Flange couplings play a crucial role in countless machines and structures around the world. Their importance in bridging the gap between two rotating shafts is well-known. Flange couplings act as a connector to enable the seamless transfer of power and motion in various mechanical systems. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of flange couplings, exploring their design, applications, advantages, and key considerations.
What Are Flange Couplings?
Flange couplings are mechanical devices used to connect two shafts together in order to transmit power or torque from one shaft to another. They have two flanges mounted on each shaft end to make a connection using nuts, bolts, and gaskets. Flange Couplings are specifically designed for applications where alignment accuracy, high torque transmission, and vibration resistance are crucial.
Components of a Flange Coupling
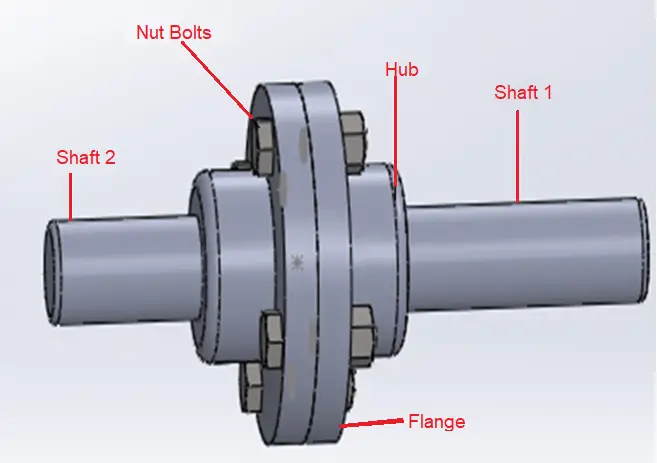
A typical flange coupling consists of two flanges, each attached to the end of a shaft. These flanges are then bolted together, with a gasket or a sealing mechanism in between. Refer to Fig. 1 below. The design of flange couplings can vary, but they generally consist of the following components:
- Flanges: These are the circular plates with holes for bolts. Flanges are typically made of materials like steel, cast iron, or aluminum for strength and durability.
- Bolts: Bolts pass through the holes in the flanges and are tightened to securely hold the two flanges together.
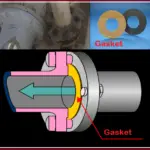
- Gasket or Seal: A gasket or seal is often used between the flanges to prevent leakage of fluids or lubricants and to maintain the alignment of the shafts.
Working of a Flange Coupling
With the flanges securely bolted together, the two shafts become mechanically linked. When one shaft rotates, it transmits torque to the other shaft through the flange coupling. The gasket or seal between the flanges prevents any leakage of fluids or contaminants.
Types of Flange Couplings
There are three types of flange couplings that are widely used in industries. They are:
- Protected Flange Coupling
- Unprotected Flange Coupling, and
- Marine Flange Coupling
Protected Flange Coupling:
A Protected Flange Coupling is a type of flange coupling designed with a protective covering or shield around the coupling assembly. The purpose of this protective enclosure is to shield the coupling from external contaminants, such as dust, dirt, moisture, or debris. It also provides a safety barrier, preventing accidental contact with the rotating components of the coupling.
Protected flange couplings are commonly used in industrial settings where there is a need to safeguard the coupling and ensure its long-term reliability. These protective enclosures can be made from materials like metal, plastic, or rubber, depending on the specific environmental conditions and safety requirements of the application.
Unprotected Flange Coupling:
An Unprotected Flange Coupling, on the other hand, does not have any form of protective covering or shield around the coupling assembly. Each shaft in these types of flange couplings is keyed to the boss of the flange with a counter-sunk key and both flanges are coupled together with rings of bolts.
Unprotected flange couplings are typically used in applications where environmental conditions are controlled, and there is little risk of contamination or exposure to moving parts. They are often found in situations where maintenance access is straightforward, and the coupling is regularly inspected and serviced.
Marine Flange Coupling:
A Marine Flange Coupling is a type of flange coupling specifically designed and manufactured for use in marine applications, particularly in ships and boats. In a Marine Flange Coupling, flanges are designed integral with the shafts. The number of bolts is decided based on the perimeter of the shafts. Marine flange couplings have headless bolts in a tapered form. These couplings are engineered to withstand the unique challenges posed by marine environments, including exposure to saltwater, high humidity, and corrosive conditions.
Marine flange couplings are constructed from materials that are highly resistant to corrosion, such as stainless steel or other non-corrosive alloys. They are also designed to maintain their integrity and functionality even in the presence of heavy vibrations and constant exposure to moisture. These couplings are commonly used to connect the engine or motor to the propeller shaft in marine vessels, ensuring efficient power transmission and reliable propulsion.
Flange Coupling Materials
Flange couplings are essential components in various industrial and mechanical systems. The choice of materials for flange couplings is critical to ensure their durability, reliability, and performance in specific applications. The selection of material depends on factors such as the environment, temperature, pressure, and the intended use of the coupling. Here are some common materials used for flange couplings:
- Cast Iron
- Carbon Steel
- Stainless Steel
- PVC
- Composites, etc
Applications of Flange Couplings
Flange couplings are used in medium to heavy-duty applications. They find applications in a wide range of industries, including:
- Industrial Machinery: Flange couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, conveyors, and other industrial machinery to transmit power efficiently and reliably.
- Marine Engineering: They are crucial in marine propulsion systems, connecting the engine’s output shaft to the propeller shaft.
- Automotive Industry: Flange couplings are used in drivetrain components, such as the connection between the transmission and the driveshaft.
- Aerospace: In aircraft and spacecraft, flange couplings are employed to connect various rotating components, ensuring precise and secure power transmission.
- Energy Sector: Power plants, both traditional and renewable, utilize flange couplings to connect turbines, generators, and other equipment.
Advantages of Flange Couplings
Flange couplings offer several advantages, making them a preferred choice in many applications:
- High Torque Transmission: Flange couplings are designed to handle high levels of torque, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Precise Alignment: The bolted design of flange couplings ensures precise alignment of shafts, reducing wear and tear and extending the life of connected components.
- Vibration Dampening: They are effective at dampening vibrations, which is crucial for machinery and vehicles to operate smoothly and quietly.
- Ease of Maintenance: Flange couplings are relatively easy to install and maintain, thanks to their simple design.
Considerations When Using Flange Couplings
While flange couplings offer numerous benefits, there are some important considerations to keep in mind:
- Alignment: Proper alignment is critical to prevent premature wear and damage to the coupling and connected machinery.
- Material Selection: Choose materials that are compatible with the operating conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and the type of fluids involved.
- Bolt Tightening: Proper torque and sequence when tightening the bolts are essential to maintain the integrity of the coupling.
- Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance are necessary to ensure the coupling continues to function optimally.
Flange couplings may not always be in the spotlight, but they are the unsung heroes of many rotating mechanical systems. Their ability to efficiently and reliably transmit power and motion while dampening vibrations and ensuring alignment makes them indispensable in a wide range of industries.
Understanding the design, advantages, and considerations of flange couplings is essential for engineers and maintenance professionals to keep machines and processes running smoothly. So, the next time you see a smoothly running machine, remember that flange couplings are likely hard at work behind the scenes, connecting the mechanical dots.