Hub connectors or hub and clamp joints are an alternate method of joining pipes as compared to traditional ASME B16.5 pipe flanged joints. Pipes and equipment can easily be joined using clamp and hub connectors as this metal-to-metal sealed connector is highly reliable and easy to assemble. The clamp and hub connector joint consists of the following components:
- Two hubs
- Two clamps
- One seal ring
- Eight nuts
- Four studs
Refer to Fig. 1 below that shows the elements of a typical clamp and hub connector.
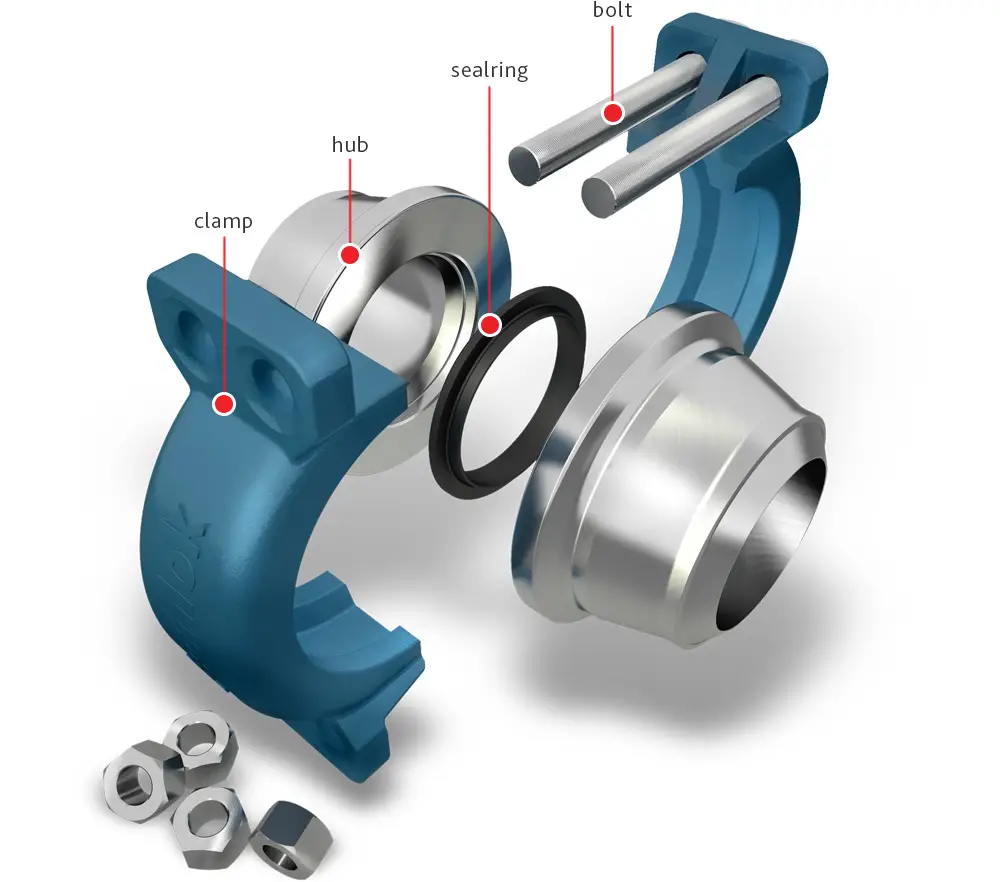
Design of Hub and clamp Connectors
Hubs are designed following ASME Sec VIII Div. 1-Appendix 24 to sustain internal pressure and clamps are designed as per ASME Sec VIII Div. 2 Part 4 to resist external loads. For the design and selection of clamp and hub connectors, the following information is required:
- Connecting pipe size (OD and ID) and thickness.
- Design pressure and temperature of the piping system where the hub connectors will be installed.
- Materials for the clamp, hub, seal ring, and bolting (as per the piping class).
- Any specific service requirements, etc.
The codes and standards used for design calculations of clamp and hub connectors are
- ASME VIII div.2,
- API 6A/17D,
- API 17 TR8,
- ISO 13628-7,
- EN-13445-3
- and DNV OS-F101 & F201.
For sub-sea applications, clamp connectors are usually made from duplex materials, and designed following DNV-RP-F112 to meet the required HISC resistance.
Welding of Components
The hubs are rigidly welded to the pipe with a seal installed. Clamps are tightened using bolts. This arrangement provides superior strength as compared to conventional flange joints and prevents leaks.
