The Greenhouse Effect and the concept of achieving Net-zero Carbon Emissions are critical topics in the context of climate change and environmental sustainability. In this comprehensive explanation, I’ll provide detailed insights into both these subjects to equip you with a thorough understanding.
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that warms the Earth’s surface. It occurs when the sun’s energy reaches the Earth, and some of that energy is reflected back to space while the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. This process is crucial for maintaining the temperatures necessary for life on our planet. However, human activities are amplifying this effect, leading to climate change and a host of environmental challenges.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
Warming of the Earth’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) in the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and other specific gases in the air is called the greenhouse effect. Of these gases known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the greatest impact. The atmosphere penetrates most of the sun’s visible light and reaches the surface of the earth. Since the surface of the earth is heated by sunlight, part of its energy is radiated into space as infrared rays.
Unlike visible light, this radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and raises their temperature. The heated atmosphere then radiates infrared rays to the surface of the earth. Without greenhouse warming, the average surface temperature of the Earth would be only about -18 ° C (0 ° F). On Venus, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is so high that it has a very high greenhouse effect, with surface temperatures up to 450 °C (840 °F).
The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon, but its effects can be amplified by the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as a result of human activity. From the beginning of the Industrial Revolution to the end of the 20th century, the carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere increased by about 30% and the methane content more than doubled. This global warming can change the Earth’s climate, create new patterns and extreme droughts and rainfall, and disrupt food production in certain regions.
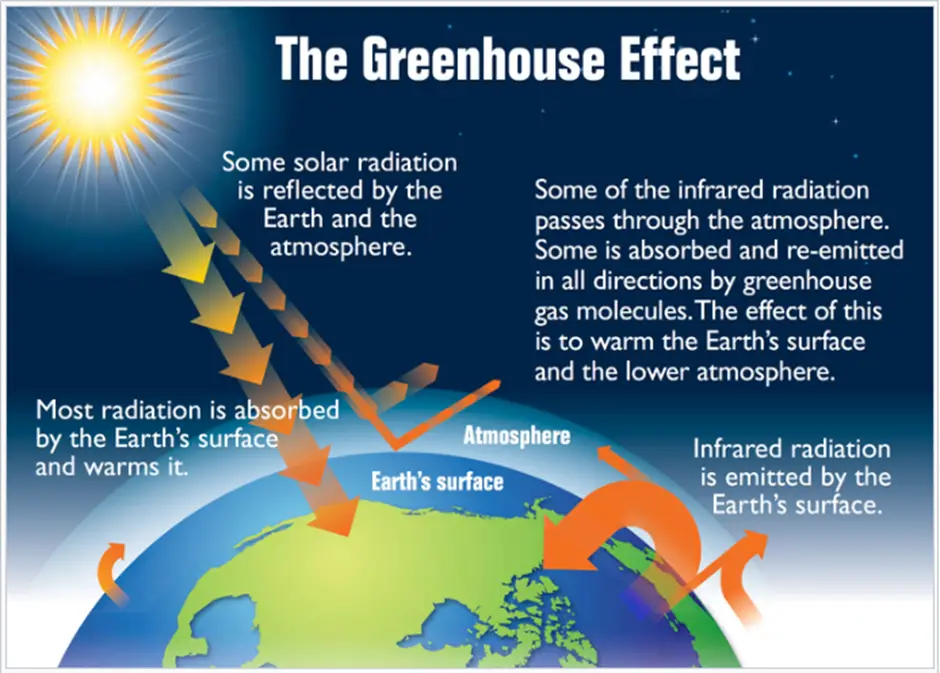
Mechanism of greenhouse effect
So, the mechanism of the greenhouse effect can be summarized as follows:
Solar Radiation:
The Earth receives energy from the sun in the form of solar radiation. Approximately 30% of this radiation is reflected back to space by clouds, atmospheric particles, and reflective surfaces (like ice and snow). The remaining 70% is absorbed by the Earth’s surface and oceans.
Infrared Radiation:
As the Earth absorbs solar energy, it warms up and re-emits this energy in the form of infrared radiation. This radiation is then either absorbed by greenhouse gases or escapes into space.
Heat Trapping:
Greenhouse gases absorb and re-radiate the infrared radiation, trapping heat in the atmosphere. This process keeps the Earth’s surface significantly warmer than it would be otherwise—approximately 33 degrees Celsius (59 degrees Fahrenheit) warmer.
What are greenhouse gases?
Greenhouse gases (also called GHGs) are gases in the Earth’s atmosphere that trap heat. During the day, the sun shines through the atmosphere, warming the surface of the earth. At night, the earth’s surface cools and radiates heat into the atmosphere. Part of the heat is however trapped by greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases on Earth trap heat in the atmosphere and warm the Earth. The main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor (all of which are naturally occurring), and fluorinated gases.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Released from various natural processes like volcanic eruptions and human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation.
- Methane (CH4): Emitted during processes like enteric fermentation in livestock, rice cultivation, and the production and transport of fossil fuels.
- Water Vapor (H2O): The most abundant greenhouse gas, its concentration varies greatly with location and climate.
- Nitrous Oxide (N₂O): Emitted during agricultural and industrial activities, as well as during the combustion of fossil fuels and solid waste.
Why is it called greenhouse gas?
Greenhouse gases are so named because they absorb infrared rays from the sun in the form of heat, which circulates in the atmosphere and eventually is lost to space.
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere act like a blanket around the Earth. When the Earth’s surface emits infrared radiation, greenhouse gases absorb some of this heat energy, preventing it from escaping directly into space. Instead, they re-radiate the heat energy in all directions, including back toward the Earth’s surface.
This process of re-radiation effectively traps heat energy in the Earth’s atmosphere, warming the planet. Without this natural Greenhouse Effect, the Earth’s average temperature would be significantly colder, making it inhospitable for most forms of life.
Why CO2 is a greenhouse gas?
Carbon dioxide molecules in the atmosphere absorb far-infrared energy (heat) from the earth and then re-emit it, and some of it returns. This effectively traps the heat around the earth. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of several greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
What are greenhouse gases made of?
Greenhouse gases are water vapor, methane, ozone, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide. Some of these gases may not be very present in our atmosphere, but they can have a significant impact. Each greenhouse gas molecule is composed of three or more loosely bonded atoms.
Is ozone a greenhouse gas?
Ozone is technically a greenhouse gas, but it can be useful or harmful depending on where it is in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Is H2 a greenhouse gas?
H2 is an indirect greenhouse gas that reacts with other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere to increase its Global Warming Potential (GWP).
The Importance of the Greenhouse Effect
Natural Regulation of Climate
The greenhouse effect plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate. Without it, the average surface temperature would be about -18 degrees Celsius (0 degrees Fahrenheit), making life as we know it impossible. This natural warming allows for liquid water to exist on the planet, which is essential for all known forms of life.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
A stable climate facilitated by the greenhouse effect supports diverse ecosystems. Plants, animals, and microorganisms all rely on specific temperature ranges and weather patterns to thrive. Disruptions to this balance can lead to biodiversity loss, habitat destruction, and extinction events.
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Human Impact on the Greenhouse Effect
Industrial Revolution and GHG Emissions
Since the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century, human activities have significantly increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. The burning of fossil fuels for energy, transportation, and industry has led to a dramatic rise in CO₂ levels.
Deforestation
Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO₂ from the atmosphere. Deforestation, whether for agriculture, logging, or urban development, reduces the planet’s capacity to sequester carbon and contributes to higher atmospheric CO₂ levels.
Agriculture and Livestock
Agricultural practices contribute significantly to methane and nitrous oxide emissions. Livestock production, rice cultivation, and the use of synthetic fertilizers are key contributors to the rise in these potent greenhouse gases.
Urbanization
The expansion of cities leads to increased energy consumption and emissions. Urban areas are often characterized by higher temperatures (urban heat islands) due to human activities and reduced vegetation.
Human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas), deforestation, and industrial processes, have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This enhanced Greenhouse Effect results in a stronger trapping of heat energy and leads to global warming, which is a major driver of climate change.
Consequences of the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
The consequences of the enhanced Greenhouse Effect are numerous and severe:
- Global Temperature Rise: The Earth’s average temperature has been steadily increasing due to the enhanced Greenhouse Effect, leading to phenomena like global warming.
- Melting Ice and Sea Level Rise: Warming temperatures cause ice caps and glaciers to melt, contributing to rising sea levels, which can lead to coastal flooding and the displacement of communities.
- Extreme Weather Events: Climate change intensifies extreme weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, heatwaves, and heavy rainfall, causing damage to ecosystems and human infrastructure.
- Disruption of Ecosystems: Many species struggle to adapt to rapidly changing climates, leading to shifts in ecosystems and potential extinctions.
- Ocean Acidification: Increased CO₂ levels are not only warming the planet but also leading to higher levels of dissolved CO₂ in oceans, causing ocean acidification. This affects marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells, such as corals and shellfish.
- Impact on Agriculture: Climate change affects agricultural productivity. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can lead to reduced crop yields, threatening food security, especially in vulnerable regions.
Mitigation Strategies
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can significantly reduce CO₂ emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Improving energy efficiency in buildings, transportation, and industries can lower energy consumption and emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): This technology captures CO₂ emissions from sources like power plants and stores it underground, preventing it from entering the atmosphere.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Adopting practices like agroforestry, organic farming, and improved livestock management can help reduce emissions from the agricultural sector.
Reforestation and Afforestation
Restoring forests and planting new trees can enhance carbon sequestration, helping to absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere. Initiatives like REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) aim to incentivize forest conservation.
Promoting Sustainable Transportation
Encouraging public transportation, cycling, and electric vehicles can reduce emissions from the transportation sector. Urban planning that prioritizes walkability and green spaces can also contribute to lower emissions.
Policy and Legislation
Governments play a crucial role in addressing climate change. Implementing policies like carbon pricing, emissions trading systems, and regulatory measures can incentivize emissions reductions.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about climate change and the greenhouse effect is essential. Education can empower individuals and communities to take action, from reducing personal carbon footprints to advocating for systemic change.
The Role of International Agreements
The Paris Agreement
Adopted in 2015, the Paris Agreement aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, with efforts to keep it below 1.5 degrees. Countries are required to set and communicate their nationally determined contributions (NDCs) to reduce emissions.
Other Global Initiatives
Various global initiatives, such as the Kyoto Protocol and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aim to address climate change and promote sustainable development. Collaboration among nations is crucial for effective action.
Net-zero Carbon Emission
The urgency to combat climate change has never been more pressing. With increasing global temperatures, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events becoming commonplace, the need for substantial action is clear. One of the most critical strategies in this fight is achieving net zero carbon emissions. But what does it mean to achieve net zero, and how can individuals, businesses, and governments work towards this goal?
Net-zero carbon emissions, often referred to as carbon neutrality or net-zero greenhouse gas emissions, is a critical concept and goal in addressing climate change. Achieving net-zero emissions is central to mitigating the effects of the enhanced Greenhouse Effect. Let’s delve into the details:
What does net-zero carbon emission mean?
Net zero means balancing the greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere with the greenhouse gases removed. Think of it like a bath-turn on the faucet, add more water, and pull out the stopper to let the water flow out. The amount of water in the bath depends on both the input from the faucet and the output from the drain. To keep the amount of water in the bath at the same level, it is necessary to balance the entrance and exit. Reaching net zero applies the same principles. It needs to balance the number of greenhouse gases we emit with the amount we remove. If you add only what you remove, you reach net zero. This condition is also called climate neutrality. However, zero emissions and zero carbons are slightly different because they usually mean that no emissions occur at all.
How you can make difference between gross zero and net zero?
Given the impact of carbon emissions on the planet, you may be wondering why we are not aiming for zero or gross zero instead of net zero. Gross zero means stopping all emissions, but this is not realistically achievable in all aspects of our lives and industry. Even with the best efforts to reduce them, there are still some emissions. Net zero makes it possible to look at emissions as a whole and eliminate all unavoidable emissions. From aviation or manufacturing. Greenhouse gas removal can come from nature, new technologies, or modified industrial processes, as trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Why is net zero important?
Net zero is a condition in which greenhouse gases flowing into the atmosphere are offset by removal from the atmosphere. At least for CO2, the term net zero is important because this is where global warming stops. So, the main Importance of Net Zero are
- Climate Stabilization: Achieving net zero is essential to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement. This temperature threshold is crucial to avoiding catastrophic climate impacts.
- Economic Opportunities: Transitioning to a net zero economy can stimulate economic growth by creating jobs in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable industries.
- Public Health: Reducing carbon emissions can lead to cleaner air and water, ultimately improving public health and reducing healthcare costs associated with pollution-related diseases.
Pathways to Achieving Net-zero Carbon Emissions
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions involves a combination of strategies and actions. Here are some key components:
- Reducing Emissions: The primary focus is on reducing emissions of greenhouse gases. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources (solar, wind, hydro, etc.), improving energy efficiency, and implementing sustainable practices in various sectors like transportation, agriculture, and industry.
- Carbon Offsetting: For emissions that cannot be completely eliminated, such as those from certain industrial processes or transportation, carbon offsetting is used. This involves investing in projects that remove or reduce an equivalent amount of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, such as reforestation, afforestation, and carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects.
- Technological Innovations: Developing and deploying innovative technologies like CCS, direct air capture (DAC), and low-carbon transportation options are essential for achieving net-zero emissions.
- Behavioral Changes: Encouraging individuals and communities to adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing energy consumption, changing dietary habits, and using public transportation, contributes to emissions reduction.
- Policy and Regulation: Governments and international bodies play a crucial role in setting policies and regulations that incentivize emissions reduction and support the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Importance of Net-zero Carbon Emissions
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions is vital for several reasons:
- Mitigating Climate Change: By stabilizing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, we can slow down and eventually halt the progression of global warming and its associated impacts.
- Preserving Ecosystems: A stable climate is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ecosystems, as many species are sensitive to changes in temperature and habitat.
- Protecting Vulnerable Communities: Many communities, particularly in developing countries and coastal regions, are disproportionately affected by climate change. Achieving net-zero emissions can help protect these vulnerable populations.
- Sustainable Development: The transition to a low-carbon economy can drive innovation, create jobs, and promote sustainable development while reducing reliance on finite fossil fuel resources.
Strategies for Achieving Net Zero
1. Transitioning to Renewable Energy
One of the most effective ways to achieve net zero is by transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources.
- Solar Power: Harnessing sunlight to generate electricity. Technological advancements have significantly reduced costs and improved efficiency.
- Wind Energy: Utilizing wind turbines to generate electricity, which has become one of the fastest-growing sources of energy.
- Hydropower: Generating electricity from flowing water, though care must be taken to minimize environmental impacts.
2. Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency across all sectors can drastically reduce emissions.
- Buildings: Retrofitting buildings with better insulation, energy-efficient appliances, and smart technology can lower energy consumption.
- Transportation: Promoting electric vehicles (EVs), improving public transportation, and encouraging non-motorized transport can reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
3. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
CCS technologies capture carbon emissions from sources like power plants and store them underground to prevent them from entering the atmosphere.
4. Sustainable Agriculture
Shifting agricultural practices can significantly reduce emissions:
- Regenerative Farming: Practices that enhance soil health and increase carbon sequestration.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes to improve biodiversity and carbon capture.
