Pipeline pigging is the process of using a specialized device called a “pig” to clean, inspect, and maintain pipelines used for transporting liquids or gases. Pigs are typically made of various materials, such as rubber, urethane, or steel, and are inserted into the pipeline through access points called “pig launchers” and “pig receivers.”
The pig is propelled through the pipeline using the fluid flow, and its design allows it to remove debris, sediment, or other buildups from the pipeline’s interior walls. This cleaning process helps to prevent corrosion, improve flow rates, and maintain the integrity of the pipeline.
In addition to cleaning, pipeline pigging can also be used to inspect pipelines for damage or defects, such as cracks, corrosion, or leaks. Specialized inspection pigs can be equipped with sensors and cameras that allow for the detection and identification of these issues, helping to prevent potential leaks or failures.
Pipeline pigging can be performed on a regular maintenance schedule, or as needed when issues are suspected. The use of pigs can help reduce downtime and maintenance costs, as well as improve the overall safety and efficiency of the pipeline. However, it is important to ensure that pigging operations are conducted safely and that all necessary precautions are taken to prevent accidents or damage to the pipeline.
The process of driving the pig through a pipeline by the fluid is called a pipeline pigging operation. The term pig was originally referred to as Go-Devil scrapers which were driven through the pipeline by the flowing fluid trailing spring-loaded rakes for removing the wax off the internal walls. People believe that “PIG” is the short form of the term “Pipeline Inspection Gauge”. During pipeline pigging a squealing noise that sounds like a pig squealing arises, hence the name “PIG” is given.
Pipeline Pigging is used to perform various cleaning, clearing, dimensioning, maintenance, inspection, process, and pipeline testing operations on new and existing pipelines. A pipeline-pigging system includes
- Pigs.
- Pig Launcher.
- Pig Receiver.
Reasons for Pipeline Pigging
A pipeline Pigging operation is performed to
- Maintain a reliable and acceptable performance of the pipeline in terms of safety and product delivery at an economical cost.
- Provide a defined margin of safety for operating the pipeline at its designated pressure.
- Provide timely information on all pipeline defects such that repairs can be carried out according to a managed schedule.
There are several kinds of flaws and defects in pipelines that can lead to pipeline failure, the main families being:-
- Metal loss
- Cracks or crack-like defects
- Laminations and other mid-wall defects
- Geometric anomalies
There are basically three reasons to pig a pipeline:
- To separate dissimilar products.
- To remove undesirable materials.
- To perform internal cleaning, inspections, and maintenance.
Working of the Pipeline Pigging Process
Pipeline Pigs are inserted into a Pig Launcher and then the pressurized flow is applied to the rear of the device. The flow forces the pig to move into the pipeline. The force applied by a pig when it moves in a pipeline can be estimated by multiplying the cross-sectional area of the back of the pig by the pressure applied to the rear of the pig.
In General, the outside diameter of most pigs will be sized to be larger than the internal bore. This size difference creates a resultant ‘interference’ that enables the pig to scrape and remove debris as it moves through the pipeline. The type of pig employed determines the degree of effectiveness in cleaning a pipeline. Various other factors like flow rate, pig speed, length of the pipeline, number of pigging runs, pressure, temperature, the volume of debris to be removed, number and type of bends, pipeline elevations, pigging frequency, etc are also to be considered.
When the pig reaches the other end of the pipeline it is captured in a Pig Receiver which is isolated via a shut-off valve, allowing the pig to be safely removed.
Which Pipelines are ‘Piggable’?
Most of the pipelines constructed of materials like Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Duplex Stainless Steel, AC, GRP, HDPE, DICL, Cast Iron, Plastic, PVC, and others can all be pigged. Additional considerations for piggable pipelines are:
- number and type of bends,
- number and type of valves,
- flow rate,
- flow media,
- pressure rating,
- internal diameter(s),
- end connections,
- operating temperature,
- pipeline length,
- pipeline elevations,
- handling of flow and debris downstream.
The decision to pig any pipeline is considered by a thorough analysis of the line in conjunction with field-proven experience and advice offered by a reputable pigging specialist.
Pipeline Pig Types
Three categories of pigs are used to accomplish the above-mentioned tasks. They are:
- Utility Pigs, are used to perform functions such as cleaning, separating, or dewatering.
- In-Line Inspection Pigs: They provide information on the line condition along with the extent and location of any problems.
