Material Test Certificate, also known as Mill Test Certificate (MTC), is a popular quality assurance document used in the metals industry. While purchasing steel pipes, plates, bars, or other steel materials, the manufacturer provides the material test certificate along with the products that certify the material’s technical specifications. It covers parameters like chemical composition, manufacturing routes, mechanical and physical properties, heat treatment details, testing results, heat traceability, or compliance with a set of international or local standards. In a nutshell, Material Test Certification is considered the ID of a particular material heat and production batch. It indicates its provenance, its quality and can offer insight into material performance under real-life service conditions.
Even though most of the required data is clearly specified in the material test certificate, many buyers sometimes find it difficult to read and understand the certificates. In this article, we will discuss the significance of material test certificates.
What is a Material Test Certificate?
A Material Test Certificate or Mill Test Certificate of a product is a document issued by the manufacturer to certify that chemical and mechanical properties are in accordance with the product specification. The material test certificate is also known as the material test report as the certificate is issued in paper form. The certificate contains the factory quality control approval, in addition to a special material test certificate stamp. Note that, it is not necessary for all commercially available materials to have a material certificate.
Contents of a Material Test Certificate
Usually, the material test certificates from different manufacturers contain different levels of information. However, in general, they include the following information in the material test certificate:
- Type of certificate and standard (For example EN 10204 3.1 or EN 10204 3.2)
- Basic information like manufacturer name, product name, weight, and dimensions
- Material heat number
- The quantity covered by the certificate
- The batch number which is physically marked on the product as well
- Chemical composition analysis results
- Mechanical test results such as tensile strength, yield strength, and more.
- Dimensional measurement results. These data check compliance with acceptable tolerances per standard (For example, for steel pipes: diameter, pipe schedule or wall thickness, length, straightness)
- Grade of Material (Example; A106-B) and applicable specification, including results of chemical and mechanical tests
- Additional test results (when performed) like hydrostatic, ultrasounds (UT), magnetic particles, metal graphic result, hardness, impact test, etc.
- Any addenda useful to appraise the full features of the product
The reference standards for testing and report content usually align with the manufacturing standards of the facility or the specific requirements of the clients.
Types of Material Test Certificates/Mill Test Certificate Types
A mill test certificate is generally issued conforming to EN 10204. There are four types of mill test certificates as specified in EN 10204. They are:
- MTC Type 2.1
- MTC Type 2.2
- MTC Type 3.1
- MTC Type 3.2
Material Test Certificate Type 2.1
The material test certificate 2.1 provides a statement declaring that the products supplied comply with the order’s requirements. However, MTC 2.1 does not require adding the test results.
Material Test Certificate Type 2.2
In the material test certificate 2.2, the manufacturer declares that supplied products conform with order requirements. The report needs to include the test results. MTC Type 2.2 differs from MTC Type 2.1 as test results are provided in the report of MTC 2.2. These testing results are derived from a non-specific inspection and the manufacturer. This means the manufacturer can determine the tests without outside counsel or requirements.
Material Test Certificate Type 3.1
The manufacturer issues the material test certificate 3.1 to provide a declaration stating that the supplied products are in conformance with the requirements of the order. The report also provides the results of the required tests which are defined by the product specification, the official regulation, and corresponding rules. The document must be validated by the manufacturer’s authorized inspection representative who is independent of the manufacturing department.
Material Test Certificate Type 3.2
The material test certificate 3.2 is validated either by the manufacturer’s authorized inspection representative who is independent of the manufacturing department or by the purchaser’s authorized inspection representative or by a third-party inspector.
In MTC 3.2, the manufacturer declares that the products comply with the requirements of the received order. Additionally, the report includes test results. Material certificate 3.2 requires the report to be countersigned by an independent inspection authority. This is the main difference with MTC 3.1, which needs validation only by a company representative, independent of the manufacturing process.
In both MTC 3.1 and 3.2, the producer needs to operate traceability procedures and provide the corresponding inspection documents as and when required.
How to Read Material Test Certificate?
