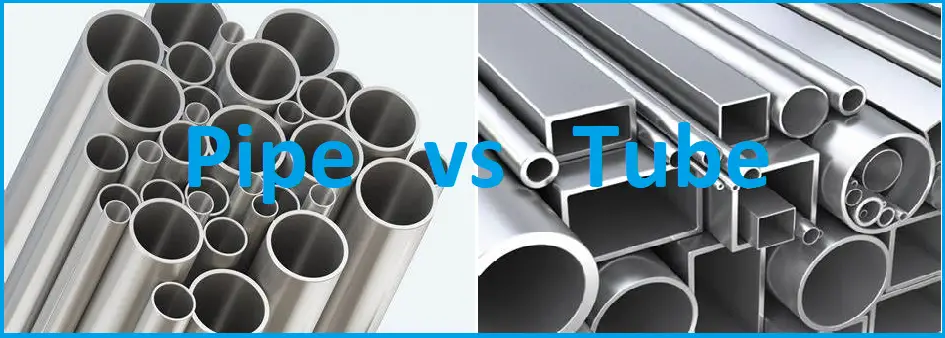
What is a Pipe?
Pipes are used for transporting fluids and gases in Chemical, Petrochemical, Power Plants, Refineries, Storage units, Compressed air systems, Plumbing systems, etc. They are circular in cross-section and specified by Nominal Pipe Size.
What is a Tube?
Tubes are used for mechanical applications (Heat Exchanger, Fired heater, Boiler, etc.), for instrumentation systems (used for measuring instruments); for structural applications, etc and could be rigid or flexible. They are specified by their outer diameter and tube wall thickness, in inches or in millimeters.
Differences between Pipe and Tube
From a layman’s viewpoint, Both Pipe and Tube seem to be the same as they have many similarities like both are hollow, usually made from metals, can transfer fluids, etc. Many a time, these terms are used interchangeably. But in actual practice Tubes and Pipes are not the same as both possess different features. Through this article, we will try to investigate all such characteristics based on a few parameters like Size, Shape, Diameter, Thickness, Use, Availability, End Connection, Design Standard, etc.
| Sr No | Parameter | Pipe Characteristics | Tube Characteristics |
| 1 | Shape | Pipes are always cylindrical or round in shape | Tubes are usually cylindrical in shape. However, tubes of different other shapes like square, rectangular, etc. are available. |
| 2 | Size | A pipe is Specified by Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) or Nominal Bore (NB). | The size of the Tubes is specified in millimeters or in inches by outside diameter. |
| 3 | Diameter | The outside diameter of pipe up to size 12” is numerically larger than the corresponding pipe size | The outside diameter of tubes is numerically equal to the corresponding size. |
| 4 | Thickness | Pipe Wall thickness is expressed in schedule numbers that can be converted into mm or inches. | Tube Wall thickness is expressed in millimeters, inches, or BWG (Birmingham wire gauge.) |
| 5 | Thickness Increment | Pipe thickness depends on the schedule, so there is no fixed increment | The thickness of tubes increases in standard increments such as 1 mm or 2 mm |
| Sr No | Parameter | Pipe Characteristics | Tube Characteristics |
| 6 | Application | Pipes are extensively used in all Process, Power & Utility lines to carry fluids. | Tubes are used in tracing lines, tubes for heat exchangers & fired heaters & instrument connections. They are more prevalent in the medical area, construction, structural, or load bearing. |
| 7 | Availability | Pipes are available as the small bore and the big bore | Normally small-bore tube is used in process piping. For structural use, tubes are available in custom sizes. |
| 8 | Structural Rigidity | Pipes are always rigid and resistant to bending | Tubes are available as rigid as well as flexible depending on the application. Rigid tubes are normally used in structural applications whereas copper and brass tubes can be flexible. |
| 9 | Joining and Stability | Joining pipes is more labor intensive as it requires flanges, welding, threading, etc. | Tubes can be joined quickly and easily with flaring, brazing, or couplings, but for this reason, they don’t offer the same stability |
| 10 | Tolerance | Pipe tolerances are not too restrictive. | Tolerances are very strict with tubes compared to pipes and tubes are often more expensive to produce than pipes |

| Sr No | Parameter | Pipe Characteristics | Tube Characteristics |
| 11 | Manufacturing | Pipe manufacturing is easier as compared to tubes | Tubes need more cumbersome tests, inspection, and quality control than pipes. |
| 12 | Cost | Cheaper | Costlier |
| 13 | Packing & Delivery | Delivered in the bundle as a bulk item. Delivery time is short. | Tubes are usually wrapped with a wooden box or thin film and delivered with much care. Delivery time is longer. |
| 14 | Production Quantity | Pipes are produced in mass quantity and for long-distance applications. | Tubes are produced in small quantities depending on requirements. |

| Sr No | Parameters | Pipe Characteristics | Tube Characteristics |
| 15 | End Connection | The end connection of pipes is normally plain or beveled for welding purposes | Tubes are available with coupling ends, irregular ends, special screw thread, etc. |
| 16 | Surface Finish | The inner and Outer surface of the pipe is rough in comparison to the tube | Tubes are manufactured on both the inner and outer surfaces as smooth |
| 17 | Common material | Common pipe material is Carbon Steel | The common tube material is Alloy Steel |
| 18 | Design Codes & Standards | The Thickness of the pipe is decided as per governing codes like ASME B31.3/ B31.1/ B31.4/ B31.8 or IBR Codes | The thickness of tubes is dependent on the use thickness is decided. |
I am sure there will be many more differences, so I request the readers to list out those in the comments section.
Few more useful resources for you.
Difference between Tee and Barred Tee
Comparison between Piping and Pipeline Engineering
Difference between Stub-in and Stub-on Piping Connection
Difference between Centrifugal and Reciprocating Compressor
Differences between Hot-dipped galvanization and Electro-galvanization
CAESAR II vs START-PROF Piping Stress Analysis Software Comparison
API vs ANSI Pump






Hi, very useful & detail difference has given between tube & pipe. It’s really helpful, which added few new point in knowledge.
Thanks
Dear Anup thanks, I am Noor ul Arefeen from Pakistan. Your above subject is very informative and you have tried to contain very big topic in short spain. I am running my own business in mechanical fabricaion. I will keep in touch with for further knowledge. Thanks once again.
I’m also a MECHANICAL ENGINEER From
INDIA…
HI ANUP SIR,
IAM ALSO A MECHANICAL ENGINEER GRADUATE AND WORKING AS PROCESS DESIGNER. AND I HAVE ALSO INTEREST TO BECOME A PIPING ENGINEER, CAN YOU PLEASE SUGGEST HOW I BECOME THE PIPING ENGINEER.
AND YOURS ARTICLES ALSO VERY USEFUL TO GAIN THE KNOWLEDGE ABOUT THIS FIELD THANK YOU VERY MUCH
Sir so many piping draftsmans are hired on temporary or contract basis. What is their future ?
Pipe has a circular cross-sectional view whereas a tube can be circular, triangular, rectangular, square, oval etc