Features of HDPE, PE-RT, PP-H, PP-R, PVC-C, PVDF
The main features of HDPE piping and other plastic piping related to steel piping are:
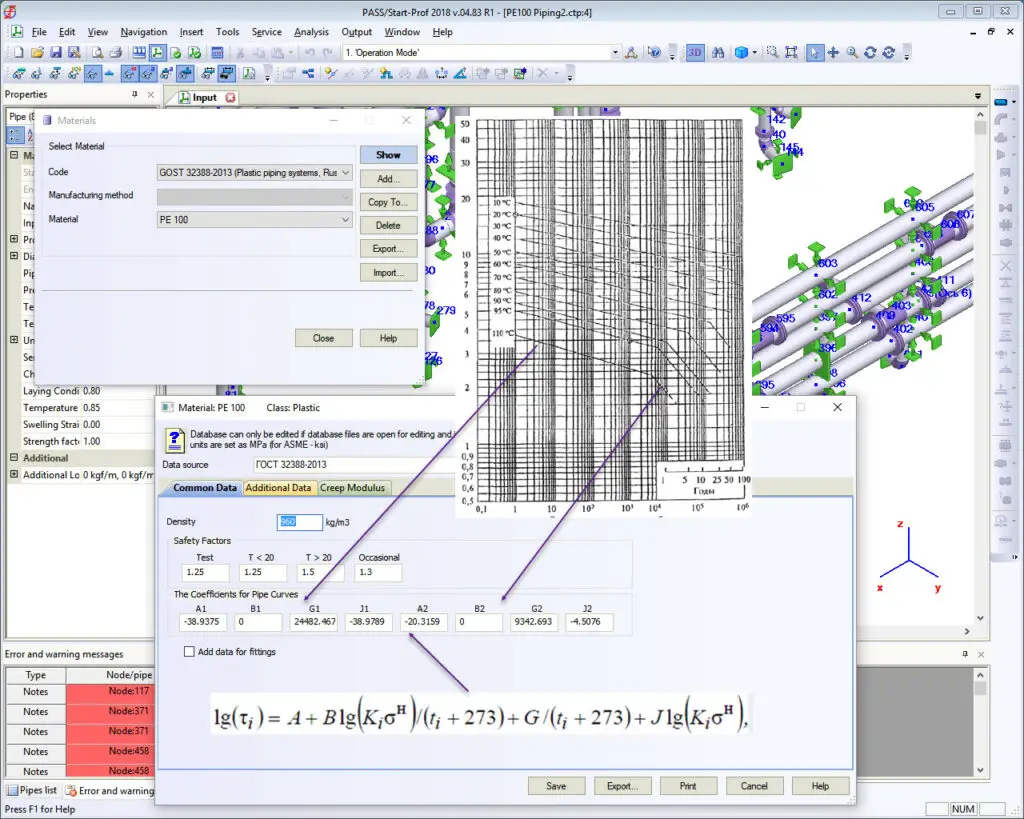
- The allowable stress of plastic piping is dependent on service life and temperature. The equation is. The A, B, G, and J factors are stored in the Start-Prof material database
- In some cases, swelling elongation due to a chemical reaction with the product should be considered. The swelling strain should be specified in the pipe properties
- Linear expansion for plastic piping is much greater than for steel piping and caused by the Bourdon effect, thermal expansion, and swelling elongation
- Pressure elongation of plastic piping is significant (Bourdon effect), and thermal expansion is also great.
- Unlike steel piping, Young’s modulus (creep modulus) for plastic piping depends on service life. For higher service life – the lower creep modulus is used. The support loads, displacements, etc. are calculated at 100 minutes of creep modulus. The seismic analysis was performed using a 0.1-hour creep modulus.
