Both crude oil and Petroleum are classified as fossil fuels because they are made up of hydrocarbon mixtures derived from pre-dinosaur creatures and plants that live in the ocean (diatoms). The remains of these plants and animals were preserved in the sediment and rock that accumulated over millions of years. The relics today referred to as crude oil or Petroleum were subjected to extreme levels of heat and pressure within these layers. In this discussion, the term “petroleum” refers to oil that is obtained by crushing rocks.
After crude oil has been recovered from the ground, it is transported to a refinery to undergo additional processing to produce more refined petroleum products. These goods derived from Petroleum include but are not limited to, certain oil and gas industry products such as gasoline, distillates such as diesel fuel and heating oil, petrochemical feedstocks, jet fuel, waxes, asphalt, and lubricating oils, to name just a few examples. A wide range of petroleum products and their uses are explained below in detail.
Properties of Petroleum
Physical properties of petroleum span various variations, such as its viscosity, density, boiling point, and color. Heavy fractions like asphaltene contain a greater concentration of metals than saturated and aromatic fractions. Light Petroleum may include trace levels of nitrogen and Sulphur, while heavier or extra-heavy crude oil is more likely to have higher nitrogen and Sulphur concentrations.
There are examples of Petroleum in the natural world in all three possible phases: solid, liquid, and gas. Petroleum fluids can be any shade from dark brown to bluish-black or black and may or may not exhibit bloom or fluorescence. In its solid or nearly solid-state, Petroleum is commonly referred to as “pitch” due to its dark color. After the lighter fractions have moved or evaporated, it was thought that these deposits would form. Gaseous petroleum deposits, sometimes including gasoline deposits, are also known as natural gas deposits.
Petroleum contains a wide variety of hydrocarbons, including simpler alkanes and more complex ones like cyclohexenes, aromatic hydrocarbons, and asphaltenes. The building blocks of both petrochemicals and Petroleum are carbon and hydrogen. The chemical properties of petroleum can vary considerably from one another due to the significant number of methods by which the elements above can mix.
Top Petroleum Products and Their Uses
There is a list of oil and gas industry products. Some of these petroleum products and their uses are:
Gasoline
There is no difference between Gasoline and petrol, both refer to the same product. This clear liquid is produced as a byproduct of the fractional distillation process, which is applied to crude oil. Because of its high demand and extensive distribution, its price has been seen to climb and fall over the past many years.
Gasoline can be used in various devices and processes in addition to motor vehicles, compressors, and generators. Three main requirements must be met by gasoline before it can be used in an internal combustion engine. The fire must be able to burn evenly, that it be able to be started quickly in cold weather, and that it complies with all environmental standards.
Jet Fuel
Jet fuel production, which is used in aircraft worldwide, currently consumes around 10% of the crude oil mined worldwide. In the same vein as diesel, it is a blend of hydrocarbons, the precise composition of which differs depending on the source of the Petroleum. Kerosene’s primary purpose as a light source may no longer be as crucial as it once was, but it is still widely used worldwide as a fuel for cooking, as a space heater, and as a fuel for modern jet engines.
Even when exposed to the low temperatures typical of high-altitude flight, jet fuels should maintain their purity and ability to flow freely without any wax particles. The boiling point for jet fuel is -50 degrees Celsius. The fuel must be free of any particles of water that may be suspended in it so that ice does not form inside the fuel system.
Diesel Fuel and Heating Oil
Diesel fuel, sometimes known as diesel oil, is a flammable liquid used to fuel diesel engines. In most cases, it is manufactured using crude oil fractions that have lower volatility compared to those used to manufacture gasoline.
Diesel fuel is a type of fuel that is frequently utilized in internal combustion engines. These engines may be found in vehicles such as cars, trucks, buses, and trains. In addition, it is used in gas turbines and other engines that use external combustion. Diesel has a higher energy and power density than gasoline. Diesel is more potent per unit of volume.
Lubricating Oils
Mineral oils are a type of lubricating oil that is obtained from various mineral sources. They are primarily made up of the distillation of petroleum hydrocarbons, which account for 80–90% of their composition, and they comprise 10–20% additives that affect the characteristics of the oil. Appliances that use this chemical as a source of heat or a coolant, for example, in the kitchen, the automobile, or other places, are highly prevalent. The temperature at which liquefied petroleum gas begins to boil is significantly lower than 25 degrees Celsius.
The viscosity of the lubricating oil is the primary criterion for classifying different types. The needs range from a dense, sticky material used to open gears or wire ropes to a fragile oil required for the high-speed spindles of textile machinery. In the middle of these two extremes is a broad spectrum of items, each with unique qualities. Oils for automobiles make up the most valuable portion of the market’s product offering.
Waxes
Kerosene and paraffin are two terms that are frequently interchanged; nevertheless, paraffin is a more refined and purified form of kerosene. Because of this, it is more suited for usage in the home, where less soot is produced when it is burned.
