for Australia and New Zealand are provided below:
| Nominal Size (DN) | Outside Diameter | Nominal Wall Thickness | Outside Diameter | Nominal Wall Thickness | Flange Class | ||
| (inches) | (inches) | (mm) | (mm) | ||||
| PN 20 | PN 35 | PN 20 | PN 35 | ||||
| 100 | 4.803 | – | 0.197 | 122 | – | 5 | 7 |
| 150 | 6.969 | – | 0.197 | 177 | – | 5 | 8 |
| 200 | 9.134 | – | 0.197 | 232 | – | 5 | 8 |
| 225 | 10.197 | 0.197 | 0.205 | 259 | 5 | 5.2 | 9 |
| 250 | 11.26 | 0.197 | 0.22 | 286 | 5 | 5.6 | 9 |
| 300 | 13.583 | 0.197 | 0.248 | 345 | 5 | 6.3 | 10 |
| 375 | 16.772 | 0.201 | 0.287 | 426 | 5.1 | 7.3 | 10 |
| 450 | 19.961 | 0.22 | 0.327 | 507 | 5.6 | 8.3 | 11 |
| 500 | 22.047 | 0.236 | 0.354 | 560 | 6 | 9 | 12 |
| 600 | 26.26 | 0.268 | 0.406 | 667 | 6.8 | 10.3 | 13 |
| 750 | 32.52 | 0.311 | 0.48 | 826 | 7.9 | 12.2 | 15 |

Thanks by your site, very usefull to clarify our doubts during a work day in the project activities.
Fast consult and quicly response for our doubts.
As per study added by Value Market Research, the Ductile iron pipe is the pipe made up of ductile iron particularly used for transmission of drinking water, slurries, sewage and process chemicals. The market is gaining growth on account of rising installation of the products in developed and developing nations. The initiatives undertaken by various governments towards water sanitation are further fuelling the market growth.
During my work I come across K7 K9 even K12 then there is C25 C30 C50.
I cannot seem to find any literature or documentation that comprehensively details what these designations mean or represent. Can you please assist or point me in the right direction
Rgds
How many holes available in DI various Pipe Dia
How is it that an 8″ DIP has a thickness of 0.27″ but an outside diameter of 9.05″? There is a difference of 0.51″.
Maybe the paint/coating.
How deep should12″ DI pipe be under a heavy haul road?