Properly supporting each pipe is one of the main aspects of piping and plumbing design. There are various supports that make this complex task possible. Pipe hangers are one such important piping support that is widely used in the piping and plumbing industry to transfer the piping load to secondary structures without damaging the pipe. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of pipe hangers, exploring their importance, types, installation, maintenance, and applications.
What Are Pipe Hangers?
Pipe hangers are a type of pipe supports that are installed from an overhead structure to support the pipe keeping it in a hanging position. The pipe runs in the horizontal direction and the pipe hangers are always installed in the vertical direction to prevent sagging, excessive movement, and stress of pipes, ensuring the stability and longevity of the entire piping and plumbing system.
The Importance of Pipe Hangers
Pipe hangers play a critical role in a plumbing or piping system by providing support and stability to pipes. Pipe hangers as pipe supports serve the following purposes:
Supporting Weight:
One of the primary functions of pipe hangers is to support the weight of pipes. Pipes, especially those carrying fluids or gases, can be heavy, and without adequate support, they can sag or even fail under their own weight. Pipe hangers ensure that pipes remain level and secure.
Preventing Sagging and Joint Leakages:
Over time, pipes can sag due to their weight and the pressure of water and other substances flowing through them. Pipe hangers lift and support pipes to prevent this sagging, which can lead to leaks, reduced water pressure, and costly repairs. By providing adequate support, the pipe hangers prevent joint leakages.
Minimizing Stress and Strain:
When pipes are properly supported, they experience less stress and strain. Stress on pipes can result from temperature changes, pressure fluctuations, or vibrations. Pipe hangers distribute these forces evenly, reducing the risk of pipe damage, such as cracks or fractures. This preserves the integrity of the piping and plumbing system.
Noise Reduction:
Pipe hangers can also dampen the noise generated by the movement of water and prevent pipes from rattling against walls or other surfaces. This contributes to a quieter and more peaceful home environment.
So, hangers in piping systems basically keep pipes organized and safe from rupture or destruction.
Types of Pipe Hangers
As already mentioned pipe hangers suspend the pipe from the top. There is a wide variety of pipe hangers available, each designed for specific applications. Some common types include:
Band Hangers:
Band hangers are simple pipe support devices consisting of a metal band or strap that encircles the pipe. They are secured to a surface, such as a wall or ceiling, using screws or nails. Band hangers are typically used for lightweight or small-diameter pipes.
Clevis Hangers:
Clevis hangers are U-shaped hangers with a clevis pin and a threaded rod. The pipe rests in the U-shaped part, and the threaded rod is used to secure the hanger to a structural element, providing vertical support for horizontal pipes. Clevis hangers are commonly used in industrial and commercial plumbing applications.
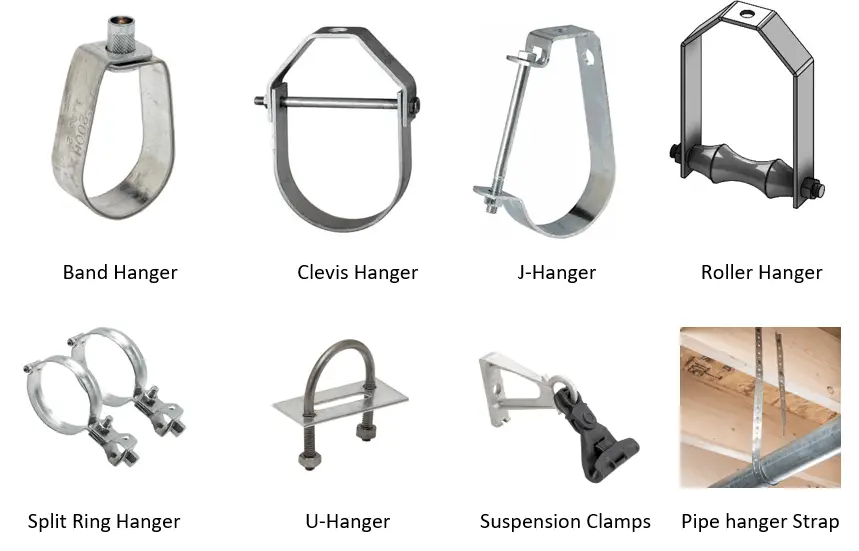

J-Hangers:
J-hangers are named for their J-shaped design. They are used to support pipes from overhead structures, such as beams or ceilings. The pipe rests in the curved part of the J, and the straight end is secured to the structure. J-hangers are suitable for a wide range of pipe sizes and are often used in suspended piping systems.