- In operating conditions, the average creep modulus is used (average between installation and operating temperature)
- Allowable stress for plastic piping depends on the chemical resistance factor, laying condition factor, safety factor, and joint strength factor
- The wall thickness check is performed only for straight pipes and not performed for fittings
Modeling of HDPE pipe in Start-Prof
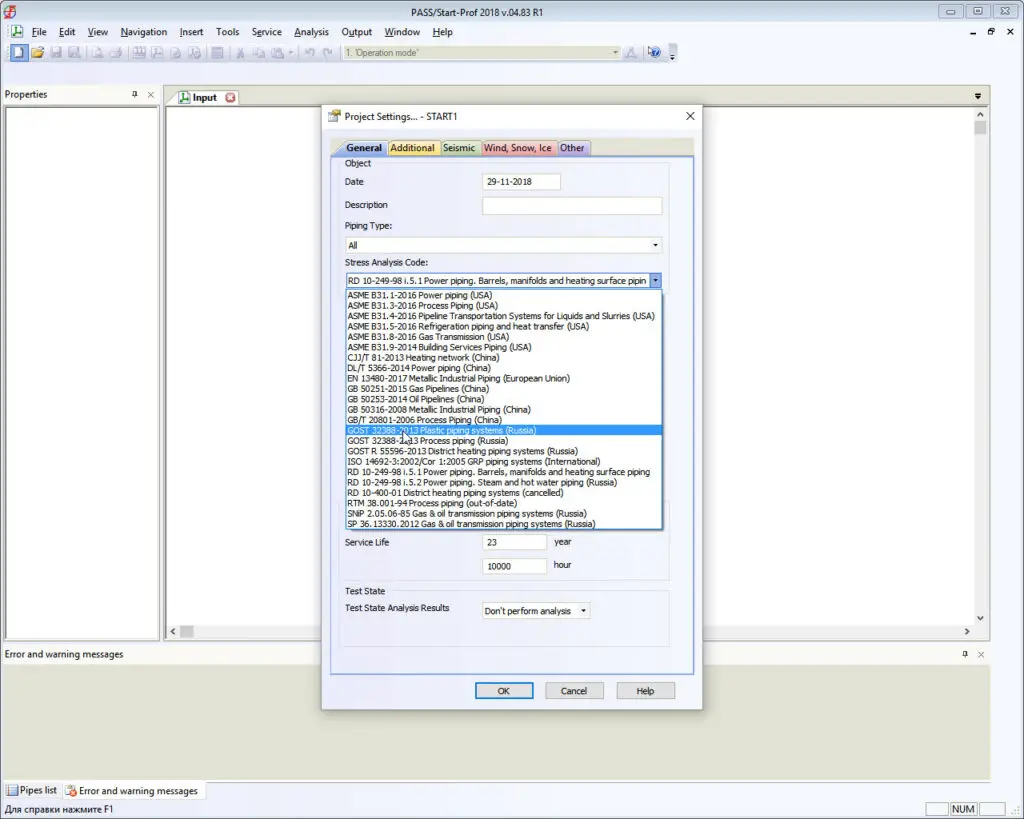
To model HDPE piping or other plastic piping choose GOST 32388 code:
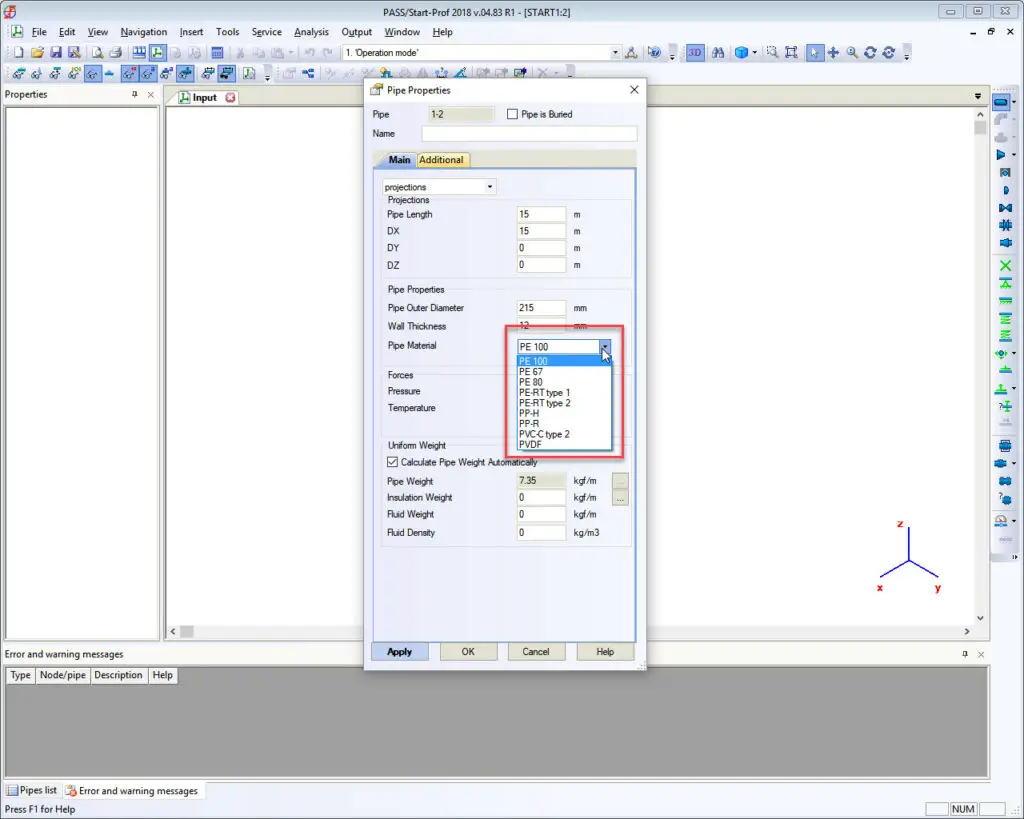
Then create a pipe and choose the appropriate material from the database:
In an additional pipe, properties specify the chemical resistance factor (usually 1.0), Joint strength factor (0.4-1.0), and Laying conditions factor (0.8 for buried piping, 0.9 for underground piping in concrete channels, 1.0 for above-ground piping). The temperature range is multiplied by this factor. It considers the nonlinear distribution of temperature across the wall thickness. For plastic piping recommended value is 1.0 and for fiberglass piping 0.85 for fluid and 0.8 for gas if no other information is available.
The swelling strain is used for a chemical swelling elongation. It is the same as temperature elongation but caused by the chemical reaction between the pipe material and the product.
