What is a Hazardous Area?
A hazardous area is an area in which an explosive gas atmosphere (flammable gases or vapors, combustible dust, flammable liquids, ignitable fibers, etc.) is present, or maybe expected to be present, in quantities such as to require special precautions for the construction, installation, and use of apparatus. The term hazardous area is associated with the installation of electrical and instrumentation equipment so special design consideration is applied to meet special requirements considering the safety of the operating personnel.
The oil and gas industry involves the handling and processing of flammable and explosive materials, which can create hazardous areas. Some examples of hazardous areas in the oil and gas industry are:
- Drilling platforms: Drilling platforms are offshore structures where oil and gas exploration and extraction take place. These platforms have several areas that are classified as hazardous, such as drilling areas, storage areas, and processing equipment.
- Refineries: Refineries are facilities that process crude oil into various petroleum products. The processing equipment, storage tanks, and pipelines in refineries are all potentially hazardous areas.
- Oil and gas pipelines: Pipelines are used to transport crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum products over long distances. The pipelines and their associated equipment, such as pumps, valves, and compressors, can be classified as hazardous areas.
- Gas processing plants: Gas processing plants are facilities that separate natural gas into its component gases and remove impurities. The processing equipment, storage tanks, and pipelines in gas processing plants can all be classified as hazardous areas.
- LNG facilities: LNG facilities are used to liquefy natural gas for transportation and storage. The liquefaction process, storage tanks, and associated equipment in LNG facilities are all potentially hazardous areas.
These are just a few examples of hazardous areas in the oil and gas industry. It’s important to identify and classify these areas properly to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
What is Hazardous Area Classification?
Hazardous area classification is the scientific evaluation of facilities where the explosive environment is present and classifies them following scientific and engineering principles. To ensure process safety, Hazardous area classification is of utmost importance. Normally, a hazardous area classification is presented on a plan view of plant drawings. These are also known as area classification drawings. To reduce the risk of fire and explosion, the electrical and electronic equipment is installed following the guidelines of hazardous area classification drawings.
During normal operations in chemical and petrochemical facilities, small releases of flammable fluids inevitably happen from time to time. The aim of hazardous area classification is to avoid the ignition of these releases. Area classification focuses on electrical equipment as a potential ignition source in a flammable atmosphere. The approach is to reduce to an acceptable minimum level the probability of coincidence of a flammable atmosphere and an electrical or other source of ignition.
Area classification is the division of a plant or installation into hazardous areas and non-hazardous areas. The hazardous areas are further subdivided into zones.
Purpose of Hazardous Area Classification
Hazardous area classification provides a basis for the selection and protection required for the electrical equipment appropriate to the defined areas. Area classification also helps for the safe positioning of other potential or continuous sources of ignition (eg. fired heaters, Internal combustion engines, gas /turbine drives, plant roads, regulating temporary or portable equipment, etc.). It enables the selection of suitable electrical and instrumentation equipment to ensure a safe work environment.
In recent times, it has been mandatory for chemical plants, oil refineries, LNG plants, sewerage treatment plants, paint manufacturers, distilling, offshore drilling rigs, Spray Booths, Petrochemical complexes, Laboratory and Fume Cupboards to prepare hazardous area classification drawings as hazardous gas vapors are normally present in all such industries.
Please note that it is not the aim of area classification to guard against the ignition of major releases under catastrophic failures of equipment e.g. Rupture of a pressure vessel or a pipeline which has a low probability of occurrence. The risk mitigation for such large releases shall be carried out by proper layout, separation distances, facility sitings, and proper design, maintenance, and operation of the plant.
Hazardous area classification has several advantages in ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment in areas where flammable or explosive materials are present. Some of the advantages are:
- Increased safety: Hazardous area classification helps to identify and evaluate the risks associated with the presence of flammable or explosive materials. By identifying the hazards, appropriate safety measures can be implemented to prevent accidents and protect personnel and equipment.