5. Afforestation and Reforestation
Planting trees and restoring forests are critical for absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere.
- Urban Green Spaces: Creating parks and green roofs can also contribute to local carbon sequestration efforts.
6. Behavioral Change
Encouraging sustainable lifestyle choices can help individuals and communities reduce their carbon footprints.
- Dietary Changes: Reducing meat consumption and increasing plant-based diets can lower agricultural emissions.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste and promoting recycling can help reduce methane emissions from landfills.
Challenges and Considerations
While the concept of net-zero carbon emissions is essential, achieving it poses several challenges:
- Technological Limitations: Some technologies required for large-scale emissions reduction and removal are still in the early stages of development and may not be economically viable yet.
- Behavioral Change: Convincing individuals and businesses to adopt sustainable practices and change their behavior can be challenging.
- Equity and Justice: Achieving net-zero emissions must be equitable, taking into account the historical contributions of different countries and the needs of vulnerable populations.
- Transitioning Energy Systems: Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources requires significant investment and infrastructure changes.
- Monitoring and Verification: Accurately measuring and verifying emissions and removals is essential for ensuring that net-zero targets are met.
What is climate change?
According to the World Meteorological Organization, the 20 hottest years on record were in the past 22 years, and the four hottest years were all very recent: from 2015 to 2018. The average global temperature is now 1℃ higher than the previous time. One degree may not seem like much, but the reality is that this gradual warming seems to be having a negative effect. Furthermore, if recent trends continue, it is expected to worsen, with global temperatures predicted to rise to 35℃ by 2100. Despite a slight increase in global temperatures, we are feeling the effects of climate change and have the following unstable weather patterns: Floods and hurricanes; polar ice loss; and sea-level rise. This is only getting worse as global warming increases.
What is causing climate change?
It is widely recognized by scientists and governments that climate change is caused by higher amounts of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Their name comes from the greenhouse effect they create by heating the Earth’s surface and the air above it. Carbon dioxide is the most abundant and dangerous of greenhouse gases, so reducing carbon emissions, creating a carbon footprint, or finding proposed low-carbon alternatives are ways to combat the change. climate.
How can we stop climate change?
Excess greenhouse gases in the atmosphere cause harmful global warming. Therefore, reducing the number of these gases will contribute to combating climate change. Stopping climate change can be done in two ways:
- reduce the emissions we send into the atmosphere from activities such as industrial processes, power generation, transportation, and intensive agriculture
- remove greenhouse gas emissions from the atmosphere, for example by capturing carbon produced in industrial processes before being released or by planting more trees.
What is green energy?
Green energy comes from natural sources like the sun and wind.
What’s the difference between renewable energy and green energy?
Renewable energy comes from sources of continuous and natural self-renewal (hence the name), such as wind power and solar energy. Renewable energy is also commonly referred to as sustainable energy. Renewable energy sources as opposed to fossil fuels, such as coal and gas, are finite sources of energy. In addition, the burning of fossil fuels to release energy is a cause of climate change.
The terms “green energy” and “renewable energy” are often used interchangeably, but there is one key and sometimes confusing difference between them. Although most green energy sources are also renewable, not all renewable energy sources are considered completely green. Take for example hydroelectricity. While hydroelectricity – the energy generated from fast-flowing water – is renewable, some argue that the process of generating large amounts of electricity from water is not green, given the associated industrialization and deforestation related to the construction of large hydroelectric dams.
What are the basic differences between green energy, clean energy, and renewable energy?
Clean energy is energy that, when used, does not pollute the atmosphere; produces little or no greenhouse gases. Again, there is a clear intersection between clean energy, green energy, and renewable
energy. Here’s a simple way to tell them apart:
- Clean energy = clean air
- Green energy = source from nature
- Renewable energy = renewable sources






Good knowledge for me.