In the oil and gas industry, a sunshade is a device that is used to protect workers, equipment, and instrumentation from direct sunlight and heat. Sunshades are commonly used in areas where there is a lot of direct sunlight, such as drilling sites, refineries, and production facilities.
Sunshades can come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they are typically designed to provide a shaded area that can be used for a variety of purposes. For example, sunshades can be used to provide shade for workers who are performing maintenance on equipment or to protect sensitive instrumentation from the heat and light of the sun.
In addition to providing shade, sunshades can also help to reduce the temperature in an area, which can make it more comfortable for workers and reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses. Sunshades can be made from a variety of materials, including metal, fabric, and plastic, and can be designed to be portable or permanent depending on the specific needs of the site.
Applications of Sunshades
Sunshades have several important applications in the oil and gas industry, including:
- Protecting workers: Sunshades provide a shaded area where workers can take breaks, perform maintenance tasks, or work on equipment without being exposed to direct sunlight and the associated heat and UV radiation. This can help to reduce the risk of heat exhaustion, sunburn, and other heat-related illnesses.
- Protecting equipment: Sunshades can be used to protect sensitive equipment, such as instrumentation and electronics, from direct sunlight and heat. This can help to prolong the life of the equipment and reduce the risk of equipment failure due to overheating.
- Improving safety: Sunshades can help to improve safety on oil and gas sites by reducing the risk of accidents and injuries caused by glare and reflections from the sun. Sunshades can also help to improve visibility by reducing the amount of sunlight that enters work areas.
- Enhancing productivity: By providing a shaded area where workers can take breaks or perform tasks, sunshades can help to improve productivity on oil and gas sites. Workers are less likely to become fatigued or suffer from heat-related illnesses, which can help to increase their efficiency and effectiveness.
- Reducing energy consumption: Sunshades can help to reduce energy consumption on oil and gas sites by reducing the amount of direct sunlight that enters buildings and work areas. This can help to reduce the need for air conditioning and other cooling systems, which can in turn reduce energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
Requirements of Sun Shade
- Any building structure used by the industry to store raw materials or for manufacturing products of the industry is known as an industrial building.
- Industrial buildings can be categorized as normal-type industrial buildings & special-type industrial buildings.
- Normal-type industrial buildings are shed-type buildings with simple roof structures on open frames.
- These buildings are used for workshops, warehouses, etc.
- Sunshades in the oil & gas industries are to be provided to cover the main equipment like compressors, turbines, and pumps, etc.
- These shades require large and clear areas unobstructed by the columns.
- The sunshades are constructed with adequate headroom for the use of an overhead traveling crane.
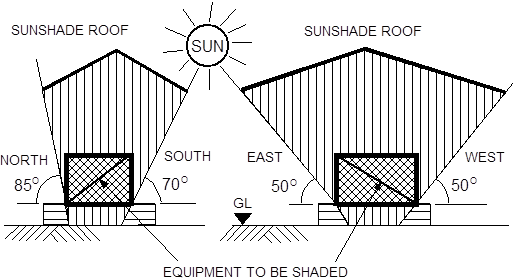
- As sun shades are specifically designed to protect equipment from solar radiation, their sizes are directly related to the angle of the sun during the most intense period of this solar radiation.
- Accordingly, the equipment that needs to be shaded shall be within the boundaries and angles shown in Fig. 1 below.
Types of Sunshades
Following are the different types of sunshades
- single side sloping roof
- double side sloping roof
- shed with roof truss
- shed with moment frames or open frames
- fully cladded shed
- partially cladded sunshade
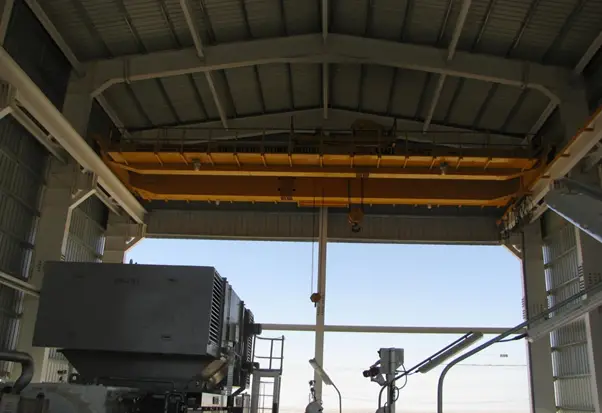
- shed with overhead electric operated traveling crane (EOT)
- shed with monorail
- prefabricated shed
Basic components of a Sunshade
Following are the main elements of sunshade
- foundation for shed columns
- base plate & anchor bolts
- column
- tie beams
- truss
- moment-resisting frames or portals
- purlins
- side runners
- sheeting
- vertical bracing system
- plan bracing system
- connection
Loads for Sunshade Design
Following are the main loads to be considered for sunshade design
- dead load
- live load
- crane loads
- wind load on the roof
- wind load on side walls & gable walls
- earthquake loads
- snow load on the roof
- sand accumulation on the roof
- heavy lighting fixture loads
Analysis of Sunshade
- Sunshade analysis can be done manually as well as with the help of software also.
- For manual analysis, anyone portal to be considered and loads will apply on 2d frames and different forces in columns, beams, and portal or truss members can be found out.
- In the recent period, different software is available for the analysis & design of 3d geometry
- Sunshade geometry can be easily modeled in STAAD
- After geometry finalization, different loads & load combinations are to be applied to the sunshade model in STAAD itself.
- After completing the load combination, run the analysis package in STAAD, and all forces and reactions will be generated.
Design of Sunshade
Different codes for designing structural steel shade
- British code: BS – 5950
- American code: AISC – allowable stress design (ASD); AISC – load resisting factor design (LRFD)
- Eurocode: 3
- DEP 34.00.01.30 : structural design & engineering
For performing sun shade design operations in STAAD following are the minimum parameter that shall be considered
- FYLD– YIELD STRENGTH OF STEEL
- BEAM– FOR DESIGN THE MEMBER AT EVERY 1/12TH SECTION LOCATION
- LY & LZ – LENGTH IN LOCAL Y & Z AXIS FOR SLENDERNESS CHECK
- MAIN– CHECKING OF SLENDERNESS RATIO.
- UNL / UNT / UNB – UNSUPPORTED LENGTH
- RATIO– PERMISSIBLE RATIO OF ACTUAL LOAD TO SECTION CAPACITY.
- TRACK– FOR PRINTING THE DESIGN OUTPUT
- DFF, DJ1 & DJ2– FOR PERFORMING DEFLECTION CHECKS.
- CHECK CODE – FOR PERFORMING DESIGN OPERATION AS PER SELECTED CODE.
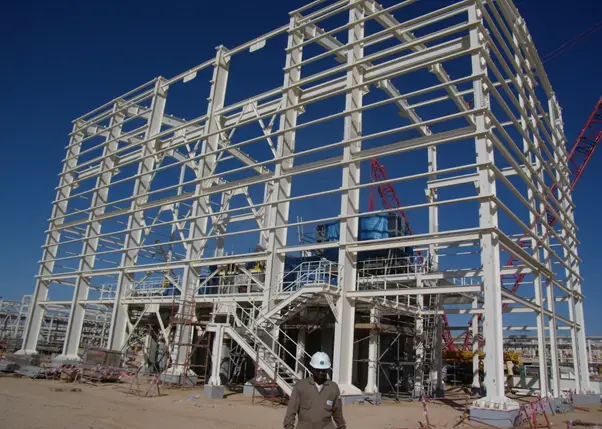
Sunshade Site Photos



Few more useful resources for you..
Structural Platforms: An In-Depth Guide
A Short Presentation on Pile Foundation and its Design
An article on Tank Pad Foundation
An Introduction to Braced Connections
A short article on “Sun Shade for oil and gas industry and their Design”
Considerations for Project Site Selection
