Both Casting and Forging are part of the mechanical manufacturing process. Both Casting and forging are widely used in the metal fabrication process and produce thousands of useful components. The method of production; whether casting or forging is decided based on end-use and required properties of the product or component. In this article, we will explore the key differences between the two most common metalworking processes, i.e Casting vs Forging Processes.
What is Casting?
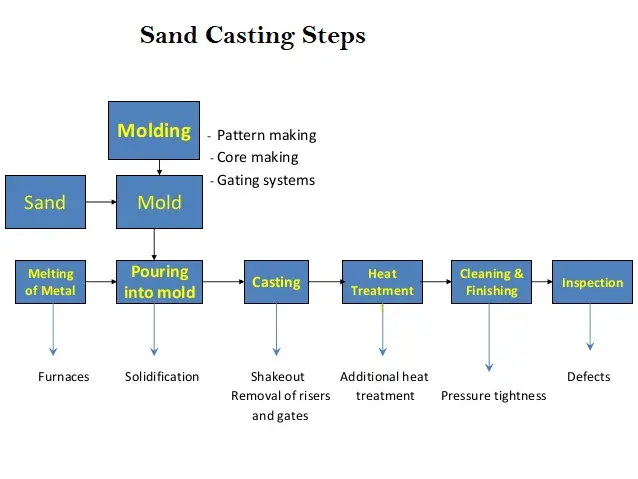
In the casting process, the metal is melted to liquid form and then it is poured into a mold or die to cool and solidify. The metal in solid form takes the form of a mold. Casting is highly beneficial for the mass production of parts as the same mold can be re-used. Fig. 1 shows typical steps followed in Sand Casting Process. Casting process is also known as foundry techniques.
What is Forging?
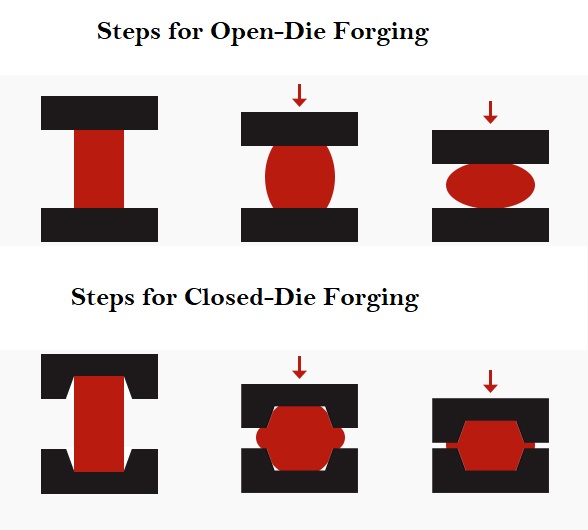
In forging, a hammer, press or die uses compressive force over a metal billet to deform it in the desired shape. The hammering effect produces superior mechanical properties, eliminating defects, porosity, inclusions, etc. Depending on how the metal is deformed, forging can be of two types. In cold forging, the metal is deformed at room temperature; whereas in hot forging, the metal is shaped in a heated condition. Fig. 2 below shows typical steps in the forging process.
Casting vs Forging: Which one is better?
The selection of the production process depends entirely on the cost involvement and end-use of the part. Where higher strength and rigidity are required, forging is the ideal choice. But for complex shapes, including spaces, Casting is the better option. Studies have found that:
- The tensile strength of cast products is around 26% lower than their forging counterparts.
- Forging products exhibit approximately 37% higher fatigue strength as compared to cast products.
Factors affecting selection between Casting and Forging
The following factors govern the selection of casting or forging (casting vs forging) for a part:
- Material Quantity
- Economic Consideration
- Tooling costs
- Machining Cost
- Design of the part (Simple/Complex)
- Tolerances required
- Mechanical properties Requirement (Ductility, fatigue strength requirement)
- Metal specification (Normal Steel or Custom alloy Materials)
- Surface finish required
- Delivery requirements
Normally it’s preferable to use casting for large and complex products and forging for simple and smaller size products.