- Gel Pigs are used in conjunction with conventional pigs to optimize pipeline dewatering, cleaning, and drying tasks.

Utility PIGs
Based on the fundamental purpose, Utility pigs can be divided into two groups as listed below:
- Cleaning pigs
- Remove solid deposits.
- Remove Semi-solid deposits.
- Remove Debris.
- Sealing pigs
- Provide an interface between two dissimilar products.
- Provide a good seal in order to sweep liquids.
Types or forms of Utility pigs:
- Spherical Pigs (inflatable, solid, foam, and soluble).
- Foam Pigs (Polly-Pigs).
- Mandrel Pigs
- Solid Cast Pigs.
Spherical PIGs (Fig. 2):
There are four basic types of spheres:
- inflatable.
- Solid.
- Foam.
- Soluble.
Spherical PIGs are normally used for
- Removing liquids from wet gas systems.
- Serving to prove fluid meters.
- Controlling paraffin in crude oil pipelines.
- Flooding pipeline to conduct hydrostatic tests.
- Dewatering after pipeline rehabilitation or after new construction.
They should never be run in lines that do not have special flow tees installed.
Foam PIGs (Fig. 2):
- They are normally manufactured in a bullet shape.
- Coated pigs may have a spiral coating of polyurethane, various brush materials, or silicon carbide coating.
- The standard dimension of foam pig length is twice the diameter.
- Foam pigs are lightweight, compressible, expandable, and flexible.
- They have the ability to travel through multiple diameter pipelines and go around mitered bends and short radius 90o bends.
- They also go through valves with as little as a 65% opening.
- Foam pigs are that they are a one-time-use product.
- High concentrations of some acids will shorten life.
- Foam pigs are inexpensive.
Foam pigs are used for pipelines for
- proving,
- drying
- wiping,
- removal of thick soft deposits,
- condensate removal in wet gas pipelines,
- pigging multiple diameters
- scraping and mild abrasion of the pipeline.
- the shorter length of runs,
Mandrel PIGs (Fig. 2):
- The mandrel pig can be used for
- cleaning pig,
- sealing pig,
- combination of both.
- The seals and brushes can be replaced to make the pig reusable.
- These pigs are designed for long runs.
- The cost of redressing the pig is high, and larger pigs require special handling equipment to load and unload the pig.
- Occasionally the wire brush bristles break off and get into instrumentation and other unwanted places.
- Smaller-size mandrel pigs do not negotiate 1.5D bends.
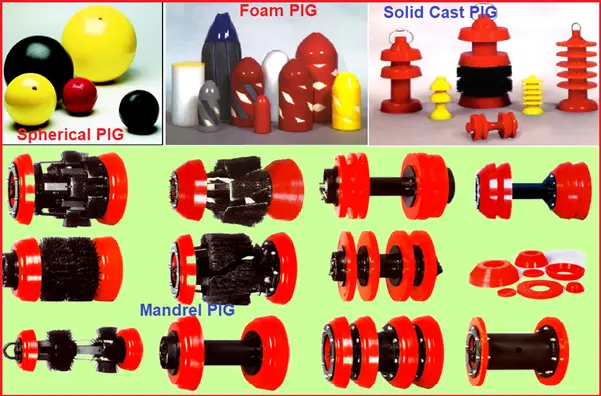
Solid cast PIGs (Fig. 2):
- Solid cast pigs are usually molded in one piece.
- The materials used for the preparation of solid cast Pig are neoprene, nitrile, Viton, and polyurethane).
- Solid cast pigs are considered sealing pigs although some solid cast pigs are available with wraparound brushes and can be used for cleaning purposes.
- The solid cast pig is available in the cup, disc, or a combination cup/ disc design.
- Because of the cost to redress a mandrel pig, many companies use the solid cast pig up to 14 inches or 16 inches.
- Solid cast pigs are used
- In removing liquids from product pipelines.
- removing condensate and water from wet gas systems.
- Controlling paraffin build-up in crude oil systems.
