GRP Pipes or Glass Reinforced Plastics pipes are composite material pipes consisting of a polymer matrix that is reinforced with glass fibres. They have very high corrosion resistance ability and are thus used widely for low-temperature corrosion-resistant applications. In recent times, GRP pipes are slowly replacing steel in various services like fire and water services. At the same time, GRE or GRP pipes can withstand high pressures. In many places, the term FRP is used interchangeably for GRP pipes. In this article, we will explore an overview of GRP Pipes.
GRP Family
- GRP: Glass–fibre reinforced plastic.
- GRE: Glass–fibre-reinforced epoxy.
- GRV: Glass–fibre vinyl ester.
- GRUP: Glass – fibre reinforced unsaturated polyester.
The different types of pipes are selected according to the required properties like chemical resistance, temperature resistance, and mechanical properties.

Characteristics of GRP Pipe
- Corrosion resistance: Corrosion resistance to both inside and outside corrosion. As a result, additional linings and exterior coatings are not required.
- When the ratio of strength per unit of weight is considered, fiberglass composites surpass CS and SS.
- Lightweight: Fibreglass piping is only one-sixth the weight of steel products and 10% the weight of similar concrete products.
- Electrical properties: Standard fiberglass pipes are non-conductive. Some manufacturers offer conductive fiberglass piping systems for transporting fluids like Jet Fuel.
- Dimensional stability: Fibreglass material meets the most stringent material stiffness, dimensional tolerance, weight, and cost criteria.
- Low maintenance cost: Fibreglass piping is easy to maintain because it does not rust, is easily cleaned and requires minimal protection from the environment.
What are the advantages of GRP Pipes?
GRP Pipes provide various beneficial advantages as listed below:
- Long life; highly durable.
- Low maintenance cost.
- High Corrosion resistance.
- Low lifecycle cost.
- No need for cathodic protection.
- Less transportation and handling costs.
- Environmental friendly.
- Wide application range.
- Economic when compared with DSS pipe (Duplex stainless steel)
Types of Manufacturing of GRP Pipes
Different types of manufacturing methods are applied for GRP pipes like
- Filament winding.
- Centrifuge
- Continuous winding or Drostholm Method.
- Helical Filament winding (Fig.1)
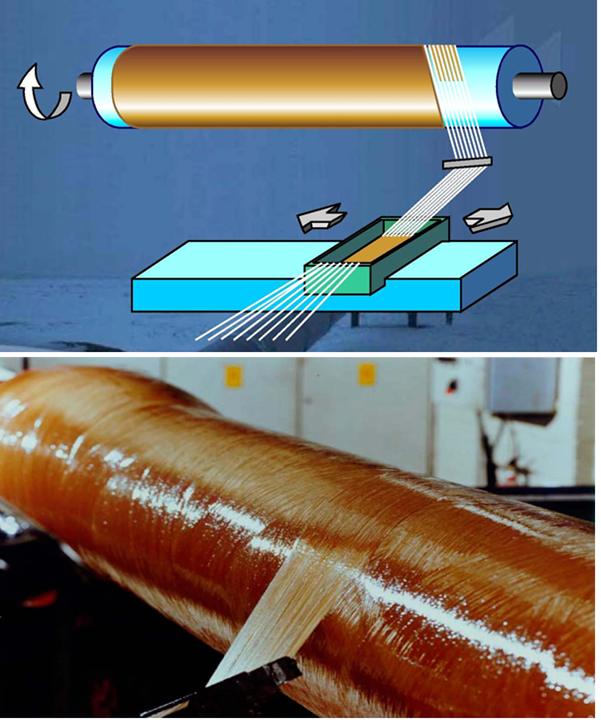
Materials used:
Polyester Resins – (Temperature limit is 70 deg C.)
- Isophthalic Polyester (Tg is 90 deg C)-Rarely used in chemical services but can be used in underground GRP gasoline storage tanks.
- Bisphenol A Polyester (Tg is 120 deg C)- High temperature, chemically resistant resin extensively used in chemical services.
- Chlorinated polyester (Tg is 110 deg C)-Properties same as Bisphenol A Polyester, but has inherent fire retardant characteristics. This property can be enhanced by the addition of antimony oxide particles to the resin mix.
Note: Tg is Glass transition temperature, shall be determined by either Differential Scanning Calorimetry according to ISO 11357 or Differential Thermal Mechanical Analyses according to ISO 6721.
Tg shall be greater than 30 deg C above the maximum design temperature.
- Vinyl ester resins – (Temperature limit is 100 deg C.)-Compared to polyester resins, vinyl ester resins have improved corrosion resistance and high-temperature resistance.
- Epoxy resins – (Temperature limit is 110 deg C.)- Epoxy resins have excellent resistance to a wide range of moderately strong acids and alkalis and most hydrocarbons. Aliphatic amines, Aromatic amines, and anhydrides are some examples of base epoxy resins.
Reinforcing materials:
- Reinforcing material shall be a suitable grade of glass fibre having a glass finish compatible with the resin system used.
- Glass-fibre materials typically used for GRP Pipes and vessels are E-Glass, C-Glass, ECR Glass, Synthetic etc.
Codes and Standards for GRP Pipes
The common codes and standards for GRP piping systems are
- BS EN ISO 14692: Petroleum and natural gas industries – Glass-reinforced plastics (GRP) piping.
- AWWA M45:Fibreglass Pipe Design.
- SHELL DEP 31.40.10.19:GRP Pipelines and Piping Systems (Supplements to ISO 14692)
- UKOOA: United Kingdom Offshore Operator Association.
GRP Pipes and Fittings
Refer to Fig. 2 which shows some typical GRP pipes and fittings.

