Distillation is a process in which a liquid or vapor mixture of two or more substances is separated into its component parts of desired purity through heat and mass transfer. The degree of separation in the distillation process depends on the relative volatility of the components to be separated. In the process of distillation, the vapor phase contains more volatile components (that have lower boiling points), this vapor is cooled and condensed at the overhead condenser and it consists of containing more volatile components. On the other hand, the original mixture will contain more of the less volatile (that have a higher boiling point) component.
There are different types of distillation columns (also known as distillation towers) that are designed to perform specific types of separation. Two main types of columns are plate columns and packed columns. There are differences between these two types of columns. In this article, we will be providing the difference between plate column and tray columns, their selection, their applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
What are the differences between the Packed Column and the Plate Column?
The main differences between packed and plate towers are given in the table below:
| Packed Columns or Packed Tower | Plate Column or Tray Tower |
| Packed columns are generally used in a smaller diameter (less than 600 mm) | Plate column is used for relatively large diameters & a large number of stages. |
| A packed column is suitable for low-capacity operation. | Plate columns can handle a wider range of gas and liquid flow rates. |
| Handling corrosive liquid-packed columns is more economical as cheap ceramic packing material or chemical-resistant packing elements which is available can be easily used. | Handling corrosive liquid-packed columns is less economical. |
| It is appropriate for accommodating the handling of foaming liquid. | It is not appropriate for handling foaming liquid. |
| For packed column maintenance work or cleaning cannot be performed easily. It consumes time and manpower. | It is much more accessible for the maintenance of plate columns by installing maintenance holes on the plates to maintain fouling. |
| For vacuum service, a packed column is more feasible as the pressure drop per stage is smaller. | For vacuum service plate column is not economical as it causes high-pressure drop. |
| For side stream applications, a packed column is not suitable. | For side stream application plate column is best suited. |
| Packed columns are differential contractors where transfer of mass happens across the length of the contactors & equilibrium is not reached at any point between the phases. | In plate columns, equilibrium is reached between stages where the mass transfer occurs intermittently. |
| In-packed column packing is used as a gas-liquid contacting device. | In a plate column, the plate is used as a gas-liquid-containing device. |
| The design of a packed tower basically involves the height of the transfer unit (HETP) calculation for a given separation. | For designing plate columns, the number of theoretical stages is to be calculated to effect a given separation. |
| Packed towers are simple to construct. | Plate columns are complex in construction. |
| Different types of packings are used for gas-liquid contacting like Raschig rings, Pall rings, Berl saddles, Intalox saddles, etc. | As a gas-liquid contactor, different types of trays are used like sieve trays, bubble cap trays, and valve trays. |
Advantages & Disadvantages of a Packed Column:
There are several advantages of a packed column as well as disadvantages too.
Advantages of Packed Tower
The main points of advantages have been captured here,
- It requires minimum structure.
- The packed column causes a minimum pressure drop.
- The liquid hold-up is relatively low in the packed column.
- The packed column can easily handle highly corrosive, foaming fluid.
- It requires low investment.
Disadvantages of Packed Tower
The disadvantages are as follows,
- The packed tower is relatively inflexible for handling a wide range of G/L ratios.
- So that it cannot easily handle wide ranges of either vapor or liquid rates per unit cross-section.
- In packing, gas-liquid mal-distribution can happen.
- It cannot handle dirty fluids that tend to deposit.
- Due to uneven distribution channeling happens frequently in the packed column which results in poor mass transfer.
- A packed column is suitable for that service where large temperature changes happen.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Plate Column
Advantages of Plate Column
The main points of advantages have been captured here,
- The plate column provides stage-wise contact so that equilibrium can be reached.
- It can operate on a wider range of gas/liquid ratios.
- Cleaning & maintenance can be done easily for plate columns.
- The packed column causes a minimum pressure drop.
- Side-stream can be easily drawn from the plate tower.
- Plate columns can be scaled up to a large diameter.
- Hydraulic & mass transfer behavior can be predicted.
Disadvantages of Plate Column
The disadvantages are as follows,
- Plate columns cannot perform properly for foaming service as it reduces the performance and efficiency of the plat columns.
- The liquid hold-up is relatively high for the plate column.
- It is not economical at all for corrosive service. If it is bound to use then corrosion resistant plate can be used whose cost is too high to use.
- The plate column requires huge support to install which increases cost.
How to select a Packed Column and a Plate Column?
The selection of a particular type of equipment for a gas-liquid application depends upon several factors like capacity, efficiency, pressure drop, fluid properties, hold-up, budget, etc. But the basic selection criteria are cost and profit but in some cases, the choice is made on the basis of quantitative analysis of the relative advantages and disadvantages of packed tower and plate tower. Some of the merits and demerits that are generally considered are,
- Plate towers can operate over a broader range of gas-liquid flow rates without flooding.
- Plate tower provides better separation by repeated mixing and separation while packed tower can lead to back mixing and channeling.
- Because of the mal-distribution of gas-liquid arising in the packed tower, the plate tower is more reliable.
- For solid-dispersed liquid plates, the tower is more suitable as maintenance and cleaning can be done easily in a plate tower.
- Design information on the plate towers is more readily available.
