What is Process Safety Management (PSM)?
Process Safety Management (PSM) is the management of hazards that can give rise to major accidents involving the release of potentially dangerous materials, the release of energy (such as fire or explosion), or both. It focuses on the prevention of leaks, spills, overpressure, equipment malfunction, excessive temperatures, metal fatigue, corrosion, and other similar conditions by the application of good engineering and design principles. In short, Process Safety Management focuses on controlling the release of highly hazardous substances. All plants handling highly hazardous materials must undergo a sound Process Safety Management program.
Functions of Process Safety Management
The foundation of a process safety management system is to manage risks and reduces them to a tolerable level, either by reducing the likelihood of the hazard release, reducing the consequences if does get released, or both. So, basically, process safety management is a blending of management and engineering skills to prevent catastrophic accidents. The main functions of process safety management are:
- the proactive and systematic identification of unsafe releases
- evaluation and mitigation or prevention of chemical releases
A sound Process Safety Management will ensure minimal risk from:
- Fire
- Explosion
- Poisoning, and
- Suffocation
Written procedures for managing those hazardous releases must be developed and implemented from the design stage itself to ensure proper process safety management.
The US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has issued a Process Safety Management standard “29 CFR 1910.119” for helping chemical companies to identify highly hazardous chemicals and take precautionary action for ensuring a safe and healthy workplace.
What is Process Safety?
Process Safety is defined as “a discipline that focuses on the prevention of fires, explosions, and accidental chemical releases at chemical process facilities”. So it is a disciplined framework for managing the integrity of operating systems and processes that handle hazardous substances. It relies on good design principles, engineering, and operating and maintenance practices. It deals with the prevention and control of events that have the potential to release hazardous materials and energy. Such events don’t only happen at chemical facilities, they occur in refineries, offshore drilling facilities, petrochemical plants, solids handling facilities, water treatment plants, ammonia refrigeration plants, off-shore operations, etc.
Why is Process Safety important?
Process safety hazards can give rise to major accidents involving the release of potentially dangerous materials, the release of energy (such as fires and explosions), or both. Process safety incidents can have catastrophic effects and can result in multiple injuries and fatalities, as well as substantial economic, property, and environmental damage.
Process safety refinery incidents can affect workers inside the refinery and members of the public who reside nearby. Process safety in a refinery involves the prevention of leaks, spills, equipment malfunctions, over-pressures, excessive temperatures, corrosion, metal fatigue, and other similar conditions. Process safety programs focus on the design and engineering of facilities, hazard assessments, management of change, inspection, testing, and maintenance of equipment, effective alarms, effective process control, procedures, training of personnel, and human factors.
Several Major incidents in both the upstream and downstream industries have highlighted the importance of having robust processes and systems in place. A major incident is typically initiated by a hazardous release; it may also result from a structural failure or loss of stability that escalates to become a major incident. For the oil and gas industry, the emphasis of process safety and asset integrity is to prevent unplanned releases which could result in a major incident.
We cannot afford to rely solely on lessons from major process incidents, which happen relatively infrequently. To strengthen safety barriers and prevent these incidents from occurring at all, it is necessary to collect, collate and analyze data from less severe incidents and shortfalls in management system performance. Process safety is required as Failures of process safety management systems are deadly and costly. It impacts people, communities, assets, and the environment.
What is Process Safety Engineering?
Process safety in Design Engineering means
- Prevention and mitigation of incidents
- Identifying Safety-critical equipment and linking them to performance standards
- Compliance with applicable standards
- Properly design, procure, build, install and test
- Hand over safe facilities
Engineering process safety emphasizes existing good practices to reduce unsafe acts and conditions. It guides daily actions one can take to prevent these incidents from happening again.
The following image briefly explains the bare minimum steps to follow for process safety in engineering.
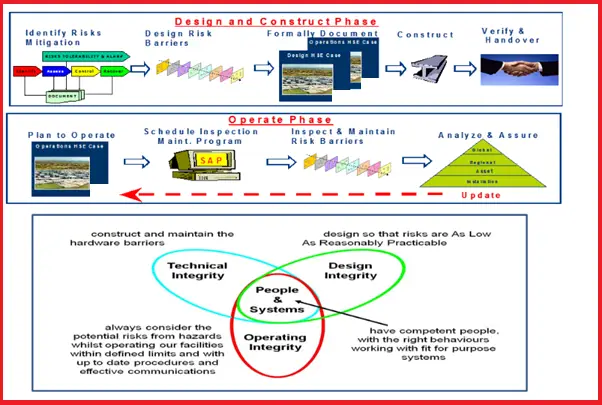
Elements of Process Safety Management
To manage chemical operations involving hazardous materials; Process Safety Management must be implemented. The main elements of Process Safety Management are
- Technology,
- Design and Engineering Facilities
- Hazard Assessment
- Management of Change
- Regular Inspection and Testing
- Equipment Maintenance
- Effective Alarm Management
- Implementation of process control,
- Proper operating procedures
- Maintaining all regulatory requirements
- and Human factors.
Reasons for Process safety management
There are numerous reasons to implement process safety management in plants. The main reasons are:
- Prevention of major accidents and potential impact of the same.
- Managing the risks inside the plant.
- increasing sustained value and boosting productivity.
- produce a high-quality product at less cost.
- Increasing profit.
- Keeping the environment safe.
- increase shareholder value.
So the main role of process safety management is to keep the hazard under control inside the equipment or pipes that are designed and maintained to handle them safely. It requires a commitment from design, engineering, operation, and maintenance personnel to follow all the roles without deviation.
Fundamental Questions for Safety Management Process
To reduce or manage the process safety risk inside a plant one must ask the following four fundamental questions:
- What can go wrong?
- Are proper controls in place if a major incident occurs?
- What does each control deliver in terms of a “safety outcome”?
- Is it confirmed that the controls will work as intended?
Process Safety Management Process
A sound process safety management can be achieved by ensuring the following:
- Design Integrity
- Technical Integrity, and
- Operating Integrity
Design Integrity:
Design integrity ensures the integrity of all activities prior to commissioning. This leads to
- compliance with the design and engineering standards
- robust assurance process during the EPC phase.
- design HSE cases
- to identify the maintenance routine for Safety-Critical Equipment.
- written Design and Operating philosophy
- with clear agreement on maintenance and inspection strategies.
Technical Integrity:
It means the safeguarding of assets through effective maintenance, inspection, repair, and assurance that can be achieved through
- Identification of safety-critical elements
- Maintaining readily accessible, up-to-date information.
- Verification of appropriate inspection and rectification of deficiencies.
Basically, technical integrity is established during the design, construction, and commissioning phases.
Operating Integrity:
It means operating facilities within safe operating limits all the time, maintaining and following the procedures. This is achieved through
- Verification of operating parameters against design parameters.
- Clear, consistent, and effective communication and shift handovers
- Accessible and up-to-date procedures, critical drawings, and documents
- Establishing a permit system only for authorized personnel