- Compliance with regulations: Many countries have regulations and standards that require hazardous area classification in certain industries, such as oil and gas or chemical manufacturing. Compliance with these regulations can help to avoid fines and legal issues.
- Cost-effective design: Hazardous area classification can help optimize the design of facilities and equipment by identifying areas that require special protection measures. This can help to reduce costs associated with over-design or unnecessary safety measures.
- Effective emergency response: Hazardous area classification helps to ensure that emergency response plans are appropriate for the risks present in the area. This can help to minimize the impact of accidents and improve the effectiveness of response efforts.
- Improved communication: Hazardous area classification provides a common language for communication between designers, engineers, and safety professionals. This can help to ensure that all parties have a clear understanding of the hazards and appropriate safety measures.
Overall, hazardous area classification is a critical process in ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment in areas where flammable or explosive materials are present. By properly identifying and evaluating the risks, appropriate safety measures can be implemented to minimize the risk of accidents and protect personnel and equipment.
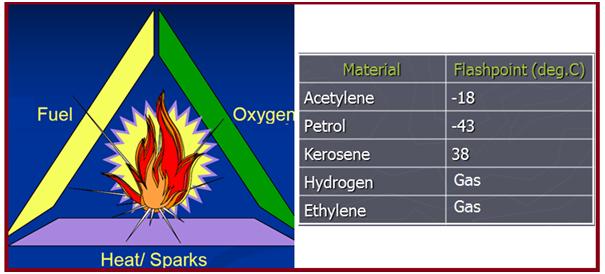
Fire Triangle
Three elements are required to be present together to cause a fire or explosion. These are
- Fuel: This is what burns
- Oxygen: Required to support fire
- Ignition: Heat energy required to start a fire
Refer to Fig. 1 which shows these elements.
Fire/explosion can happen only if all three are present together in an appropriate proposition.
Gas properties
Flashpoint- The lowest liquid temperature at which, under certain standardized conditions, a liquid gives off vapors in a quantity such as to be capable of forming an ignitable vapor/air mixture. It is the vapor that mixes with air to form a flammable vapor.
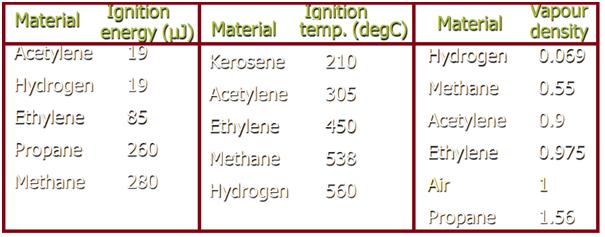
Lower Explosive Level (LEL): Concentration of flammable gas or vapor in the air, below which the gas atmosphere is not explosive.
Upper Explosive Level (UEL): Concentration of flammable gas or vapor in the air, above which the gas atmosphere is not explosive.
Ignition energy (Fig. 2): Minimum energy of a spark that can ignite a flammable gas or vapor.
Ignition temperature (Fig. 2): The lowest temperature at which flammable gas or vapor gets ignited by itself.
Vapor density (Fig. 2): Density of a vapor or gas relative to the density of air, at the same temperature and pressure.
Grades of hazardous release
The release of hazardous elements is grouped as follows:
- Continuous grade: Release that is continuous or is expected to occur frequently or for long periods. continuous grade release is present for more than 1000 hours per year (>1000 hours per year). E.g.: Light hydrocarbon interceptor, the seal of a floating roof tank, the area inside a tank, sump, etc.
- Primary grade: Release which can be expected to occur periodically or occasionally during normal operation ( > 10 hours per year to < 1000 hours per year). E.g.: Sampling points, equipment nozzle
- Secondary grade: Release which is not expected to occur in normal operation and, if it does occur, is likely to do so only infrequently and for short periods (<10 hours per year). E.g.: Piping flanges and valves, instrument fittings, etc.