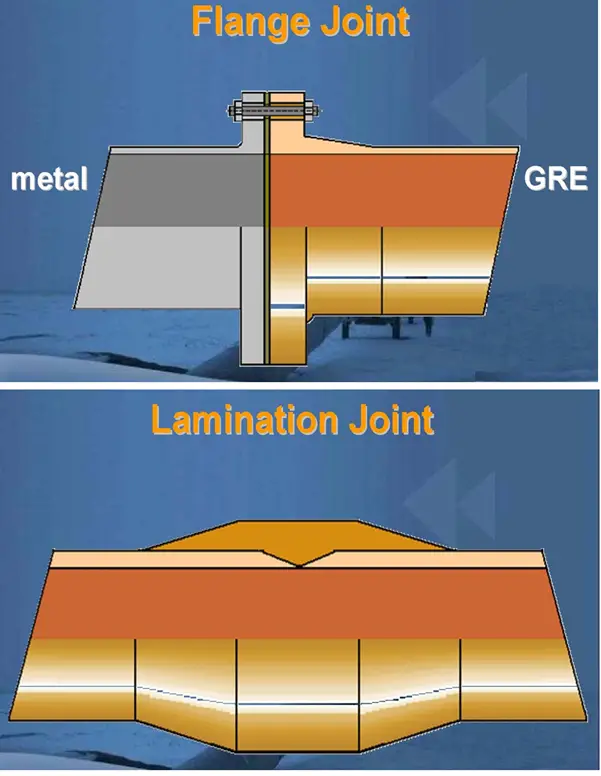
GRP Pipe Joining methods
- Adhesive Joint (Fig. 3)
- Flange Joint (Fig. 5)
- Lamination Joint (Fig. 5)
- Rubber Seal Lock Joint (Fig. 4)


Applications of GRP and GRE Pipes
GRP Pipes are widely used in the following plants:
- Chemical process.
- Desalination.
- Industrial effluents.
- Mining.
- Oil fields.
- Potable water.
- Power plant cooling and raw water.
- Seawater intake and outfalls.
- Metal Production
- Slurry piping.
- Water distribution.
- Pulp and Paper Mills.
- Sewerage & Drainage
- Transportation of oils, alcohols, fats, disposal, and solutions for food industries.
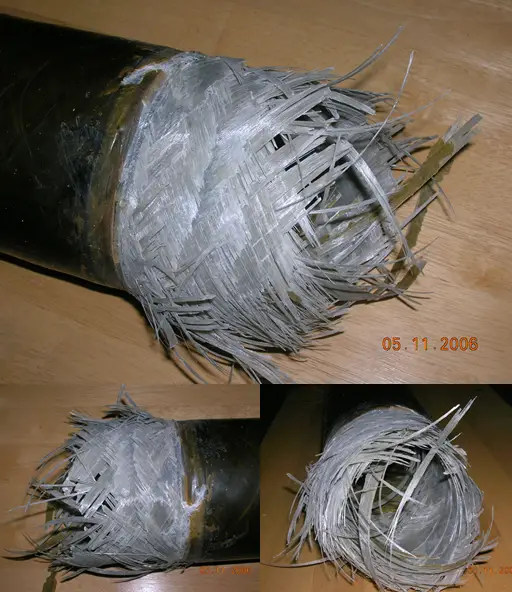
GRP Pipe Failures
Fig. 6 shows a typical failed GRP pipe.