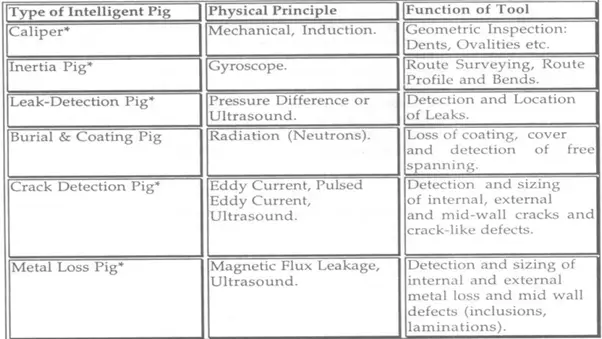
Inline Inspection PIGs
In-line inspection PIG tools are used to carry out various types of tasks including:
- Measuring pipe diameter/geometry
- Monitoring pipeline curvature
- Determining the pipeline profile
- Recording temperature/pressure
- Measuring bend
- Detecting metal loss/corrosion
- Performing photographic inspection
- Detecting crack
- Measuring wax deposition
- Detecting leak
- Taking product samples, and
- Mapping
Types of Pipeline Defects
- Metal Loss
- Gouging
- Cracks
- Dents and Buckles
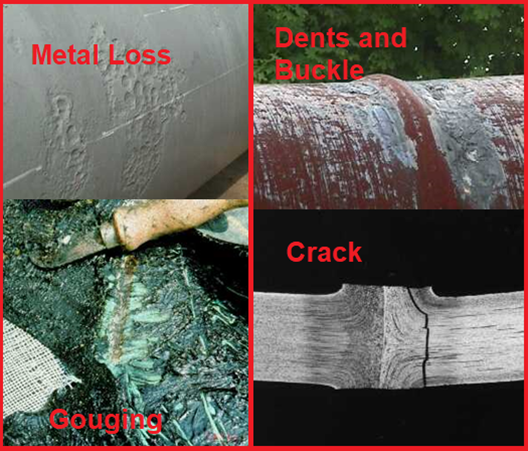
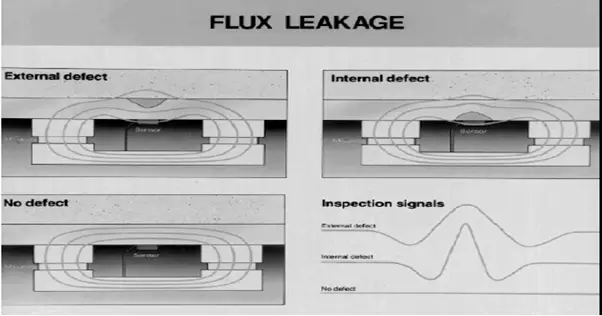
Metal Loss (Fig. 4):
- Pipeline operators typically use MFL to find metal loss due to corrosion or gouging.
- Metal loss is found when an MFL tool measures a local change in the magnetic field.
Gouging (Fig. 4):
- Gouging is the mechanical removal of metal from a local area on the surface of the pipe.
- The gouged area may contain shallow cracks, which further reduce the pressure-carrying capability of the pipe
Dents and Buckles (Fig. 4):
- Dents are depressions in the pipe surface, and buckles are a partial collapse of the pipe due to excessive bending or compression.
- MFL tools detect dents and buckles when the sensors lose contact with the wall.
Crack (Fig. 4) :
- Cracks in pipelines are due to fatigue, stress corrosion, and weld defects.
- Cracks can sometimes be found when they are oriented in a direction that significantly affects the magnetic field around the defect.

Magnetic Flux Pigging
- History
- Flux leakage techniques were used as early as 1868 by the Institute of Naval Architects in England.
- In 1918, magnetic particle inspection accidentally discovered magnetic particles
- The first MFL in-line inspection tool for pipelines was introduced in 1965 by Tub scope.
Working Principle of MFL IN-LINE INSPECTION PIG (Fig. 5):
Ultrasonic Intelligent Pig
- History
- The first-in-line inspection – 1980.
- Crack inspection tools – 1990.
- A new generation of ultrasonic tools – 2002
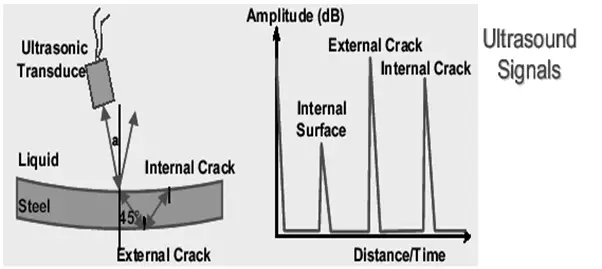
- They work in a pulse-echo mode with a rather high repetition frequency.
