Buckling analysis for Vacuum Piping Systems is very important that every piping stress engineer should perform while analyzing Vacuum Piping. Vacuum piping analysis in the START-PROF software is analyzed according to the Russian Code GOST 32388-2013.
What is Vacuum Piping?
Vacuum piping is a piping system that operates at negative operating pressure. For example, if we remove all the air from a closed pipe then the pressure inside the pipe will be zero. This is called an absolute vacuum condition. The pipe thickness for such a condition must be designed for external pressure conditions, as well.
Setting Vacuum Pressure in START-PROF
The vacuum pressure in START-PROF software is specified by entering a negative operating pressure, the difference between internal absolute pressure and atmospheric pressure. Note that, The operating pressure that we set in START-PROF is not absolute pressure. It’s a relative pressure that indicates the difference between absolute internal and external pressures. So, If the internal absolute pressure is zero (absolute vacuum), then the operating pressure should be -0.1 MPa.
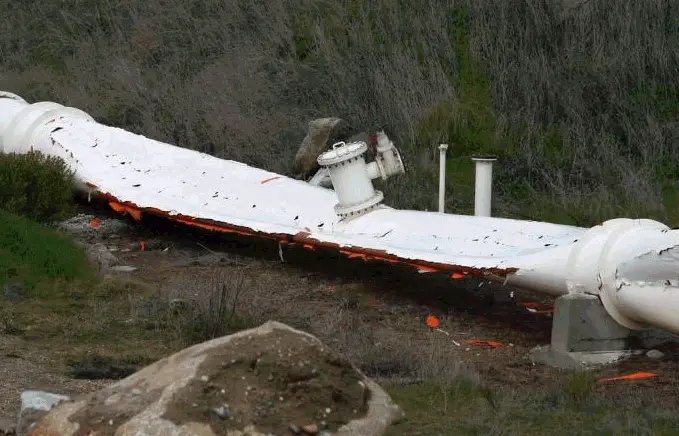

Features of vacuum piping
The main features of vacuum piping are as follows:
- Pipes are shortened under external pressure instead of elongating.
- Unbalanced axial expansion joints are shortened under external pressure instead of elongating.
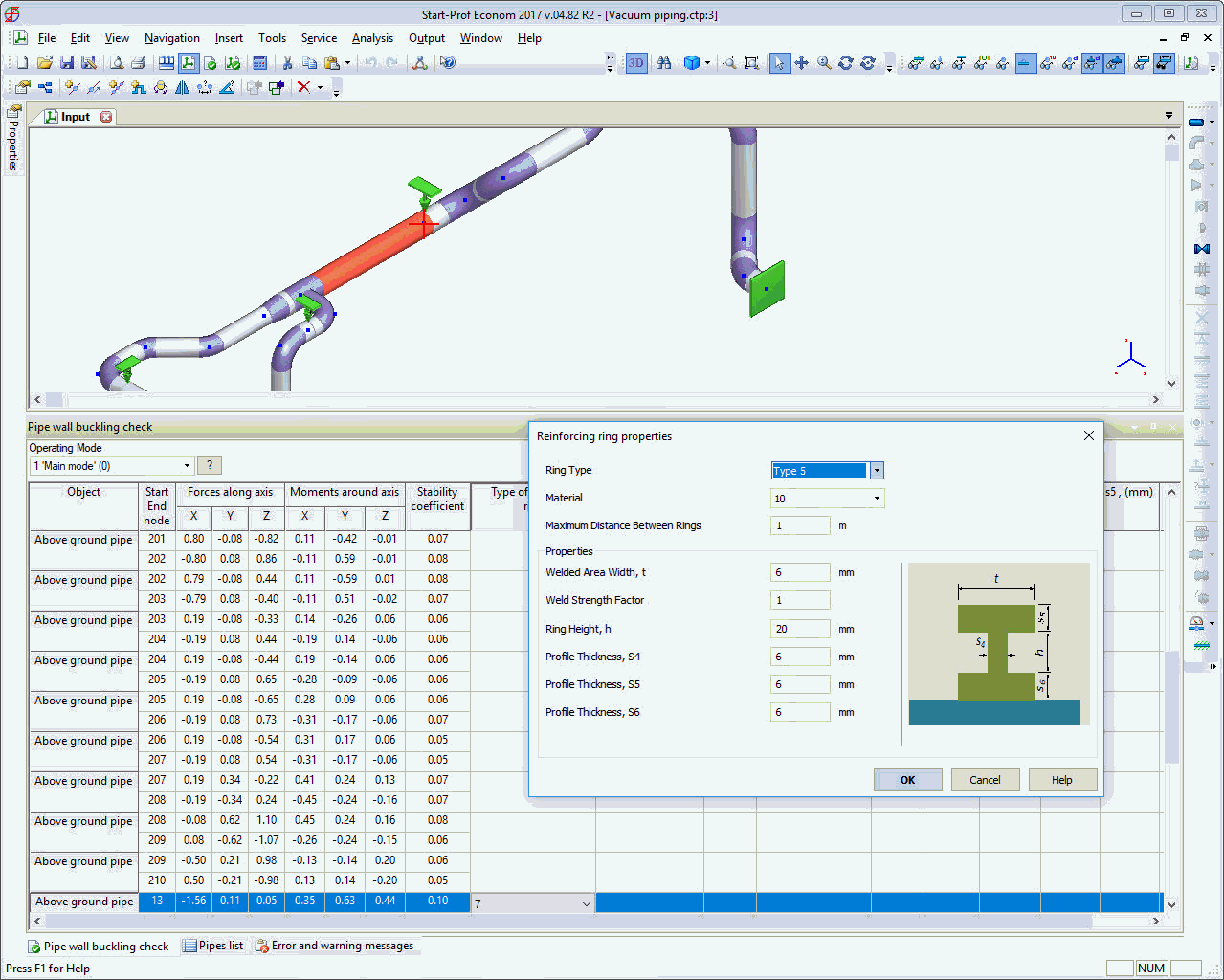
- The pipe wall buckling (stability loss) may happen under external pressure.
Buckling Analysis for vacuum Piping
After the START-PROF analysis is done the pipe wall buckling check table must be analyzed. Also, the additional check analysis could be done in Start-Elements. In this case, stability analysis for vacuum and strength under test pressure is checked.
If the buckling analysis is failed the wall thickness should be increased or stiffening rings must be added. The shape and distance between rings should be checked by analysis.
The buckling check of high-temperature piping is not possible because the method of analysis doesn’t consider the creep effect. See 14.1.1 GOST 32388-2013: This code applies to pipe operating under vacuum or external pressure, without metal creep. Wall temperature should not exceed 380 °С for carbon steel, 420 °С for low alloy steel, and 525 °С for austenitic steel.
Click here to learn more about START-PROF Stress Analysis theories and tutorials

Is there a theoretical analysis available for pipe failure under vacuum? ( Not interested in software)
GOST 32388 code (https://www.passuite.com/kbase/doc/start/WebHelp_en/stp.htm) has theoretical analysis and also a lot of books exist that explain how to do that
https://www.passuite.com/kbase/doc/start/WebHelp_en/result5.htm