Placement of Bolts & Seal Ring
To prevent direct pressure and avoid bending, the bolts are installed in a perpendicular direction with respect to the pipe axis. The seal ring, resembling, the shape of a ‘T’ in cross-section is used to seal the connector. The design of the connector helps to:
- Withstand higher tensile loads
- Provide higher strength with lower seal size and weight
- Allow proper seating of the seal
- Reduce bolting torque
Benefits of Using Hub & Clamp Connectors
As compared to the conventional flange joints, the clamp and hub connection joint provides the following advantages:
- Simple Connection requiring only four bolts.
- Lightweight & Smaller in size; Compact Design: Hub and clamp connectors usually have around 80% less weight, 10% less outside diameter, and 50% less overall length than the standard ASME B16.5 flanges. Hence, they use significantly less space.
- Reduce Downtime as can be assembled or dismantled quickly with fewer bolts.
- Economical Solution: A hub and clamp connector provide an economical solution for piping joints by reducing the total cost of installation.
- Leak-Free: Clamp and hub connectors can withstand higher temperature and load variations and ensures leak-free operation when installed correctly.
- 360° orientation around the pipe is possible.
- Lower Bolt torque.
Applications of Hub & Clamp Connectors
The hub and clamp connector joints are used in piping systems requiring high-integrity seals. They are suitable for applications involving corrosive, erosive, high-pressure-temperature, and cyclic conditions. This is the reason that clamp and hub connectors are used in the following industries:
- Oil and Gas Production
- Chemical and Petrochemical processing
- Petroleum refining
- Food processing
- Industrial gas manufacturing
- Fossil and nuclear power generation
- Coal gasification and liquefaction
- Synthetic fuel processing
- Research and Development
- Aerospace manufacturing, etc
Hub connectors can also be used in pumps, compressors, manifolds, pipeline pig closures, and valves. Specially designed hub and clamp connectors are also suitable for pressure vessel nozzles.
Materials for Hub and Clamp Connectors
The following table provides some typical materials used in hub and clamp connector piping joints.
| Hub Material | Seal Ring Material | Material of Clamp | Bolting Material | |
| Carbon Steel | A105N/A694 F60/F65/F70/F75 | AISI 4130 / 4140 + PTFE coated | Forged AISI 4130/4140 | A193 B7/A194 2H for non-sour service and A193 B7M/A194 2HM for sour service. |
| Low Temp Carbon Steel | A 350 LF2 | AISI 4130 / 4140 + PTFE coated | Forged AISI 41430/4140 | A320 L7/A194 7 for non-sour service and A320 L7M/A194 7M for sour service. |
| Stainless Steel | A182 F316/F316L | A 182 F316 + PTFE coated | SS316/SS316L | A193 B8M/A194 8M |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | A182 F51/ A182 F53/A182 F55 | A182 F51/ A182 F53/A182 F55 + PTFE coated | SS316/SS316L | A 276 UNS S32760 |
| Nickel Alloy UNS N06625 | B564 UNS N06625 or CS with Inconel625 weld overlay | Alloy 718 + PTFE coated | Forged AISI 4130/4140 | A193 B7/A194 2H for non-sour service/ A193 B7M/A194 2HM for sour service. |
Flange vs Hub Connector
The main differences between a flange connection and a hub and clamp connection are provided below:
| Flanges | Hub and Clamp Connector |
| Flanges are the weakest links in a piping installation and may develop leakage problems. | Clamp and hub connectors provide better tightness and withstand more loads and stresses as compared to flanges. |
| Gaskets must be replaced during the maintenance of flanged joints. | Self-energized metallic seal rings are reused. |
| Bolt holes must be aligned during installation | No bolt holes to align in hub connectors |
| Multiple bolts depending on the pressure class rating and size | Only 4 bolts for tightening. |
| Larger diameter and length. | Shorter overall length and a smaller diameter. |
| Installation takes a longer time. | Quick assembly or disassembly. |
| Multiple sizes and a wide variety of manufacturers and hence the range of choices. Standardized items. | Limited manufacturers and non-standard items. |








Excellent Article on Hub Connectors clarifies its application and advantages over conventional Flanges specifically for High Pressure Piping
سلام تا چه فشار کار میتوان استفاده کرد
Clamp Connectors have been used in pressures up to 60,000psi.