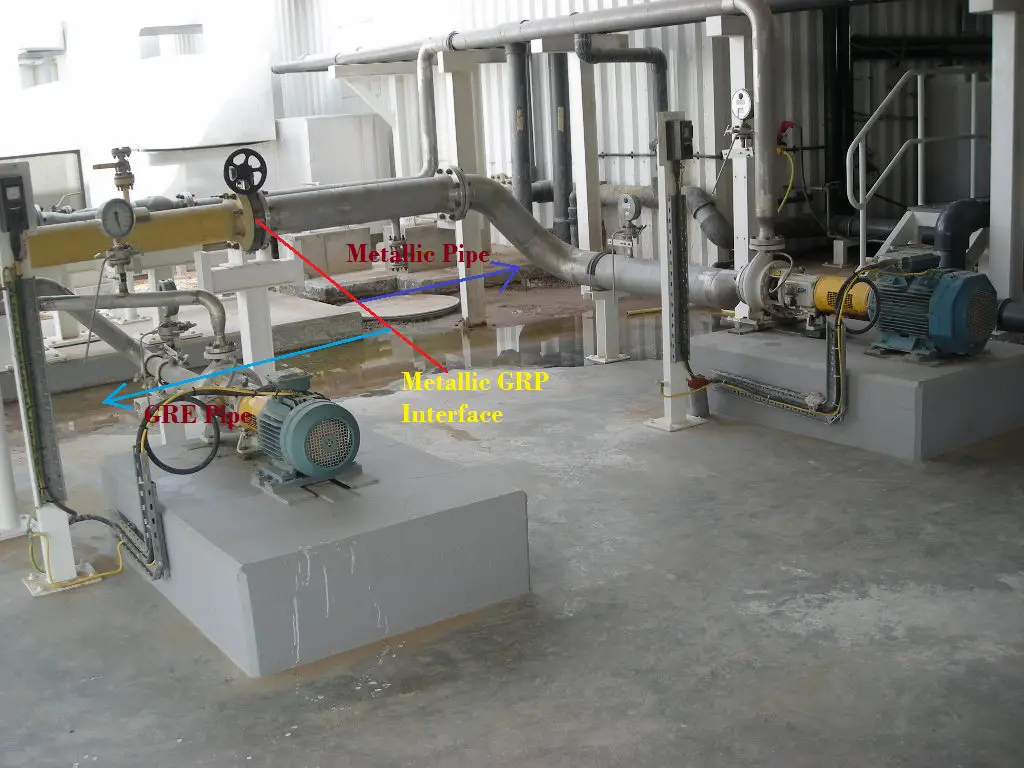
Metallic-GRP Piping interface
- In order to have reliable flange sealing, generally, steel ring elastomer gaskets are used.
- Gasket material should match with pressure, temperature, and chemical resistance requirements
- PTFE-envelope-type gaskets should be avoided for large sizes and high pressure.
- Refer to Fig. 7 which clearly shows the GRP-Metallic interface in a piping system.

