Surface coating for corrosion prevention is a critical aspect of preserving the integrity and longevity of steel structures and components. Corrosion, which is the gradual deterioration of metal due to chemical reactions in its environment, can lead to significant economic losses and safety hazards. Therefore, protecting steel surfaces from corrosion is essential in various industries, including piping, pipeline, construction, infrastructure, automotive, aerospace, and marine.
Surface coatings are designed to act as a barrier between the steel substrate and the corrosive environment, preventing the interaction that leads to corrosion. These coatings can be applied to various forms of steel, including sheet metal, structural steel, pipelines, and more.
What is Surface Coating?
Surface coating decorates and protects the surface on which it is applied. It can be defined as a homogeneous mixture of pigments, binders, solvents, and additives. The surface coating covers the surface completely and serves as an anti-corrosive agent. The success or failure of any coating is influenced by the following factors:
- Substrate Condition
- Surface condition and method of application
- Environmental condition at which it is applied and expected to withstand during service
- And last but not least the quality of paint used
Why Coat a Surface?
- Decorates the surface on which it is applied.
- Protects the surface from rust
- Protects from micro-organisms like fungi and algae maintaining their original body.
RUST NEVER SLEEPS!!!
Corrosion of Steel
Before delving into surface coatings, it’s crucial to understand the mechanisms behind corrosion. Corrosion occurs due to electrochemical reactions between metal, moisture, and other corrosive agents. The most common types of corrosion include:
Uniform Corrosion: This is the most straightforward form of corrosion, where the entire surface of the steel corrodes uniformly. It typically occurs in environments with a consistent level of corrosivity.
Localized Corrosion: Localized corrosion includes pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking (SCC). Pitting corrosion forms small, deep pits on the steel surface, while crevice corrosion occurs in gaps or crevices where moisture and oxygen are trapped. SCC is the result of tensile stresses and specific environmental conditions.
Galvanic Corrosion: Galvanic corrosion happens when two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact and immersed in an electrolyte. One metal corrodes rapidly (the anode), while the other remains protected (the cathode).
- Environmental Corrosion: Unstable condition of steel
- Chemical Corrosion: Chemicals like acids, and alkalies attack metal
- Corrosion Prevention: Isolation of metals from the corrosive environment by using paint coatings
Corrosion Control
- Using Inhibitive Primers Zinc phosphates/Chromate forms a passive layer with adhered rust.
- Using Sacrificial Primer. Indirect catholic Protection by Zinc in Zinc-rich primers
- Barrier Coatings. High DFT Coating System Isolates Surface from Corrosive Environment
Types of Surface Coatings
Surface coatings can be categorized into three main types: organic coatings, inorganic coatings, and metallic coatings.
Organic Coatings
Organic coatings are based on carbon-containing compounds and are widely used for corrosion prevention. They include:
- Paints: Traditional paints consist of pigments, binders (resins), solvents, and additives. Epoxy, polyurethane, and acrylic paints are commonly used for steel surfaces. They provide good barrier protection and are available in various colors.
- Powder Coatings: Powder coatings are applied as dry powder and then cured with heat. They are known for their durability, resistance to chemicals, and smooth finishes. Epoxy, polyester, and epoxy-polyester hybrid powders are commonly used.
- Coil Coatings: Coil coatings are applied to steel coils before they are formed into specific shapes. They are commonly used in the automotive and construction industries.
- Marine Coatings: Marine coatings are designed for steel structures exposed to harsh marine environments. They offer excellent corrosion resistance and are often used on ships, offshore platforms, and bridges.
Inorganic Coatings
Inorganic coatings are based on non-carbon compounds and include:
- Zinc-rich Coatings: These coatings contain a high concentration of zinc particles, which act sacrificially to protect the steel substrate. Zinc-rich coatings are often used in harsh environments and as a primer for other coatings.
- Phosphate Coatings: Phosphate coatings are commonly applied as a pre-treatment to improve the adhesion of organic coatings. They also provide some corrosion resistance.
- Chromate Conversion Coatings: These coatings, often used on aluminum and zinc-coated steel, provide corrosion protection and enhance paint adhesion.
Metallic Coatings
Metallic coatings involve the deposition of a layer of another metal onto the steel surface. Common metallic coatings include:
- Galvanizing: Galvanizing involves coating steel with a layer of zinc through hot-dip galvanizing or electro-galvanizing. Zinc provides sacrificial protection, and galvanized steel is widely used in construction and outdoor applications.
- Aluminizing: Aluminizing involves applying a layer of aluminum to the steel surface, offering excellent corrosion resistance at high temperatures.
- Tin Coatings: Tin coatings are used in the food and beverage industry for corrosion protection and as a barrier against contamination.