In addition to its function as a lubricant, paraffin wax has a solid state and a waxy consistency. Most of the time, it is stored in a room with a stable temperature. Paraffin, which has a melting temperature above 370 degrees Celsius, is used to make a wide variety of products, including waxing materials like Sealand and crayons, wax for surfboards and floors, candles, and cosmetics like Vaseline.
Asphalt
Asphalt, which can be either black or brown, is a substance that resembles Petroleum and can either be a sticky liquid or glassy solid in consistency. Mining it from subsurface sources is one option, although it can also be obtained as a byproduct of the processing of Petroleum.
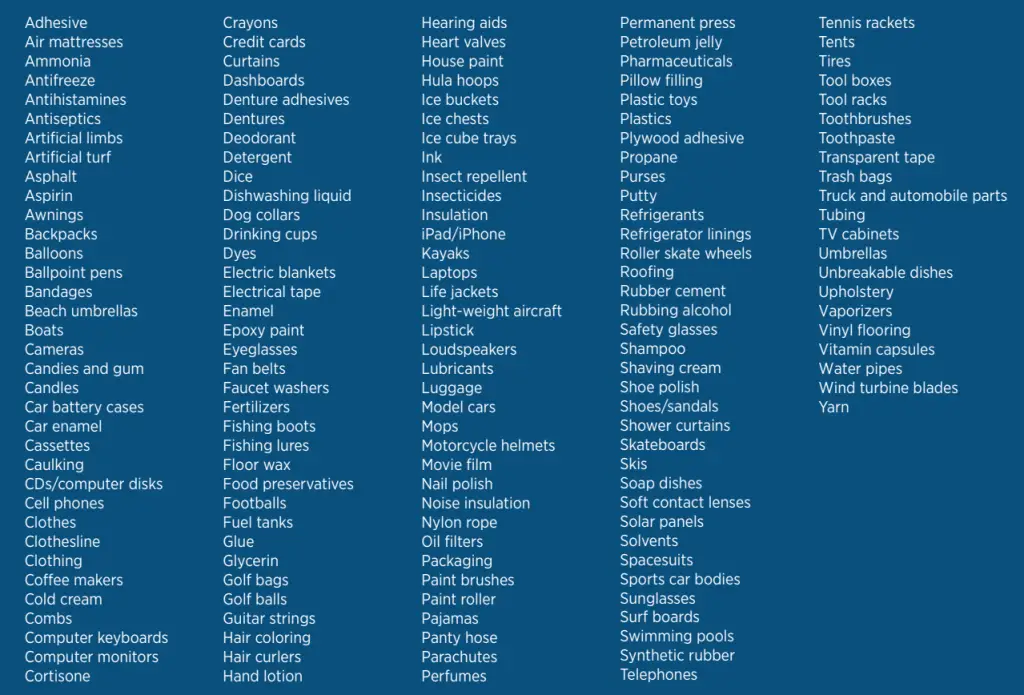
The asphalt used for these applications can take the form of a thin membrane sprayed on and then covered with earth for protection against weathering and mechanical damage. Alternatively, the asphalt can be of a greater thickness and typically include riprap, as is the case with dam facings, canal and reservoir linings, and other harbor and sea constructions (crushed rock). Asphalt is used in various applications, including coatings, floor tiling, roofs, soundproofing, waterproofing, and other aspects of building construction, in addition to several industrial products, such as batteries. An asphaltic emulsion is made by suspending tiny globules of asphalt in water, and this emulsion is subsequently put to use for various applications. The following table lists most of the products produced by the petroleum industry:
| Telephones | Cameras | Bandages | Hair Curlers | Drinking Cups | Ammonia | Gasoline |
| Solvents | Diesel fuel | Motor Oil | Bearing Grease | Heart Valves | Crayons | Parachutes |
| Ink | Floor Wax | Ballpoint Pens | Football Cleats | Enamel | Pillows | Dishes |
| Upholstery | Sweaters | Boats | Insecticides | Anesthetics | Artificial Turf | Artificial limbs |
| Bicycle Tires | Sports Car Bodies | Nail Polish | Fishing lures | Dentures | Model Cars | Folding Doors |
| Dresses | Tires | Golf Bags | Perfumes | Cold cream | Movie film | Contact lenses |
| Cassettes | Dishwasher parts | Tool Boxes | Shoe Polish | Fan Belts | Car Enamel | Shaving Cream |
| Motorcycle Helmet | Caulking | Petroleum Jelly | Transparent Tape | Refrigerators | Golf Balls | Toothpaste |
| Footballs | Detergents | Tents | House Paint | Surf Boards | Shower Curtains | Safety Glasses |
| CD Player | Faucet Washers | Antiseptics | Clothesline | Clothes | Toothbrushes | Ice Chests |
| Curtains | Food Preservatives | Basketballs | Soap | Combs | CD’s & DVD’s | Paint Brushes |
| Vitamin Capsules | Antihistamines | Purses | Shoes | Vaporizers | Balloons | Sun Glasses |
| Dashboards | Cortisone | Deodorant | Shoelace Aglets | Nylon Rope | Candles | Trash Bags |
| Putty | Dyes | Panty Hose | Refrigerant | Water Pipes | Hand Lotion | Roller Skates |
| Percolators | Life Jackets | Rubbing Alcohol | Linings | Shampoo | Wheels | Paint Rollers |
| Skis | TV Cabinets | Shag Rugs | Electrician’s Tape | Guitar Strings | Luggage | Aspirin |
| Tool Racks | Car Battery Cases | Epoxy | Paint | Antifreeze | Football Helmets | Awnings |
| Mops | Slacks | Insect Repellent | Oil Filters | Denture Adhesive | Linoleum | Ice Cube Trays |
| Umbrellas | Yarn | Fertilizers | Hair Coloring | Speakers | Plastic Wood | Electric Blankets |
| Roofing | Toilet Seats | Fishing Rods | Lipstick | Tennis Rackets | Rubber Cement | Fishing Boots |
| Eyeglasses | Synthetic Rubber | Glycerin | Dice | |||
Indirect products obtained from Petroleum
CDs and DVDs
The creation of CDs and DVDs involves the utilization of polycarbonate plastics, which are generated from Petroleum. When compact discs were first manufactured, lubricants made from Petroleum were necessary to ensure that the discs could spin freely.