That’s all. All other job is the same as steel piping.
The Database contains all material properties. If there’s no material you need in the database, you can add its properties manually.
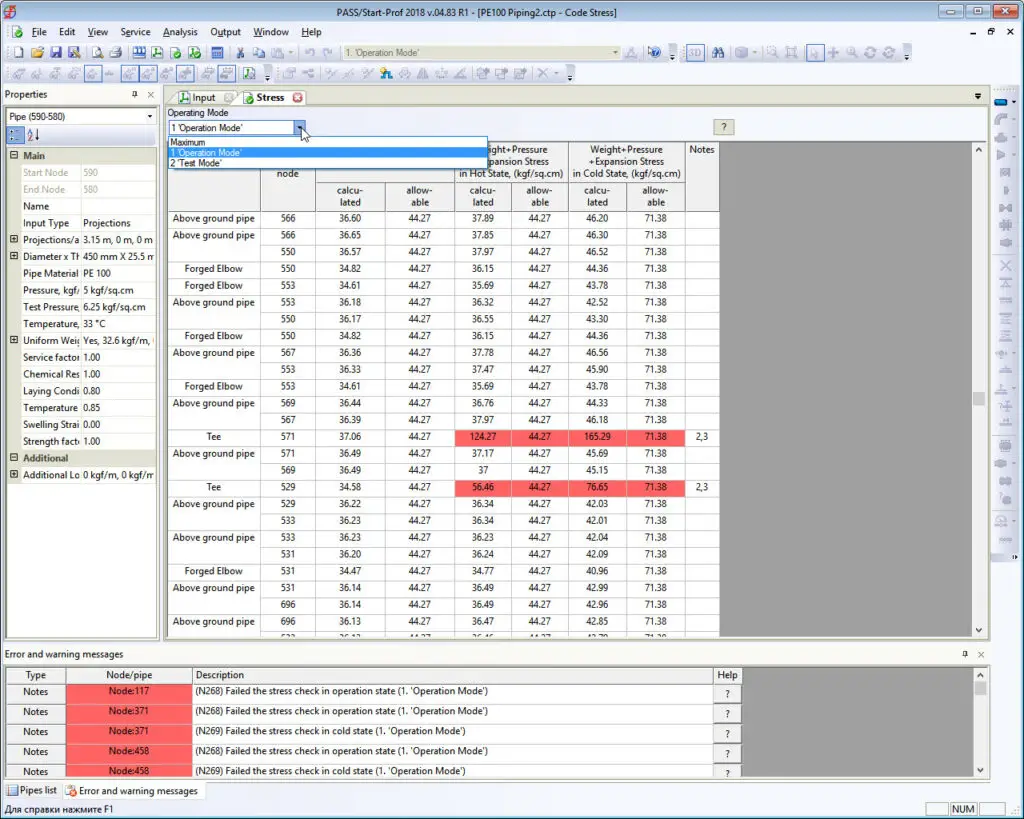
All load cases for analysis will be created automatically. After analysis, you get results according to the code.
Videos for HDPE Piping Stress Analysis in START-PROF
Part 1 of HDPE Piping Stress Analysis video:
Part 2 of HDPE Piping Stress Analysis Video:
Download the HDPE piping example file. See how to open the piping model file


Hi, May i know what is allowable stress for PE100 (HDPE) pipe during installation above ground?
Also what is allowable stress during hydrotest and operation conditions.
Which codes can be referred to.
Thank you
Allowable stress depends on the temperature and service life. It calculated automatically using the characteristic equation. See “Thermoplastic Piping Systems” here
https://www.passuite.com/kbase/doc/start/WebHelp_en/index.htm#t=materials.htm
You just need to select the “PE 100” material in the pipe properties
HI,
Regarding the SIF in correspondence of branch and elbow, how is the way to calculate them?
Regards
It is described in my pipe stress training course https://www.passuite.com/trainings/ondemand/start