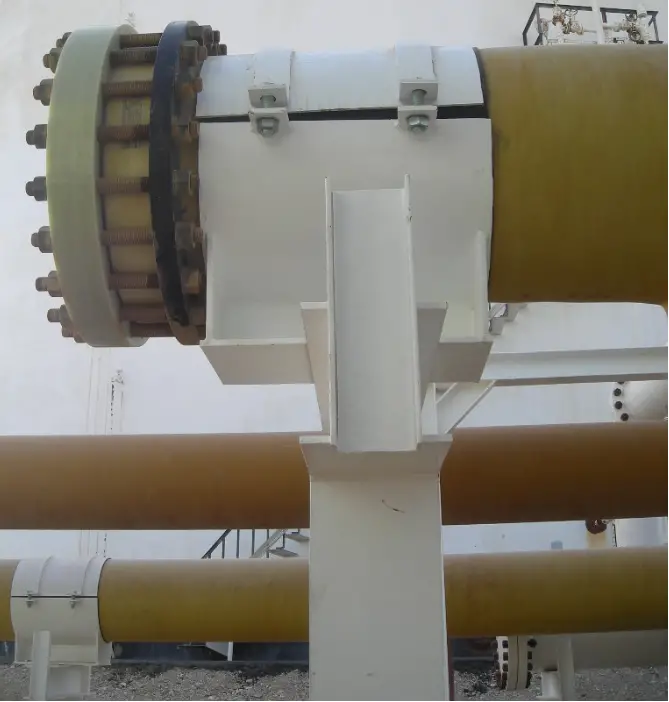
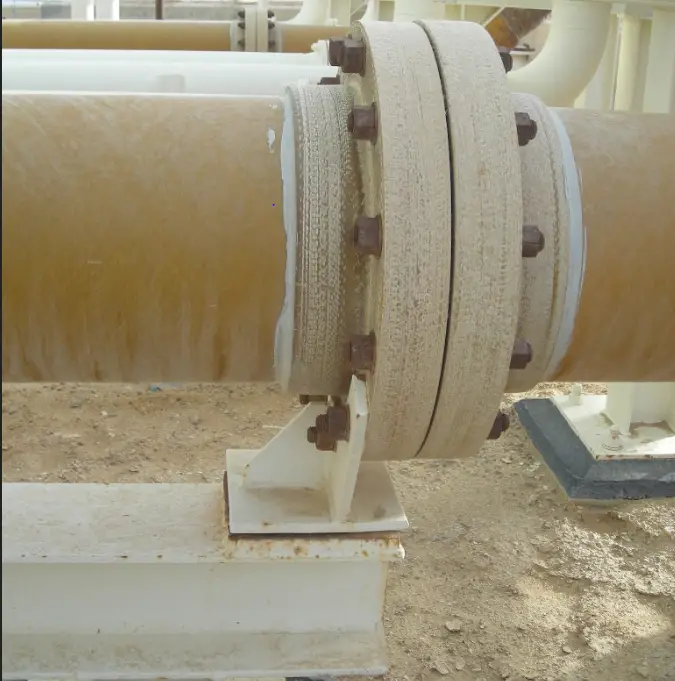
GRP/GRE pipe Supporting
Refer to Fig. 8 to Fig. 10 for typical GRP piping supports.

- Standard CS support may not match GRP as pipe’s Outer Diameter may be different.
- The use of Saddles & Elastomeric pads may allow the use of standard support.
- The support design should be as per the vendor catalog.
- GRE pipes are generally rested with clamp & shoe for all supports.
- Heavy in-line items like valves and strainers should be independently supported.
- Parasite support (pipe to pipe) is not allowed.
- Supports on fittings to be avoided.
- Excessive clamping forces can cause pipe crushing.
- GRP spans are much less than the CS spans, in absence of vendor data ISO 14692 can be used.
- Piping should be supported for shock loadings
- Special care is to be taken in a freezing environment.


Few more related articles to give you more insights into the subject.
An Article on HYDROSTATIC FIELD TEST of GRP / GRE lines
Stress Analysis of GRP / GRE / FRP piping system using Caesar II
Basic Principles for an aboveground GRP piping system
Buried GRP/FRP pipe Laying and Installation Procedure
Stress Analysis of GRP / GRE / FRP Piping using START-PROF
Stress Analysis of the GRP Piping System
In piping stress analysis guides or flexibility specifications, GRP/GRE composite lines are considered critical irrespective of their sizes. So, a formal stress analysis must be performed to investigate the stresses, loads, displacements, supports, etc. to decide if the GRP piping system will work smoothly throughout its design life. I have developed an online course explaining step-by-step procedures for GRP piping stress analysis. You can check it out here.








Great piece of advice. The way you have described in this article is simply awesome. Thanks for sharing!!!
Sir please guide on lamination joint,
Also the thickness of lamination joint.
How much will be its thickness ? How much will be its temperature at time of jointing etc.
Please also mention standard of iso or astm for lamination joint.
Thanking you in anticipation.
The lamination joint is purely depends on its handling pressure and area environment.
Chemical mixing depends only on the experience , there is no specific thumb rule for this.
Many companies recommending 1;100;1 ratio for the catalysators, resin and hardener.
If you need technical assistance please call 9462411003.
Thanks for the excellent info
what is the acceptable limits of vibrations on pumps discharge pipes from GRP
Sir tell me about installation, joint and advantage of grp pipes
The way of explanation was great! I Good points raised by you.
Keep sharing these types of articles.
Sir, I want to know about tubing and there end joint/ connection of semiconductor plant
The way you have described it in this article is simply awesome. Thanks for sharing!!!
Thanks for such a nice and useful post.
thank you for this info.
Interested I knowledge of GRP
DID THE LAMINATION JOINTS NEED A TRUST BLOCK OR NOT ??
what is the situation of studying grp pipes for gas transportation
Thanks