Chewing Gum
Petroleum wax is used as the starting material in the production of chewing gum. This medication is permitted by the FDA, provided that particular UV absorbance constraints are satisfied. The same paraffin wax coating minimizes foaming while preparing cheese, fresh vegetables, and chicken nuggets. Also, some over-the-counter medications for gas relief contain paraffin wax.
Aspirin
Without the use of Petroleum, one of the world’s most widely prescribed medicines could not be produced. Benzene, a hydrocarbon derived from Petroleum, is utilized to treat pain and inflammation.
Clothing
You probably have quite a few pieces of polyester clothes, even if you strive to wear solely wool or cotton. Sixty percent of the world’s clothes are made from polyester, a synthetic fabric derived from petroleum. We can recycle cotton garments, but polyester garments cannot be recycled in this manner.
Dentures
Dentures can be constructed using various components, such as acrylic resin, a hydrocarbon petroleum product, porcelain, metal, nylon, and even nylon fibers. The hue of this acrylic resin can alter to make it appear more like gum by mimicking its texture. Since oil is also an ingredient in toothpaste, consuming it might contribute to the upkeep of healthy teeth. The widespread use of poloxamer 407, derived from Petroleum, facilitates the dissolution of oil-based compounds in water.
Lipstick
It’s possible to make lipstick and other cosmetics out of paraffin wax, a synthetic wax also frequently used to produce chewing gum and scented candles.
Shampoo
A cosmetic spray called dry shampoo, also known as liquified petroleum gas is applied to wash and air-dried hair freshly. Propane and butane are the two components that makeup liquefied petroleum gas, also known by their acronym LPG. Keep in mind, as well, that the refining of oil results in the production of petrochemicals, which are then employed in the manufacturing process of the plastic shampoo bottle. This cycle includes items such as plastic water bottles and other everyday plastics.
Fig. 1 below shows a comprehensive list of products made from the oil and gas industry.
Conclusion
Tar (or oil) sands on the earth’s surface and underground pools or basins in the microscopic cracks and fissures inside sedimentary rocks contain crude oil and other hydrocarbons in liquid or gaseous form. Petrol is the term used to describe fuels refined from crude oil and gas’s naturally occurring hydrocarbons.
The manufacture of petrochemicals can also use coal, natural gas, and biomass. Density, viscosity, and boiling point variations are the most frequently cited examples of the physical properties of petroleum. The oil and gas industry products include gasoline, diesel, jet fuel, heating oil, diesel fuel, asphalt, road oil, and feedstocks. These petroleum products and their uses include manufacturing the chemicals, polymers, and synthetic materials that are included in virtually every product we use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which product derived from Petroleum has been used the most frequently daily?
Gasoline use in the United States is far higher than any other petroleum product. In 2021, the United States used around 8.8 million barrels per day, or 369 million gallons per day, of finished motor gasoline, which accounted for approximately 44% of the country’s overall consumption of Petroleum.
Do you know how to characterize the chemical properties of Petroleum?
The primary components of Petroleum are hydrogen and carbon; however, it also contains minute amounts of other elements, such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and various metals, such as vanadium, cobalt, and nickel. Alkanes (also known as paraffin), naphthenes, aromatics, and hetero compounds are a few examples of the most common organic molecules.
How many products can you think of related to the oil industry?
There are around 6,000 everyday oil and gas industry products, including dishwasher detergent, solar panels, food preservatives, eyeglasses, DVDs, children’s toys, tires, and heart valves, to name just a few examples.