Differences between Casting and Forging: Casting vs Forging
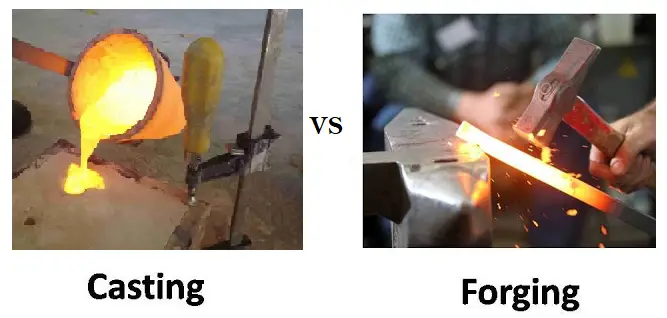
The Key differences between Casting and Forging are:
Metal Casting vs Metal Forging: Mechanical Properties
Metal products produced from forging have higher strength and toughness than metal processed in castings. The metal working process by pressing and hammering during forging is attributed to the increased strength. On the other hand, the mechanical properties of products made by the casting process are relatively inferior. Casting products possess low impact strength and tensile strength.
Forging vs Casting: Process
The casting process involves heating the metal into a liquid state and then pouring the liquid metal into a die or mold. Whereas in forging, the heating of material if required is below the recrystallization temperature.
Casting vs Forging: Process Limitations
A wider range of products is manufactured using the casting process as it involves only melting the material and pouring it into the proper mold. As the casting process is easier, complex shapes can easily be produced. Practically, any material can be cast. Hence, the casting process provides greater flexibility.
However, forging has size limitations due to the difficulty in shaping metal in a solid state. There’s a limit on the material size and thickness as changing the metal’s shape is more difficult with forging.
Other differences between forging and casting are tabulated below:
| Casting | Forging |
| Casting items are cheaper than forged items. | Forged Products are costlier than cast products. |
| Wide Material Range is suitable for casting operations. It includes metals, ceramics, and plastics. | Forging has a selected material range. Primarily the forging process is suitable for metals and alloys with good ductility. |
| The grain Structure of casting products is random and it affects mechanical properties. | Grains of forged products are aligned in one direction that creates better mechanical properties. |
| For producing hollow cavities, casting is the best option | Forging is not suitable for hollow spaces. |
| Casting products are relatively lighter in weight as compared to forged products | The forging process produces heavier products as compared to casting. |
| The machining requirement of cast products is less as the mold is approximate to the required shape. | Forging parts need more secondary machining to match the final shape. |
| Casting provides a higher production rate once the mold is prepared. So, the mass production of a specific component by casting method is quite easy. | In forging, the production rate is lower. Mass production is difficult and time-consuming in forging. |
| The reliability of cast parts is less. | Forged components are highly reliable |
| Casting requires high labor costs as precision control is required to avoid defects. | Labor cost is low in the case of the forging process. |
| Casting is preferred in low-end applications and products requiring highly complex geometries and intricate shapes. So, casting process provides greater design flexibility for complex shapes and thin-walled structures. | Forging is widely used for high-end applications and for components with simpler shapes. Hence, Design flexibility for forging process is somewhat limited compared to casting, especially for complex shapes with intricate details. |
| In the casting process, custom alloy addition to change the material composition and properties is possible. | Forging is not flexible for new material additions. |
| The cost of tools in the casting process is cheaper. | Forging dies are costly as compared to casting molds. |
| Any modifications in component design and molds are easier and quicker to implement in the casting process. | In forging, modifications in components are very difficult. |
| The density of the cast components may not be uniform. | Parts produced in forging possess uniform density. |
| Common casting defects include porosity, shrinkage, and gas inclusions, which may require additional inspection and repair. | Fewer defects compared to casting due to the absence of porosity and better material flow during deformation. |
| May sometime need heat treatment to improve mechanical properties and relieve internal stresses. | In forging, the heat treatment is often an integral process for enhancing material properties and reducing internal stresses. |
Some FAQ’s related to Casting and Forging Process
1. How does the choice between casting and forging affect the strength and durability of a metal part?
Forged parts typically exhibit higher strength, better fatigue resistance, and improved mechanical properties due to the grain structure refinement and elimination of porosity. In contrast, cast parts may have lower strength and durability due to potential defects like porosity and inclusions.