Do u have provision for ASME B31.3 or Iso standard
How can HDPE material be modeled in Caesar II?
Please don’t ask me about Caesar, I’m PASS/START-PROF developer
Which code should be used for analysis CPVC lines?
START-PROF successfully use DVS 2210/DVS 2205
Hi Alex, Could you please let me know what is allowable stress for PE100 (HDPE) pipe during installation above the sea?
Thank you very much.
Hi! It calculated by code. Details in my training course: https://passuite.com/trainings/ondemand/start
Hi Alex, currently we use horizonral directional drilling(HDD) to install the gas pipeline PE100(HDPE), can Start _Prof can calculate the pulling stress during HDD?
I think it’s possible. Just model the pipeline and apply the pulling force on the end
Dear Alex Matveev, Can these lines be evaluated per ASME B31.3?
ASME B31.3 doesn’t contain any method and criteria for stress anlaysis of such lines
Hi Alex.
I’ve studying the Pipe Stress Analysis Course from PASSc and i get that the key is the GOST 32388 code. I only have CAESAR II in my company and clearly, it don’t have this code.
Is possibly to incorporate it in CAESAR for HDPE to work?
Regards, Tomas Gomez
I don’t think so
Hi Alex,
How can I get access to Start-Prof software.
How much does it cost?
Does the software contain ASME NM1 and DVS 2210.1 code?