Roller Hangers:
Roller hangers are designed for pipes that need to move due to thermal expansion or contraction. They consist of a roller mechanism that allows the pipe to glide back and forth as it expands and contracts. Roller hangers are often used in systems where pipes experience significant temperature variations.
Rod Hanger:
A rod hanger pipe support, also known simply as a rod hanger, is a type of pipe support system used in plumbing and piping installations. It consists of a metal or threaded rod, which is suspended from an overhead structure such as a ceiling or beam, and a hanger assembly attached to the rod. This hanger assembly is designed to secure and support pipes in a suspended manner.
Split Ring Hangers:
Split ring hangers are circular hangers with a break in the ring, allowing them to be easily installed around pipes without the need to thread the pipe through the hanger. Once in place, they are secured to a surface, providing support for the pipe. Split ring hangers are commonly used for copper and plastic pipes.
Spring Hangers:
Spring hangers are designed to absorb pipe thermal movement while still supporting the pipe. It also isolates pipes from vibrations and shocks. They consist of a coil spring within a housing. The spring absorbs and dampens the vibrations, protecting the pipe from damage. Spring hangers are often used in applications where minimizing pipe movement and noise is crucial. Click here to learn more about Spring Hangers.
U-Hangers:
U-hangers are U-shaped pipe hangers that provide support for pipes from beneath. The pipe rests inside the U-shaped part of the hanger, which is secured to a structural element, such as a beam or floor joist. U-hangers are versatile and can be used for various pipe sizes and configurations.
Pipe Hanger Straps:
Pipe hanger straps are simple metal bands that wrap around pipes and are secured to a surface with screws or nails.
Stainless Steel Band Hangers:
These hangers are designed for corrosive environments, such as those found in chemical plants or coastal regions.
Suspension Clamps:
Suspension clamps are used to hang pipes from overhead structures, such as ceilings or beams.
Materials for Pipe Hangers
Pipe hangers are essential components in plumbing and piping systems, providing support and stability to pipes. These hangers come in various materials, each selected based on factors such as the type of pipe being supported, the environmental conditions, and the specific application requirements. Based on the materials of construction, there are broadly two types of pipe hangers; metallic pipe hangers and non-metallic pipe hangers.
Here are some common materials used for pipe hangers:
- Steel Pipe Hangers: Steel pipe hangers are strong and durable, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They are often used in industrial and commercial settings.
- Stainless Steel Pipe Hangers: Stainless steel hangers are corrosion-resistant and ideal for environments where moisture or corrosive substances are present, such as chemical plants or coastal areas.
- Galvanized Steel Pipe Hangers: Galvanized steel hangers are coated with a layer of zinc to provide corrosion resistance. They are used in outdoor applications or where moisture is a concern.
- Copper Pipe Hangers: Copper pipe hangers are commonly used for supporting copper plumbing pipes. They are corrosion-resistant and have a natural aesthetic appeal.
- PVC Pipe Hangers: PVC pipe hangers are used primarily with PVC pipes. They are resistant to moisture and corrosion and are commonly used in residential plumbing systems.
- Polyethylene Pipe Hangers: Polyethylene pipe hangers are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for use with plastic pipes.