Reading a material test certificate can sometimes be difficult. The main information that has to be taken from the report is explained below by taking a sample material test certificate as shown in Fig. 1 (Image Courtesy: Material Welding) below.
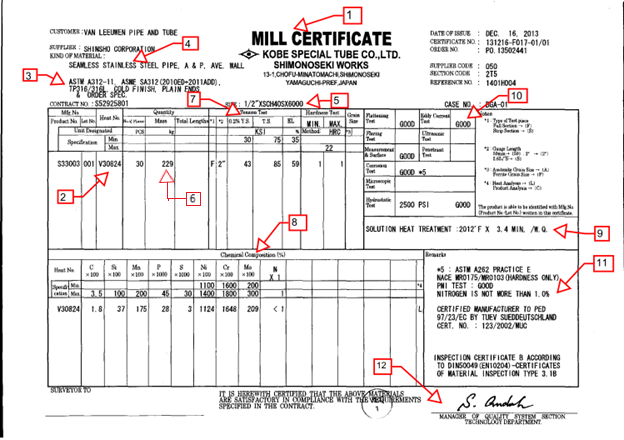
Refer below mentioned numbers corresponding to the numbers mentioned in Fig. 1.
1. Name of the manufacturer
At the top of the material test certificate, the name of the manufacturer who produced the product is mentioned. In this example, the company name along with their address is provided clearly. In general, MTC contains the manufacturer’s name, logo, country of origin, workshop location, etc.
2. Lot Number/Material Heat Number/Cast Number
The lot number or material heat number must be provided in MTC to provide the primary traceability for any given material. The metal’s matching heat number must always match the heat number mentioned on the certificate. Mechanical and chemical properties of the material are linked with this lot number for proper identification.
3. Material Grade and Specification
The material specification and grade provide the material’s chemical, mechanical, and physical properties. As you can see in Fig. 1, the material is dual-certified stainless steel TP 316/316L. So, when reading the material test certificate, the grade and specification of the product must be noted.
4. Delivery Condition
The material test certification confirms the delivery condition of the material as per the order. This categorization may include how a product is made, the type of manufacturing process, whether hot or cold finished, seamless or welded, etc. MTC includes abbreviated forms in the report as follows:
- W – Welded (RT or UT)
- SMLS – Seamless
- WX – Welded (100% RT)
- WU – Welded (100% UT)
5. Material Dimensions
The material test certificate also includes the dimensions of the product. The dimensions vary depending on the type of product. For example, a plate material is designated by its length, width, thickness, and weight.
6. Weight of the Material
The weight of the material per unit length is also specified in the material test certificate report. Some of the material’s price also depends on the weight of the product.
7. Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties inform the strength, hardness, and elongation properties of the material under procurement. MTC should confirm that the mechanical properties are as intended as per the purchase order.
8. Chemical Analysis
The chemical analysis is provided in MTC corresponding to heat number. The chemical composition of each alloying element should match the element requirements as per the order.
9. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment requirements also form part of the MTC. Specific heating or cooling processes that the material has undergone shall be listed on the material test certificate.
10. Hydrotest and Non-Destructive Testing requirements
The details of all the tests performed are listed in this section. Hydrotest or any type of non-destructive examination must be specifically mentioned in the MTC report.
11. Supplementary
The section includes any additional details like PMI test, NACE compliance, etc.
12. Certified Mill Signature
Finally, each MTC must be signed and stamped by authorized professionals. The accuracy of the information is only ensured by the sign and stamp of authorized personnel.
Purpose of Material Test Certificate
The Material test certificate of any material serves the following two important purposes:
Verification of Product Quality
The material test certification certifies the product’s quality. It ensures that the product has undergone the required testing and satisfies the required standards. The MTC should be supplied along with the product. All different types of products have their own individual Material Test Certificates.
Improved Transparency and Traceability
The mill test certificate also provides transparency and traceability during the manufacturing process. By reviewing the material test certificate corresponding to each heat number, any specific material can easily be traced.