Such grading is not dependent on the total rate of release or the characteristics of the released material, but only on the probability of the release. Also, some sources may be considered to have a dual grade release with a small continuous or a primary grade and a large secondary grade eg. a vent with a dual purpose or a pump seal.
Steps for Hazardous Area Classification
Following are the general steps for hazardous area classification:
- All potential leak sources in the area under review are determined like vents, pump seals, flanges, sample points, instruments, etc.
- For each potential leak source the grade of release is determined (that is no. of hours per annum that the leak of flammable material can be expected to occur.
- The degree of ventilation in the area around the potential leak source is established (whether there is adequate ventilation or not).
- Together it is the grade of release and the degree of ventilation near the potential leak source that determine the type of hazardous zone around the leak source.
- The hazard radius around the potential leak source is determined from the category of fluid leaking. The hazard radius forms a horizontal circle around the potential leak and is valid at the elevation of the leak.
- From the hazard radius and based on whether the release is lighter or heavier than air and the presence/absence of platforms – the extent of the three-dimensional hazardous zone around the potential leak source is determined.
- In a similar way, the hazardous zones from all potential leak sources are determined and superimposed. This gives contours of hazardous areas for the concerned facility both in the horizontal and vertical planes.
Hazardous Area Classification Guide
Two widely used systems are followed in industries for hazardous area classification.
- the Class/Division system and
- the Zone system
While Canada and the United States predominantly use the class/division system, other parts of the world use the zone system of Hazardous area classification. In the below paragraphs, we will explore the hazardous area zone classification.
Hazardous Area Zone Classification
The Zone system of hazardous area classification, defines the probability of the hazardous material, gas, or dust, being present in sufficient quantities that can generate explosive or ignitable mixtures. Refer to Fig.3 which shows the hazardous area zone classification based on hazardous gas release grade. There are three zones, Zone 0, Zone 1, and Zone 2.
The grade of release determines the designation of hazardous zones in the immediate vicinity of the release. In open-air situations with adequate ventilation, a secondary grade release will lead to Zone 2, a primary grade release will lead to Zone 1 and a continuous grade release will lead to Zone 0
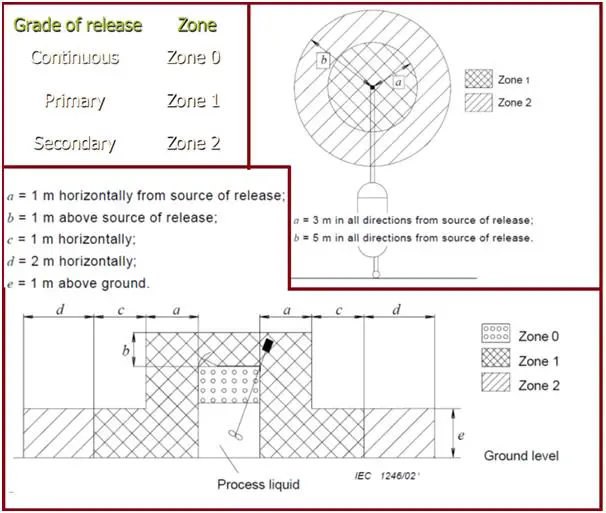
Zone classification will be influenced by ventilation also. IEC 60079-10 categorizes ventilation degrees as High, medium, and low. Poor ventilation may push the zone higher by one level. Poor ventilation may result in a more stringent zone while with high ventilation, the converse will be true. A secondary grade source of release may give rise to Zone 1 if local ventilation is restricted. (Example in a sump).
Adequate Ventilation is defined as ventilation sufficient to avoid a flammable atmosphere within a sheltered or enclosed area. This will normally be achieved by a uniform ventilation rate of 12 air changes per hour with no stagnant areas.
Depending on the presence of combustible dust or ignitable fibers and flyings, the hazardous area is classified into three zones: Zone 20, Zone 21, and Zone 22.
In both the above zone classifications, the probability of explosion severity reduces when we move from zone 0 (or zone 20) to zone 2 (zone 22).
The Extent of the Hazardous Area Zone
Distance in any direction from the source of release to the point where the gas/air mixture has been diluted by air to a value below the lower explosive limit. Refer to Fig. 3 above which shows a typical example of a hazardous area zone extent.
- Pressure breathing valve (Fig. 3) in the open air, from the process vessel.
- A fixed process mixing vessel (Fig. 3); liquids are piped into and out of the vessel through all-welded pipework flanged at the vessel.
For a given release the extent of the zone will vary with the vaporizing potential of the fluid release, the ventilation rate, and the buoyancy of the vapor. The 3rd edition of IP 15 provides three methods for determining the extent of hazardous zones:
- Direct Example Approach– limited to common facilities in open areas
- Point Source Approach– release rates are dependent on process conditions
- Risk-based Approach– an optional rigorous methodology that may reduce the hazardous area determined by the point source approach
Fluid Category of Petroleum Products
The hazard radius for each point of release is a function of fluid characteristics (vapor forming potential) under the circumstances of the release, the release rate, and the rate of vaporization. Hydrocarbon fluids are classified into four fluid categories based on their vaporizing potential.
| Fluid Category | Description |
| A | A flammable liquid that on release would vaporize rapidly and substantially. This category includes: (a)Any LPG or lighter flammable liquid; (b)Any flammable liquid at a temperature sufficient to produce, on release, more than 40% vol. vaporization with no heat input other than from surrounding. |
| B | A flammable liquid, not in category A, but at a temperature sufficient for boiling to occur on release. |
| C | A flammable liquid, not in Category A and B, but which can on release be at a temperature above its flash point or form a flammable mist or spray. |
| D | Flammable gas or vapor (Natural Gas, Hydrogen, etc) |
With the fluid category leaking from the particular leak source established, the extent of vapor travel (radii) around the leak source can be determined.
Hazardous Area Classification Drawing
The hazardous area classification drawings are of sufficient scale to show all the main items of equipment and all the buildings in both plan and elevation. The boundaries of all hazardous areas and zones present shall be clearly marked using the clear shading convention for Zone 0, Zone 1, and Zone 2.
It has to be recognized that however, well-protected electrical equipment may be, there will always be a residual risk if it is placed in areas where explosive atmospheres may occur.
Electrical Equipment Selection in Hazardous Area Classification
Once the Hazardous Area classification of a facility is determined, it is used as a basis for selecting suitable electrical equipment. To reach the intended level of safety, equipment must then be installed correctly, operated within its design envelope, and maintained adequately.
As a general policy, electrical equipment should not be located in a hazardous area if it is possible to place it in a non-hazardous area, nor should be placed in Zone 1 if it can be placed in Zone 2. The installation and maintenance requirements for electrical equipment in Zone 1 locations are more stringent than for Zone 2 locations and Zone 0 are more stringent than Zone 1 locations.
ATEX directives for electrical apparatus for hazardous areas distinguish between two equipment groups as listed below:
- Group I – For use in mines (Methane)
- Group II – Other than mines
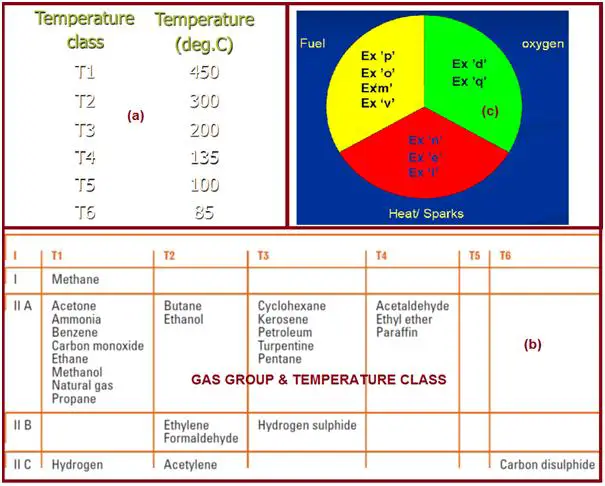
Sub-divisions in group II based on ignition energy requirement
- IIA – Atmospheres containing acetone, ammonia, ethyl, alcohol, gasoline, methane, propane, or similar gases
- IIB – Atmospheres containing ethylene, acetaldehyde, or similar gases
- IIC – Atmospheres containing acetylene, hydrogen, or similar gases
Hazardous Area – Temperature class
Classification based on ignition temperature (Fig. 4 (a)) of gas or vapor. The maximum surface temperature of selected equipment is not to exceed the limiting value.