2. Is forging better than casting?
Whether forging is “better” than casting depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of the part, the desired properties of the final product, and the constraints of the manufacturing process. Both forging and casting have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between them often comes down to the specific needs of the application.
3. What is the difference between casting and forging microstructure?
The microstructure of cast metals typically consists of randomly oriented grains, often with dendritic or columnar growth and larger, irregular shapes due to the slower cooling rates inherent in casting. In contrast, forged metals exhibit finer, more homogeneous grains that are elongated and aligned along the direction of deformation. This results in superior mechanical properties such as increased strength, toughness, and fatigue resistance in forged parts compared to cast parts.
4. What’s the difference between forging and foundry?
Forging involves shaping metal through compressive forces, often at elevated temperatures, resulting in refined, aligned grains for improved mechanical properties. Foundry, or casting, is the process of pouring molten metal into a mold to create a desired shape. Forging produces parts with superior strength and better mechanical properties, while casting allows for the production of complex shapes with intricate details. Foundry is suitable for producing parts with intricate geometries, while forging is favored for its strength and durability.
5. How to tell if metal is cast or forged?
Distinguishing between cast and forged metal can be challenging but certain characteristics can help differentiate them. Examine the surface: cast parts often have a smoother surface with less defined grain structure, while forged parts may display grain lines or directional patterns from the forging process. Inspect for porosity and irregularities: cast parts may exhibit more visible pores and irregularities due to the casting process, while forged parts typically have a more uniform and dense structure. Additionally, consider the part’s complexity: intricate shapes with fine details are more likely cast, while simpler, stronger parts are often forged.
6. Is forging cheaper than casting?
The cost comparison between forging and casting depends on factors such as part complexity, material type, production volume, and required mechanical properties. Generally, forging tends to be more expensive upfront due to higher tooling and equipment costs, as well as the need for skilled labor. However, forging often results in stronger, more durable parts with better mechanical properties, potentially reducing long-term costs associated with part failure or maintenance. Casting may be cheaper for large production runs or complex shapes due to lower tooling costs, but it can lead to lower strength and increased material waste, impacting overall cost-effectiveness.
7. What are the latest advancements in casting and forging technologies?
Advanced casting technologies include investment casting, die casting, and additive manufacturing (3D printing). Forging advancements involve the use of computer-controlled hammers and presses, as well as the integration of robotics for automation.
8. How can I optimize the design of a part for casting or forging?
Design for casting involves minimizing sharp corners, avoiding thin sections, and incorporating draft angles to facilitate mold release. For forging, design considerations include maintaining uniform wall thickness, minimizing undercuts, and avoiding sudden changes in cross-section.
9. What materials are commonly used in casting and forging processes?
Common materials for casting include steel, aluminum, iron, and various alloys. Forging commonly uses steel and its alloys, as well as titanium, aluminum, and other metals suitable for deformation processes.
10. What are the environmental impacts of casting and forging processes, and how can they be minimized?
Casting and forging processes can generate emissions, waste, and energy consumption. Minimization strategies include recycling scrap metal, optimizing energy usage, and implementing cleaner production techniques.
11. Are there any emerging trends in automation and robotics in the casting and forging industry?
Yes, the industry is witnessing increased adoption of automation and robotics for tasks such as material handling, quality inspection, and process control. This trend aims to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance safety.
12. How do heat treatments affect the properties of cast and forged metals?
Heat treatments such as annealing, quenching, and tempering are used to modify the microstructure and properties of cast and forged metals. These processes can improve hardness, toughness, and other mechanical properties depending on the desired outcome.
13. What safety measures should be taken during casting and forging operations?
Safety measures include wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), implementing proper ventilation systems to control fumes, ensuring equipment is properly maintained, and providing training on safe operating procedures to workers.







Hi I’m a Metallurgical Engineer and my second degree in mechanical (industrial production). Currently I’m into piping/structural fitting.
May I get some materials on pipe/ structural fabrication and calculation?
My email is here in attached
Best Regards
Louis Ekezie