Composition of Paint or Surface Coat
The basic constituents of paints are
- Pigments 5 to 25%
- Binders 60 to 65%
- Solvents 15 to 25%
- Additives 1 to 5 %
The relative proposition of these ingredients can be varied to produce films with any desired physical and application characteristics
Pigments for Surface Coating
A finely divided powder that can disperse in media of various types to produce paints. It is insoluble in the medium. Important properties are
- Color
- Tinting Strength
- Opacity
- Fastness to light
- Resistance to heat
- The oil absorption of pigment
- Particle size: Hiding Power, Gloss or smoothness, Rate of settling of pigment
Binders for Surface Coating
Binders are the heart of the paint system. Binders bind or cement the pigment particle into a coherent film that adheres to the substrate. The mechanical and resistive properties of the film are controlled very largely by the binder.
The durability of the paint depends on the quality and quantity of binder used!!!!
- Convert the liquid coating on application to a solid dry film.
- Provide gloss to film
- Making the coating adhere to the substrate
- Given the elasticity of the film
- Resistance to water, chemicals, and abrasion
- Disperse the pigments and extenders
- Hold the pigment in suspension.
The Choice of Binder for Paint depends on the end use of the paint
Type of Binders
- Drying oils: Vegetable oils on exposure to air, convert from liquid to solid through a process of oxidation. Can be a sole film former but most often mixed with resin
- Resins: Most surface coatings contain a synthetic resin-based film former. Most decorative paints are based on oil-modified resins.
Few Important Binders/Resins
ALKYD Resins
- Largest groups of synthetic resins.
- They are oil-modified polyester
- Good exterior durability
- Low alkali and water resistance.
AMINO Resins: Melamine and urea-formaldehyde
Epoxy Resins:
- Has excellent adhesion, hardness, chemical, and corrosion resistance
- Can be used to do high-build paint
- Poor exterior durability
Poly-amide Resins: Used as curing agents for epoxy resins.
Polyurethane Resins:
- Good resistance to high temp, chemical and acid resistance, good resistance to various gases, alkali resistance.
- Low resistance to solvents like ketones, esters
Chlorinated Rubber:
- It is one pack of thermoplastic.
- Have good Chemical resistance and good acid and alkali resistance.
- Can be applied as high-build paint.
- Disadvantage: Poor resistance to high temp and solvents like ketones, aromatic HC
- Vinyl Resins:
- Cellulose Resins: Widely used in auto-finishing
- Acrylic Resins: Possess good light fastness, good adhesion, and excellent durability.
Solvents for Surface Coating
The primary function of the solvent is to dissolve film formers, thereby consistency suitable for the application. Choice solvent influences viscosity, drying and flow, and leveling.
Solvents are lost in the atmosphere, so it is an economic loss.
Solvents, in isolation or combination, are used in making thinner for the paints.
Examples of solvents:
Hydrocarbon Solvent: Aliphatic, aromatic, solvent Naptha, alcohols, ketones, esters, etc.
Additives for Surface Coating
Used in a small amount to give a coating one or more desirable properties. The only difference between additives and other raw materials is that the amount of additives is very small. Properties that can be controlled through additives are:
- Viscosity
- Setting
- Drying
- Gloss
- Opacity
- Bacterial action
- Thickness
- Deodorants, etc.
Classification of Paints and Surface Coatings
Paints can be classified based on:
- The Physical state: Liquid Paint and Stiff Paint
- The Thinner Used: Water thinnable and solvent thinnable
- The End used: Decorative and protective.
- Modes of film formation: Thermosetting and Thermoplastics
- The order of application: Undercoat and topcoat
- The extent of gloss: Glossy, semi-glossy, egg-shell. matt
- Modes of Film Formation: Film formation is either by thermosetting or thermoplastics.
Thermoplastic (Non -convertibles):
In these coatings when the paint is applied on a surface, the solvent evaporates living resin to its original form spread over the surface. So change is only physical and can be reversed to its original form by using thinner. E.g Chlorinated Rubber
Thermosetting (Convertible):
Chemical changes occur in the coating and dry film is different from its liquid state. Ex. Epoxy, alkyds, etc.
Surface Preparation
Surface preparation is a crucial step before applying any coating. It involves the removal of contaminants, oxides, and rust from the steel surface to ensure proper adhesion and performance of the coating. Surface preparation is the most important part of a coating system. The surface preparation of the coating system is what a foundation is for a building.
Surface Preparation of Steel
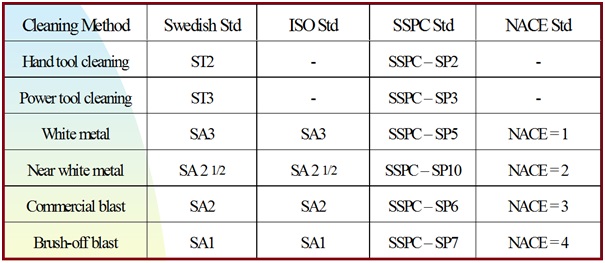
Some of the common surface preparation methods are
- Mechanical Cleaning: This includes techniques such as abrasive blasting (sandblasting), grinding, and wire brushing. Abrasive blasting is particularly effective in removing rust and scale.