Sour area
The area with H2S (Hydrogen Sulphide) concentration above 50 ppm. H2S is highly toxic even in very low concentration
Properties:
- LEL – 4% (40,000ppm)
- UEL – 46%
- Autoignition temperature – 260degC
- Gas group IIB
- Sour areas with H2S concentration below 4% in the process stream need not be classified as a hazardous area
The Ingress Protection or IP rating
Ingress of moisture or other material could affect electrical equipment and cause it to break down electrically and possibly cause arcs and sparks which could be possible sources of ignition. Also, personnel protection is required against contact with internal live or rotating parts inside the enclosure, and to the apparatus against ingress of solid objects, dust, etc.
The IP rating (or International Protection Rating, sometimes also called Ingress Protection Rating) provides users with more detailed information than vague terms such as waterproof. The IP rating consists of the letters IP followed by two digits.
The first digit indicates the level of protection the fixture provides its internal parts (electrical and moving parts) from the ingress (interaction or contact) of solid foreign objects (like dust). The second digit indicates the protection of the equipment inside the fixture against harmful ingress (contact) with water.
Examples of IP Rating
- IP44 is protected against solid objects greater than 1mm (0.04 inches) and liquid sprays from all directions.
- IP64 is protected against liquid sprays from all directions.
- IP65 is protected against liquid low-pressure jets of water from all directions
- IP66 is protected against strong jets of water from all directions
Standards for Hazardous Area Classification
Codes and standards define minimum electrical design and installation requirements for electrical equipment to be used in hazardous areas. The following are some of the codes and standards that are commonly used for hazardous area classification
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 70, National Electric Code (NEC): This standard provides guidelines for electrical installations in hazardous locations, including classification of hazardous areas, selection, and installation of electrical equipment, and wiring methods.
- American Petroleum Institute (API) RP 500 and RP 505: These standards provide guidance for the classification of hazardous locations in petroleum facilities, including refineries, petrochemical plants, and onshore and offshore production facilities.
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60079 series: This series of standards provides guidelines for the design, installation, and maintenance of electrical equipment in hazardous areas. The standards cover equipment protection methods, zone classification, and explosion prevention.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) 29 CFR 1910.307: This regulation provides requirements for electrical installations in hazardous locations, including classification of hazardous areas, equipment selection and installation, and wiring methods.
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA) C22.1, Canadian Electrical Code: This standard provides requirements for electrical installations in hazardous locations in Canada, including classification of hazardous areas, selection, and installation of electrical equipment, and wiring methods.
- IECEx Scheme: This is an international certification scheme for equipment used in explosive atmospheres. The scheme provides a framework for conformity assessment of equipment and systems, including testing, certification, and ongoing surveillance.
- IP 15
- DEP 80.00.10.10
- ATEX – EU Directives
The hazardous area classification and location of equipment must be ascertained before the choice of appropriately certified electrical equipment is made.
Hazardous Area Classification FAQs
What is a hazardous area classification chart?
A hazardous area classification chart is a graphical representation of the classification of hazardous areas according to the types of hazardous materials present and their potential for ignition. The chart typically includes a legend that describes the various types of hazardous materials and the criteria used to classify them.
