Proper pipe supporting is synonymous with proper working and longevity of the piping and pipeline system. A pipe saddle helps in this activity by supporting the pipe weight. Installing pipe saddles is one of the easiest ways to transfer the pipe’s load generated due to weight, pressure, temperature, and occasional events onto a supporting base. By definition, a pipe saddle is a type of structural pipe support consisting of a saddle and an integral base.
What is a Pipe Saddle?
A pipe saddle is any pipe support that cradles a pipe and transfers the load of the piping system onto secondary members through its supporting base. In the piping industry, a pipe saddle is characterized by two distinct features:
- A saddle that supports the pipe, and
- An integral base for transferring the loads from the piping system to the civil structure.
What are the applications of Pipe Saddles?
Pipe saddles serve the following purposes:
- It elevates pipes. So wherever the pipe is running at an elevation from the support structure, pipe saddles can be used.
- It can be used to anchor pipes. Similar to pipe shoe supports, saddles can be used to anchor a pipe at the support location.
- It can be used as adjustable support. Using some special arrangements, piping saddles can be used to work as adjustable support.
- Pipe saddles can be used to reduce frictional forces by utilizing PTFE or graphite plates in between the structure and saddle bottom. However, special design arrangements must be done for that.
- Piping saddles can be used to reduce corrosion of the piping system. As with pipe saddles, the pipe will be elevated, and thus the pipe material will not rest on dirty surfaces which in turn will reduce corrosion. Elevating a pipe also separates dissimilar pipe and structural material which reduces the possibility of galvanic corrosion.
- As with pipe saddles, the saddle rubs on the structural surface during pipe movement, Hence the pipe metal does not get affected by the metallic wear mechanism.
Design Parameters for Pipe Saddles
The factors on which the design of pipe saddles depends are:
Saddle material:
Pipe saddle material should be compatible with the parent pipe material. Also, the material should have sufficient strength to handle the loads generated in the pipe system. The common saddle material is Carbon Steel (CS). However, they can be made of other materials as well. Sometimes, to reduce the cost a combination of materials can be used. For example, to support stainless steel (SS) pipe using a pipe saddle the complete design of the saddle may not use SS material. It can easily use the SS+CS combination to reduce costs. Wherever it touches the SS pipe, the material must be SS but other parts can be of CS material.
Piping Loads:
Piping load is the main important input required while designing saddle supports. The material thickness, strengthening requirement, weld size, etc all will be based on the load that needs to be supported. Loads in all directions must be considered in saddle design.
Thermal movement of pipe at the Support Location:
The maximum thermal displacement at the saddle location must be known while designing the saddle base. The base of the pipe saddle support must be sized such that it does not fall off the structural member due to pipe thermal movement.
Pipe Insulation thickness:
For insulated pipes, the height of the pipe saddle must also consider the piping insulation thickness.
Pipe Saddle Configuration
The following images in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 are showing typical pipe saddle configurations used in piping systems.
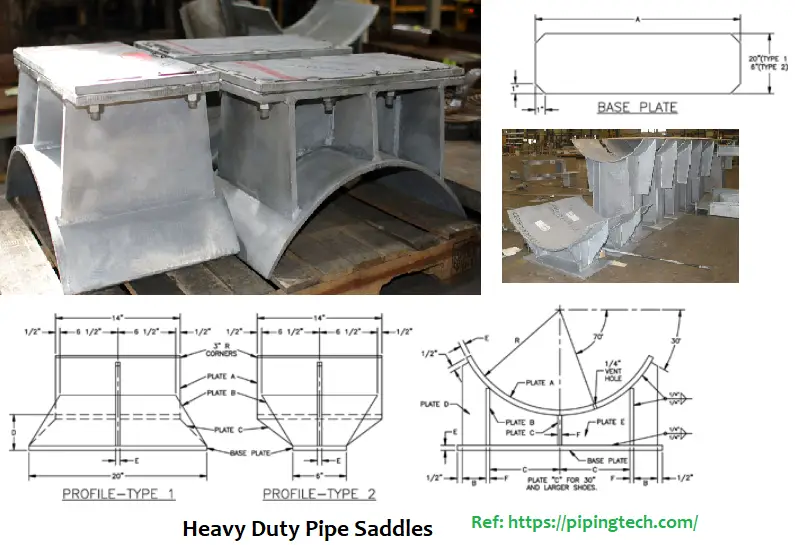
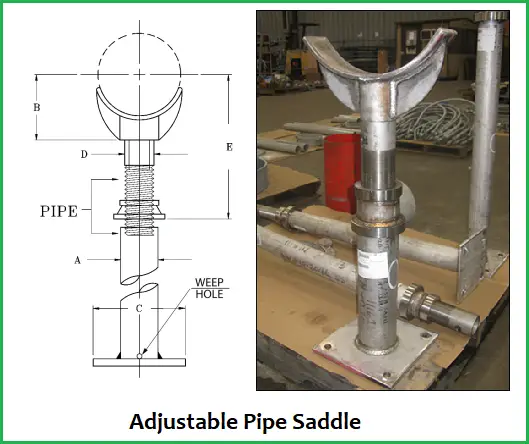
Equipment Saddles
As saddles have very high load-carrying capability, they are quite popular to use as equipment saddles. They are widely used for supporting horizontal vessels and heat exchangers. Usually, horizontal vessels and heat exchangers are supported by two saddles; One saddle is fixed and acts as a fixed anchor while the other acts as the sliding saddle. The thermal displacement starts from the fixed saddle support and the sliding saddle can axially move. For modeling nozzles of heat exchangers and horizontal vessels during piping stress analysis, both fixed and sliding saddles should be modeled to get proper thermal displacement.

Can you pl inform , load calculation on the various supports ( fixed / guide) of horizonal and inclined pipe or circular duct.
Any excel / simple manual / online calculator… available on internet
At pipe rack side which saddle is located for exchanger, fixed saddle or sliding saddle.pls reply with explanation.
I just had a heat pump installed.
The lines run through a heated crawl space (plenum) under the house. The suction line (7/8 inch) is wrapped in Armaflex.
The suction line is of concern as the installer hung the suction line from the floor joints using a 2 inch wide plastic webbing.
But instead of the webbing being just a sling,they wrapped the webbing at about 6 foot intervals around the suction line insulation (Armaflex) and the pulled it tight before securing it to the floor joints. I’m looking at redoing those hanger points and planning on cutting a three inch plastic water or sewer pipe in half, and then making each cut piece 6 to 12 inches in length (a pipe saddle). Then undoing the webbing, insert the saddle under the pipe insulation, and then using the webbing as a sling (no wrapping) such that the saddle will remain in place from the weight of the pipe, and the sling will hold the saddle and pipe (+ Armaflex) up near the bottom of the floor joints. Since your a pipe saddle expert, does this sound as a viable option to spread the weight and keep the Armaflex from being compressed? Thanks for your time.
can i ask your pdf file for education purpose..
can you share how to perform saddle’s local stress?