- Chemical Cleaning: Chemical methods involve the use of acids, alkaline solutions, or solvents to remove contaminants and rust. Pickling and phosphating are common chemical cleaning methods.
- Electrocleaning: This process uses an electric current to remove contaminants from the steel surface. Electrocleaning is effective for removing organic residues.
- Conversion Coatings: Conversion coatings, such as chromate and phosphate coatings, chemically modify the steel surface to enhance adhesion and corrosion resistance.
Some of the various surface preparation methods of steel are
- Degreasing
- Hand tool cleaning
- Power tool cleaning
- Flame Cleaning
- Pickling
- Abrasive Blast Cleaning
- Wet Abrasive Blast Cleaning
International Standard of Blast Cleaning
Paint or Surface Coat Application Methods
The choice of coating application method depends on factors such as the type of coating, the substrate, and the intended use. Common methods include:
a. Brushing and Rolling: Suitable for small-scale projects and touch-ups, this method involves manually applying coatings using brushes or rollers.
b. Spraying: Spraying is a versatile method suitable for both small and large projects. It includes airless spraying, air-assisted spraying, and electrostatic spraying, among others.
c. Dipping: Dipping involves immersing the steel substrate into a tank of coating material. It is often used for small, complex parts.
d. Powder Coating: Powder coatings are applied using an electrostatic gun that charges the powder particles, making them adhere to the grounded steel substrate. The coated part is then cured in an oven.
e. Hot-Dip Galvanizing: This method involves immersing the steel in molten zinc. It is commonly used for large structures and provides excellent corrosion protection.
Theoretical Coverage (Sq.M/Ltr) =(%Volume Solids X100)/DFT in microns
Surface Coating Performance Evaluation
To assess the effectiveness of a surface coating for corrosion prevention, various tests and standards are employed:
a. Salt Spray Test (ASTM B117): This test assesses a coating’s resistance to corrosion in a salt-laden atmosphere. It involves exposing coated samples to a salt spray and monitoring their corrosion over time.
b. Adhesion Test (ASTM D3359): Adhesion tests measure the ability of a coating to adhere to the substrate. Various methods, including cross-cut and pull-off tests, are used.
c. Cyclic Corrosion Tests: These tests simulate real-world corrosion conditions, including wet and dry cycles, temperature variations, and UV exposure.
d. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): EIS measures the electrical impedance of a coated surface and can provide insights into the coating’s corrosion resistance.
e. Coating Thickness Measurement (ASTM D7091): This test ensures that the coating thickness meets the specified requirements, as inadequate thickness can compromise corrosion protection.
Factors Affecting Surface Coating Performance
The performance of a surface coating can be influenced by several factors:
a. Substrate Quality: The condition and cleanliness of the steel surface before coating application are crucial for adhesion and overall performance.
b. Environmental Conditions: The exposure environment, including temperature, humidity, and corrosive agents, can impact the rate of corrosion.
c. Coating Thickness: The thickness of the coating layer affects its ability to provide a barrier against corrosion. Thicker coatings generally offer better protection.
d. Coating Quality: The quality of the coating application, including uniformity, coverage, and absence of defects, is critical for long-term performance.
e. Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of coated surfaces are essential to identify and address any damage or degradation of the coating.
Maintenance and Repair of Coated Steel Surface
Maintenance and repair of coated steel surfaces are essential to ensure long-term corrosion protection. Common maintenance practices include:
a. Regular Inspection: Periodic visual inspections to detect any signs of coating damage, corrosion, or defects.
b. Cleaning: Removing dirt, debris, and contaminants from the coated surface to maintain the coating’s effectiveness.
c. Touch-up Painting: Repairing small areas of coating damage with compatible coatings to prevent further corrosion.
d. Recoating: When the existing coating reaches the end of its service life, recoating may be necessary to maintain protection.
e. Cathodic Protection: In some cases, cathodic protection systems can be used alongside coatings to provide additional corrosion protection.
Emerging Trends in Corrosion Prevention
The field of corrosion prevention is continually evolving. Some emerging trends include:
a. Nanotechnology: Nanocoatings, which incorporate nanoparticles, offer enhanced corrosion resistance and durability.
b. Smart Coatings: Smart coatings can sense and respond to changes in the environment, providing real-time corrosion protection.
c. Biodegradable Coatings: Environmentally friendly coatings that degrade over time without harming the environment are gaining popularity.
d. Self-healing Coatings: Self-healing coatings contain materials that can repair small defects and cracks, extending the life of the coating.
e. Corrosion Inhibitors: Advanced corrosion inhibitors, both organic and inorganic, are being developed for improved corrosion protection.








This is really great. I learned a lot from you. I will surely follow your guide for painting.
Great article. Learned a lot on industrial paints and coatings.
Would love to have some more details on tank inside coating spec, application techniques and surface preparation for hydrocarbon and water rich environments.
Thanks.