The hazardous area classification chart is used to identify and evaluate the risks associated with the presence of flammable or explosive materials in a particular area. The chart provides a visual reference for the classification of the area and the associated safety measures that must be implemented.
The chart typically includes several zones, which are defined by the probability of the presence of flammable materials and the duration of their presence. The zones are used to determine the type of equipment and safety measures that must be used in each area. For example, Zone 0 is an area where flammable materials are present continuously or for long periods of time, while Zone 2 is an area where flammable materials are present only intermittently or in small quantities.
The hazardous area classification chart is an important tool in the design, construction, and maintenance of facilities where flammable or explosive materials are present. It helps to ensure that appropriate safety measures are implemented to protect personnel and equipment from potential hazards.
What are the differences between NEC hazardous area classification and NFPA hazardous area classification?
The NEC (National Electric Code) and NFPA (National Fire Protection Association) are two organizations that provide guidelines for hazardous area classification. While there are some similarities between their guidelines, there are also some differences.
One key difference between the NEC and NFPA guidelines is their approach to classification. The NEC provides specific requirements for classifying hazardous locations based on the types of materials present, while the NFPA provides general guidelines for assessing the potential for ignition based on factors such as temperature, pressure, and ventilation.
Another difference is in the terminology used for hazardous area classification. The NEC uses Class, Division, and Group to describe hazardous areas, while the NFPA uses Class and Division. The definitions of these terms can also differ slightly between the two organizations.
In terms of the industries they serve, the NEC is primarily focused on electrical installations and equipment, while the NFPA covers a wider range of fire protection and safety issues.
Despite these differences, both the NEC and NFPA guidelines are widely recognized and used in hazardous area classification. It’s important to understand the specific requirements and terminology used by each organization when applying their guidelines to a particular situation.
What are the three classes of hazardous locations?
The three classes of hazardous locations are defined by the National Electric Code (NEC) in the United States. They are:
- Class I: Locations where flammable gases or vapors are present in the air in sufficient quantities to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures. Class I locations are further divided into Division 1 and Division 2, depending on the likelihood and duration of the presence of these materials.
- Class II: Locations where combustible dust is present in sufficient quantities to produce explosive or ignitable mixtures. Class II locations are also divided into Division 1 and Division 2.
- Class III: Locations where easily ignitable fibers or materials producing combustible flyings are handled, stored, or processed. Class III locations are not divided into divisions.
The classification of a hazardous location is important for determining the appropriate electrical equipment and wiring methods that can be used in that location. This helps to reduce the risk of ignition and explosion caused by electrical equipment.
References and Further Reading for Hazardous Area Classification Guide
- https://www.emerson.com/documents/automation/product-bulletin-hazardous-area-classifications-protections-en-123358.pdf
- https://www.hse.gov.uk/comah/sragtech/techmeasareaclas.htm
Few more useful resources for you…
What is Engineering Process Safety?
Safety Rules during A Field Visit By A Design Engineer
An article on Crane safety during Construction
HAZOP (Hazard and Operability) Study: A brief introduction
An article on Excavation Hazards at Construction Sites
Hazardous Area- Theory, Classification and Equipment selection: A short presentation
An article on THE HAZARDS OF PRESSURE TESTING









Thanks for Sharing, You can also add Diesel Flash point is >52 °C & Auto Ignition temp is 350-625.
Auto Ignition temp of Diesel is 350-625 Deg F (210 Deg C)
Thanks for sharing the great information on hazardous and risky atmospheres. Explosion-proof cameras can widely be used in a hazardous and risky atmosphere.
What is the procedure to study hazardous zone classification in Petroleum Storage area and Steel plan Coke Oven area, Is there any HZC software.
Subrata Kumar Bera
skbera123@gmail.com
How can I reach out to you