- Straight incidence of the ultrasonic pulses is used to measure the wall thickness and 45º incidence is used for the detection of cracks.
Working principle of Ultrasonic Inline inspection Pig (Fig. 6):
GEL PIGs
Types of Gel Pigs
- High-viscosity sealing gels
- Commissioning cleaning gel systems
- Polymer Gel Pig
- Debris pickup gel.
- Batching or separator gel.
- Hydrocarbon gel.
- Dehydrating gel.
The Principal Pipeline applications for gel pigs are as follows:
- Product separation.
- Debris removal.
- Line filling/ hydro testing.
- Dewatering and drying.
- Condensate removal from gas lines.
- Inhibitor and biocide laydown.
- Special chemical treatment.
- Removal of stuck pigs.
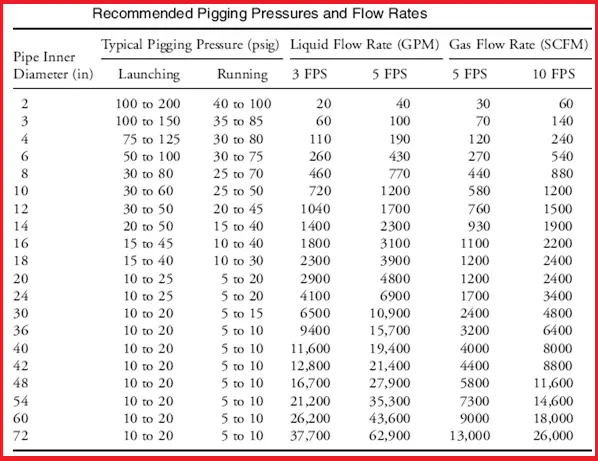
Pipeline Pigging Pressure
The following table gives the recommended pipeline pigging pressures and flow rates for pipeline pigging operations.
Applications of Pipeline Pigging
- During pipeline construction, pigging is used for debris removal, gauging, cleaning, flooding, and dewatering.
- During fluid production operations, pigging is utilized for removing wax in oil pipelines and removing liquids in gas pipelines.
- pigging is widely employed for pipeline inspection purposes such as wall thickness measurement and detection of spanning and burial.
- Pigging is also run for coating the inside surface of the pipeline with inhibitors and providing pressure resistance during other pipeline maintenance operations.
In recent times, Smart PIG is used to travel through a pipeline which gathers important pipeline data like the presence and location of corrosion or other irregularities on the inner walls of the pipe. That’s why the pipeline pigging using smart pigs are often termed as Intelligent Pigging.
What is a PIG Launcher?
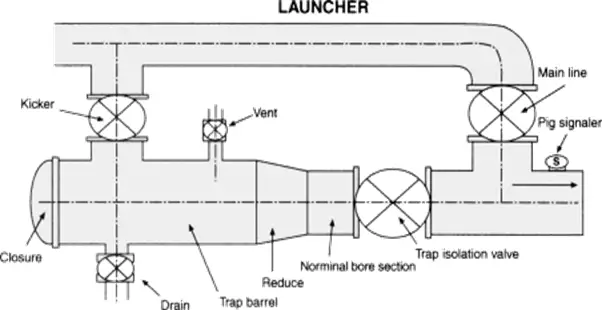
A Pig Launcher is a device, generally, a Y-shaped funnel section of a pipeline system from where the PIG is launched. It is basically a pressurized container that can be opened to insert the PIG. Refer to Fig. 8 and Fig. 9 for a clear idea of what a Pig Launcher looks like.
What is a PIG Receiver?
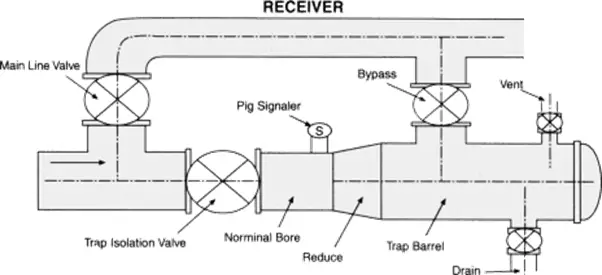
A pig receiver is a container or device to receive a pipeline pig out of the pipeline without interrupting the flow. This forms a part of the pipeline pigging system. Both pig launchers and receivers are known as pig trap assemblies.