- For an exothermic mixture, intermediate cooling can be required which can easily be provided to remove excess heat by providing a cooling arrangement.
- Pump around pump can be easily used in the plate-type column.
- For foaming liquid packed tower is usually preferred.
- As the pressure drop in a packed tower is relatively low so for vacuum service it can be easily used.
- Hold-up liquid is low in the packed tower so they are used for heat-sensitive material where they can deteriorate under exposure to high temperature
Column Internals
Column internals is the components of the column that provided a contact area for gas-liquid separation.
For the Tray column, the internals are,
- Sieve Tray
- Valve Tray
- Bubble-cap Tray
- Others (Like Max-Frac trays)
Packed column internals are packings which are two types which are Random packing and structured packing. Random packing or stacked packing has different types of packing rings that are,
- Raschig rings
- Pall rings
- Berl saddle
- Intalox saddle
For structured packing, there are packing rings that are proprietary items of vendors like Mellapak, Flexi Grid, Sulzar type, etc.
Bubble Cap Tray:
Bubble cap tray distributes them as phase into the liquid phase like fine bubbles or droplets. It prevents weeping that is drainage through the gas passage at low gas flow rates. A bubble cap tray is not used normally as it causes high-pressure drops and higher costs.
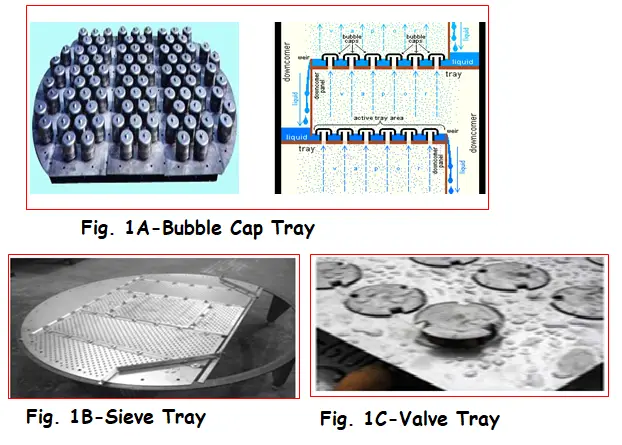
Sieve Tray:
This type of tray consists of a perforated plate which is having holes through which gas can be dispersed into the liquid on the plate. It is basically a metal sheet and it has hundreds of perforations of sizes of 3-12 mm. The area that the holes consist of is almost 5-15% of the tray area. These trays are commonly used nowadays as it is very simple in construction, as well as their cost is low.
Valve Tray:
A valve tray is nothing but a perforated metal sheet where the holes are covered with movable caps or discs. The diameter of the discs is up to 38 mm and held in the plate by legs that prevent upward motion of the discs for gas flows.
Raschig Ring:
This type of packing is the tubular type generally used in the fractional distillation columns. They are basically cylindrical tube and their length and diameter are almost equal. It can be made of carbon steel, ceramic, and plastics.

Pall Ring:
This type of ring is made of SS04, SS316L metal alloy. Besides this, it can be made of Carbon steel and specialty alloys such as Monel 400 and Hastelloy, C276. Various sizes of pall rings are available such as 16 mm, 25 mm, 38 mm, and 50 mm.
Berl Saddle:
This type of ring causes low-pressure drop and high efficiency. It provides a large effective interfacial area along with high mechanical strength. The cost of this packing material is not high as it contains fewer metal parts. It is available in various sizes that give different combinations of efficiency and pressure drop.
What is Random Packing?
Random packing used in separation columns like distillation column increases surface area for mass transfer between vapor/liquid so that separation becomes easier. The small pieces of random packing material in a distillation column are made to provide a large surface area. Random packing provides a maximum surface-to-volume ratio and lowers the pressure drop. The degree of efficiency of random packing depends upon several factors like pressure drop and capacity, porosity, etc. Typically, when random packing is large in size, capacity is increased at the cost of lower efficiency. On the other hand, when random packing is smaller in size, efficiency increases at the cost of lower capacity. Examples of random packing are Raschig rings, Pall rings, etc.
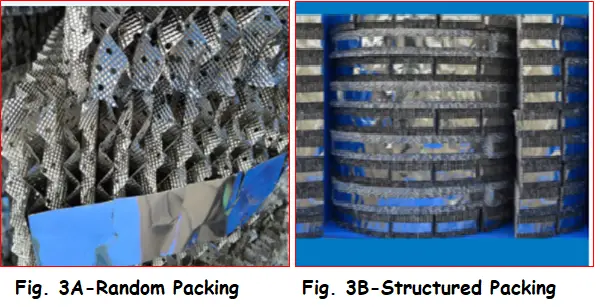
What is Structured Packing?
Structured packing gives uniform distribution of packing materials which is usually large in size. It is usually made of thin corrugated metal sheets which force the fluid into specific, preordained arrangements within the tower. This type of packing is usually used in offshore applications. It spreads the liquid into a thin film. This configuration causes more contact & increases the degree of separation. Structured packing usually leads to low-pressure drop so it can handle larger volumetric flow than random packing. For natural gas dehydration, styrene manufacturing structured packing is used.