- Fiberglass Pipe Hangers: Fiberglass pipe hangers are lightweight and corrosion-resistant. They are often used in applications where metal hangers might corrode, such as in corrosive chemical environments.
- PEX Pipe Hanger: A PEX pipe hanger is a specific type of pipe support designed for use with PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) pipes in plumbing and heating systems. PEX is a flexible and durable piping material used extensively for water supply lines, radiant floor heating, and other plumbing applications. PEX pipe hangers are specially designed to securely support and position PEX pipes in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Design of Pipe Hangers
Pipe Hangers are designed following the guidelines mentioned in MSS-SP-58. Carbon steel and Stainless steel pipe hangers are generally used up to a pipe temperature of 343 degrees C. Pipe Hangers and supports for fire protection systems shall conform to standards published by the National Fire Protection Association, NFPA-13. The selection of pipe hangers and supports shall be based on the overall design concept of the piping systems and any special requirements that may be called for in the specifications. The supporting systems shall provide for the free or intended movement of the piping system with the degree of control that its operating characteristics require. The design of pipe hanger supports must consider the Deadweight loads, Hydrostatic loads, Thermal loads and movements, Expansion joint thrust loads, spring loads, friction loads, and any dynamic load present.
Installing Pipe Hangers
Proper installation of pipe hangers is crucial for their effectiveness. Here are the basic steps for installing them:
- Determine Placement: Identify where hangers are needed based on the pipe size, weight, and material, as well as local building codes.
- Select the Right Hanger: Choose the appropriate type of hanger for the specific application and pipe material.
- Attach Hangers Securely: Use the appropriate fasteners (screws, bolts, or nails) to attach the hangers securely to the mounting surface.
- Space Hangers Correctly: Ensure that hangers are spaced at the recommended intervals to provide adequate support.
- Adjust for Expansion and Contraction: Account for thermal expansion and contraction by allowing some flexibility in the installation.
Maintaining Pipe Hangers
Regular maintenance of pipe hangers is essential to keep your plumbing system functioning smoothly. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Inspect Hangers: Periodically check the condition of hangers for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Tighten Fasteners: Ensure that the piping fasteners securing the hangers are tight and secure.
- Replace Damaged Hangers: If you notice any damaged or deteriorating hangers, replace them promptly to prevent further issues.
- Reevaluate Over Time: As your plumbing system ages or undergoes changes, reevaluate the placement and type of hangers to ensure they remain effective.
While pipe hangers may not be the most glamorous part of a piping/plumbing system, they are undeniably vital. These unassuming devices provide the support and stability that pipes need to function reliably for years. Whether you’re a homeowner or a plumbing professional, understanding the importance of pipe hangers and how to install and maintain them is crucial for the long-term health of your plumbing system. So, the next time you turn on the tap, take a moment to appreciate the unsung heroes behind the scenes – your trusty pipe hangers.
FAQ
What is the purpose of pipe hangers?
Pipe hangers are designed to support and secure pipes in plumbing and piping systems. They prevent sagging, shifting, and excessive movement of pipes, ensuring the stability and longevity of the system.
What are the different types of pipe hangers?
Pipe hangers come in various types, including clevis hangers, band hangers, J-hangers, roller hangers, split ring hangers, spring hangers, and U-hangers, each designed for specific applications.
How do I select the right type of pipe hanger?”
The choice of pipe hanger depends on factors like pipe material, size, weight, environmental conditions, and whether flexibility or vibration damping is required.
What materials are pipe hangers made of?
Pipe hangers are constructed from various materials, including metal (steel, stainless steel, galvanized steel), copper, plastic (polyethylene, PVC), rubber, EPDM, fiberglass, aluminum, wood, and composite materials.
Are there building codes or standards for pipe hangers?
Yes, there are industry standards and building codes that provide guidelines for the design, installation, and inspection of pipe hangers. Refer to ASME, MSS, NFPA, and local building codes for relevant standards.”