Both the Pig launcher and receiver constitute the following components:
- Major barrel
- Minor barrel
- Pig signaller
- End closure
- Kicker line connection
- Pressure gauge connection
- Utility connections
- Vent and drain connection
Pig launcher and receiver systems are normally installed in a horizontal direction and designed based on pipeline design code.
Pipeline Pigging Products
Pipeline pigging products refer to the various types of pigs and related equipment used in pipeline pigging operations. These products include both cleaning and inspection pigs, as well as the launchers, receivers, and other tools used in the pigging process.
Cleaning pigs are used to remove debris, sediment, and other buildups from the interior walls of pipelines. These pigs can be made of various materials, including rubber, polyurethane, or steel, and can be designed with different shapes and sizes to accommodate different pipeline diameters and cleaning requirements.
Inspection pigs are used to detect and identify issues such as cracks, corrosion, or leaks in pipelines. These pigs are typically equipped with sensors, cameras, or other specialized equipment that can provide detailed information about the condition of the pipeline.
Launchers and receivers are used to insert and remove pigs from the pipeline. These are typically large, heavy-duty vessels designed to withstand the high pressures and temperatures present in pipelines.
Other pipeline-pigging products may include various tools and accessories, such as brushes, scrapers, and gauges, that can be used to clean or inspect pipelines.
The selection of pipeline-pigging products will depend on the specific requirements of the pipeline and the pigging operation. Working with a qualified pigging equipment supplier or engineer can help ensure that the appropriate products are selected for the specific application and that they meet all necessary safety and performance standards.
Pipeline Pigging Companies
There are many renowned pipeline-pigging companies around the world that offer a range of pigging products and services. Here are a few examples:
- Baker Hughes: A multinational oilfield services company that offers a range of pigging products and services, including pigging tools, cleaning and inspection pigs, and data analysis software.
- T.D. Williamson: A global pipeline services company that offers a range of pigging products and services, including pigging tools, inspection pigs, and pipeline cleaning services.
- ROSEN Group: A leading provider of inspection, integrity, and maintenance services for the energy industry, including pipeline pigging products and services.
- Pigs Unlimited International: A leading supplier of pipeline pigging products, including cleaning and inspection pigs, launchers, receivers, and other pigging equipment.
- NDT Global: A provider of advanced pipeline inspection and integrity services, including high-resolution geometry and mapping tools and inspection pigs.
- Quest Integrity: A global provider of advanced inspection and engineering services, including pipeline pigging products and services.
- Pigtek Ltd: A UK-based manufacturer and supplier of pipeline pigging products and services, including cleaning and inspection pigs, launchers, receivers, and other pigging equipment.
Conclusions:
Pigging is a vital tool that helps to achieve Pipeline integrity by providing
- Safety and product delivery at an economical cost.
- Reduces the failure
- Overall pressure drop.
- Pipeline flow efficiency.

This is a very nice piece. Thanks for the enlightenment about pigging. I have learnt a great deal from your work.
Hi. Please, if the pig gets stuck in the pipe, it is possible to release the pig by shocking method. How many times is this operation allowed?……..thanks
the best you can do is to inquire asssistance from the product manufacturer.
Coated lines inside sleeves ,it travel not in one plane,road crossings,45deg jumps, 90deg loops. How pigging can manage.
This pipeline comes under challenging pipeline and has special tools to address these challenges
Hi,
Do you use PIG STOPS in trap barrels or no?
Congrats on your job!
N.
I need to decide , need mandrel pig with disc to make it bi directional or cup to make it uni directional
Mandrel with disks- bidirectional
Mandrel with cups – uni directional
for pipeline works which runs around 80 km with GRE material and CS with HDPE lining material required any pigging. Service of media is treated water.
80km for treated water. then what is distance for other fluids like crude and others.
how to calculate distance? can u please explain…
Dear Sir,
We are exploring vendors of pigging system in India.
Kindly suggest few pigging system manufacturers in India.
Thank you,
Vinod Kumar
Looking for a Procedure in Pigging. This is a great start/template. You’re saving lives every time you share your experiences. Thank you for sharing.
sir this lecture is very useful for me because i am now in this industry and i looking my career in pipe line field
lecture is very knowledgable who want to build his career in pipe line