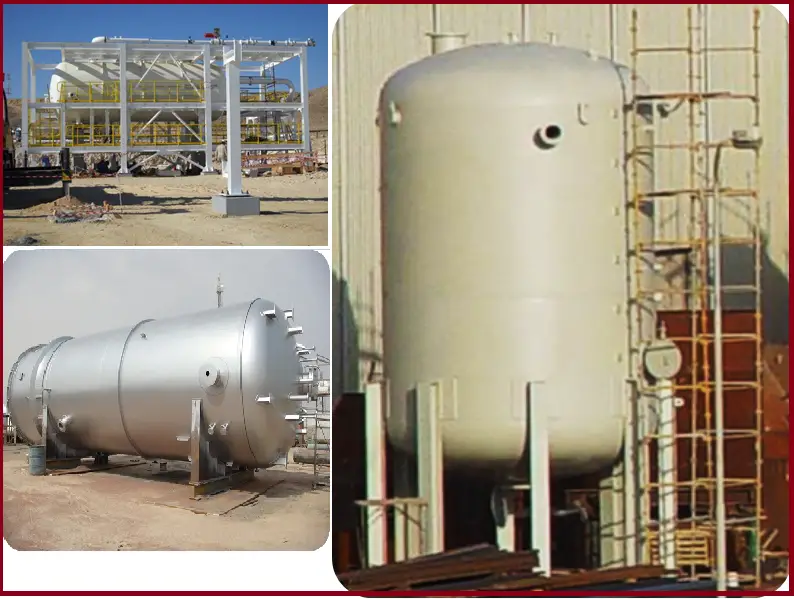
Pressure vessels serve as vital components in various industries, safeguarding gases and liquids under high pressure. The manufacturing process of these vessels is a careful blend of art and science, ensuring structural integrity, material compatibility, and adherence to safety standards. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of pressure vessel manufacturing, exploring the key steps involved and the critical considerations that go into producing these essential engineering marvels.
What is Pressure Vessel Manufacturing?
Pressure vessel manufacturing refers to the process of designing, fabricating, and constructing containers that are specifically designed to hold gases or liquids at pressures significantly different from ambient pressure. These vessels are crucial components in various industries, ranging from oil and gas, petrochemicals, power generation, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals to water treatment, food processing, and many others.
Stages of Pressure Vessel Manufacturing
There are various types of pressure vessels used in chemical, petrochemical, and power industries. The manufacturing steps for each type of pressure vessel usually differ significantly. The major steps that are followed while pressure vessels manufacturing are as follows:
Design and Engineering:
The manufacturing process of pressure vessels begins with meticulous design and engineering. Experienced engineers work closely with clients to understand their specific requirements, including operating conditions, material choices, pressure ratings, and applicable codes and standards (e.g., ASME BPVC, PED, or others). Computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools are employed to create detailed 3D models, facilitating thorough analysis and optimization of the vessel’s geometry and stress distribution.
Material Selection:
Selecting the appropriate material is crucial for the vessel’s performance and longevity. Engineers consider factors such as fluid properties, temperature, pressure, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness when choosing materials. Commonly used materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steels, aluminum, and various high-performance alloys.
Cutting and Forming:
Once the design is finalized, the pressure vessel fabrication process commences with cutting and forming the metal sheets or plates. Advanced cutting techniques like plasma cutting, laser cutting, or waterjet cutting are used to achieve precise shapes. The plates are then shaped and formed using rolling machines, presses, or hydraulic equipment to create the vessel’s desired configuration.
Welding and Joining:
Welding is a critical aspect of pressure vessel manufacturing. Skilled welders use various welding processes, such as submerged arc welding (SAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), to join the components together. The welds must be of high quality, meeting stringent non-destructive testing (NDT) requirements to ensure the vessel’s structural integrity.
Heat Treatment:
In certain cases, heat treatment is employed to improve the material properties and relieve residual stresses. Post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) is often used to reduce the risk of cracking and enhance the weld’s mechanical properties.
Machining and Finishing:
After welding and heat treatment, the pressure vessel undergoes machining to achieve precise dimensions and smooth surfaces. This step ensures that all openings, nozzles, and flanges are accurately aligned for proper installation and operation. Surface finishing and painting may also be applied to protect against corrosion and enhance aesthetics.
Inspection and Testing:
Comprehensive inspection and testing are fundamental to ensure the pressure vessel’s safety and compliance with standards. Radiographic testing (RT), ultrasonic testing (UT), dye penetrant testing (PT), and magnetic particle testing (MT) are some of the NDT methods used to detect defects. Pressure testing is conducted to evaluate the vessel’s integrity under high-pressure conditions.
Certification and Documentation:
Once the vessel successfully passes all inspections and tests, it is certified by authorized agencies, confirming its compliance with the applicable codes and standards. Detailed documentation, including material certificates, fabrication records, inspection reports, and test results, is prepared to maintain a traceable record of the vessel’s manufacturing process.
Pressure Vessels Manufacturers
There are a large number of companies that manufacture pressure vessels and have a solid reputation in the industry. They have supplied pressure vessels for various applications, including power plants, petrochemicals, refineries, and industrial processes. Some of the reputed pressure vessel manufacturers are:
- Babcock & Wilcox (B&W) – United States
- Doosan Heavy Industries & Construction – South Korea
- Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems (MHPS) – Japan
- Larsen & Toubro (L&T) – India
- Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) – India
- Samsung Heavy Industries – South Korea
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) – Japan
- IHI Corporation – Japan
- General Electric (GE) – United States
- Amec Foster Wheeler (now part of Wood Group) – United Kingdom
Video Tutorial of Pressure Vessel Manufacturing
The following video shows the steps of pressure vessel manufacturing in a very simple and handy way:
Conclusion
The manufacturing of pressure vessels is a complex and highly regulated process, demanding a blend of engineering expertise, skilled craftsmanship, and unwavering commitment to safety and quality. These vessels play a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth functioning of various industries, from chemical plants and refineries to power generation and aerospace. By adhering to stringent design, fabrication, and inspection practices, manufacturers produce pressure vessels that not only meet the demands of modern engineering but also ensure the safety and well-being of people and the environment.
Online Course on Pressure Vessels
If you wish to learn more about Pressure Vessels, their design, fabrication, installation, etc in depth, then the following online courses will surely help you: