In the world of plumbing and piping systems, efficiency, durability, and flexibility are crucial aspects that professionals and homeowners alike seek to achieve. When it comes to connecting four pipes together at right angles, there’s one fitting that stands out for its versatility and reliability: the cross fitting. In this article, we will delve into the world of cross fittings, exploring their uses, benefits, and why they are a preferred choice in a wide range of applications.
What are Cross Fittings?
A cross fitting is a plumbing or piping component designed to connect four pipes at 90-degree angles, forming a “cross” shape. These pipe fittings typically have one inlet and three outlets, allowing for the smooth and efficient flow of fluids or gases through the interconnected pipes. Cross fittings come in various sizes and materials, such as brass, copper, steel, and PVC, to cater to different system requirements and environmental conditions.
Materials for Cross Fittings
Cross fittings are available in various materials, each chosen based on their specific properties and suitability for different applications. The common materials used for cross fittings include:
- Brass: Brass cross fittings are popular due to their excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for both water and gas applications. They offer good durability and are often used in plumbing and industrial settings.
- Copper: Copper cross fittings are widely used in plumbing systems for their superior heat and electrical conductivity. They are commonly used for hot and cold water supply lines, as well as in HVAC systems.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel cross fittings are known for their exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. They are commonly used in harsh or corrosive environments, such as industrial settings, chemical processing, and marine applications.
- Steel: Carbon steel cross fittings are used in applications where high strength is required. They are commonly used in industrial and construction projects.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC cross fittings are widely used in residential and commercial plumbing systems because of their affordability, lightweight nature, and resistance to chemical corrosion. They are commonly used for cold-water applications.
- CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride): CPVC cross fittings are a variant of PVC and are designed to handle higher temperatures. They are commonly used in hot water supply lines and industrial applications.
- PEX (Cross-linked Polyethylene): PEX cross fittings are used in PEX piping systems for their flexibility and ease of installation. They are commonly used in residential plumbing and heating applications.
- Ductile Iron: Ductile iron cross fittings are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure applications and underground installations.
- Bronze: Bronze cross fittings offer good resistance to corrosion and are often used in marine and saltwater applications.
Versatility in Piping Systems
The main advantage of cross fittings lies in their versatility. They find applications in various industries, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Some common uses of cross fittings include:
- Plumbing Systems: Cross fittings are frequently employed in plumbing systems, especially in scenarios where multiple pipes need to intersect. Whether it’s a residential bathroom or a large commercial building, cross fittings offer a stable and reliable solution for distributing water supply or draining wastewater efficiently.
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): HVAC systems often require intricate piping networks to manage airflows and temperature control. Cross fittings facilitate the junction of multiple ducts and pipes, ensuring the smooth operation of the HVAC system.
- Fire Sprinkler Systems: In fire protection installations, cross fittings help in creating branch lines to connect sprinkler heads, ensuring adequate coverage and quick response during emergencies.
- Industrial Processes: Many manufacturing and processing facilities utilize cross fittings to create complex pipelines for transporting various fluids or chemicals in their production lines.
- Oil and Gas Industries: Cross fittings are also found in certain oil and gas applications. However, their use is normally limited for critical applications as the stress intensification increases and it becomes difficult to correctly calculate those values in pipe stress analysis. Pipe crosses are very important in molten sulfur application piping; they are used in place of piping elbows to take care of rodding when sulfur solidifies.
Benefits of Cross Fittings
Cross pipe fittings provide various benefits as listed below:
- Space-Efficient: Unlike other fittings that may require additional space to accommodate multiple connections, cross fittings create a compact intersection of pipes, optimizing the use of available space.
- Easy Installation: Cross fittings are designed for straightforward installation, reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of leaks when installed correctly.
- High Flow Capacity: Due to their smooth internal design and minimal pressure drop, cross fittings enable a high flow capacity, ensuring efficient fluid or gas transfer through the interconnected pipes.
- Durability: Cross-fittings made from high-quality materials, such as stainless steel or brass, offer exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for long-term use.
- Adaptable to Different Pipe Types: Cross fittings come in various materials and connection types, allowing them to adapt to different pipe materials like PVC, copper, PEX, or steel.
Types of Cross Fittings
Cross pipe fittings can be categorized depending on various parameters like end connection, outlet diameter, etc.
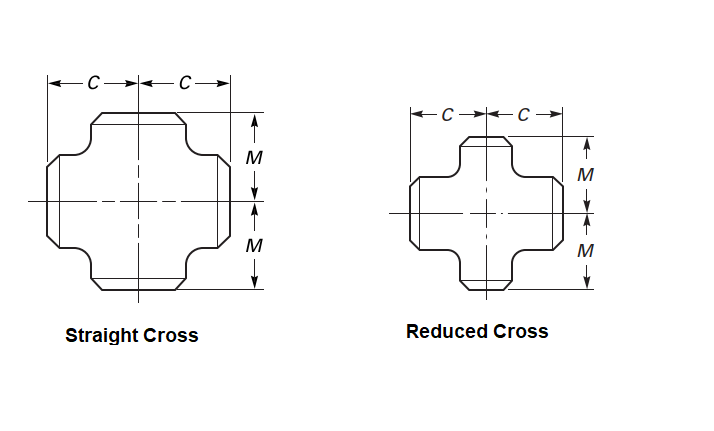
Based on outlet diameter, there are two types of cross fittings; Straight Cross and Reduced Cross Fittings. In the case of straight cross fitting the run diameter and outlet diameter are equal whereas for reduced cross fitting the outlet diameter is smaller than the run diameter.
Again depending on the end connection methods, the following types of piping cross fittings are available:
- Sweat or Solder Cross Fittings
- Threaded Cross Fittings
- Compression Cross Fittings
- Push-Fit or Quick Connect Cross Fittings
- Flanged Cross Fittings
- Grooved Cross Fittings
- Welded Cross Fittings
- Push-On Cross Fittings
Cross Pipe Fitting Dimensions
Industrial Cross Pipe fittings are designed based on ASME B16.9. The dimensions for Straight cross fittings and reduced cross fittings are provided in Table 1 and Table 2 below. The tables must be referred to in conjunction with Fig. 1 for understanding C and M dimensions.
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Outside Diameter at Bevel (mm) | Center to End Run, C (mm) | Center to End Outlet, M (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2 | 21.3 | 25 | 25 |
| 3/4 | 26.7 | 29 | 29 |
| 1 | 33.4 | 38 | 38 |
| 1 1/4 | 42.2 | 48 | 48 |
| 1 1/2 | 48.3 | 57 | 57 |
| 2 | 60.3 | 64 | 64 |
| 2 1/2 | 73.0 | 76 | 76 |
| 3 | 88.9 | 86 | 86 |
| 3 1/2 | 101.6 | 95 | 95 |
| 4 | 114.3 | 105 | 105 |
| 5 | 141.3 | 124 | 124 |
| 6 | 168.3 | 143 | 143 |
| 8 | 219.1 | 178 | 178 |
| 10 | 273.0 | 216 | 216 |
| 12 | 323.8 | 254 | 254 |
| 14 | 355.6 | 279 | 279 |
| 16 | 406.4 | 305 | 305 |
| 18 | 457.0 | 343 | 343 |
| 20 | 508.0 | 381 | 381 |
| 22 | 559.0 | 419 | 419 |
| 24 | 610.0 | 432 | 432 |
| 26 | 660.0 | 495 | 495 |
| 28 | 711.0 | 521 | 521 |
| 30 | 762.0 | 559 | 559 |
| 32 | 813.0 | 597 | 597 |
| 34 | 864.0 | 635 | 635 |
| 36 | 914.0 | 673 | 673 |
| 38 | 965.0 | 711 | 711 |
| 40 | 1016.0 | 749 | 749 |
| 42 | 1067.0 | 762 | 711 |
| 44 | 1118.0 | 813 | 762 |
| 46 | 1168.0 | 851 | 800 |
| 48 | 1219.0 | 889 | 838 |
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Outside Diameter at Bevel-Run (mm) | Outside Diameter at Bevel-Outlet (mm) | Center to End-Run, C (mm) | Center to End-Outlet, M (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 X 4 X 3-1/2 | 114.3 | 101.6 | 105 | 102 |
| 4 X 4 X 3 | 114.3 | 88.9 | 105 | 98 |
| 4 X 4 X 2-1/2 | 114.3 | 73.0 | 105 | 95 |
| 4 X 4 X 2 | 114.3 | 60.3 | 105 | 89 |
| 4 X 4 X 1-1/2 | 114.3 | 48.3 | 105 | 86 |
| 6 X 6 X 5 | 168.3 | 141.3 | 143 | 137 |
| 6 X 6 X 4 | 168.3 | 114.3 | 143 | 130 |
| 6 X 6 X 3-1/2 | 168.3 | 101.6 | 143 | 127 |
| 6 X 6 X 3 | 168.3 | 88.9 | 143 | 124 |
| 6 X 6 X 2-1/2 | 168.3 | 73.0 | 143 | 121 |
| 8 X 8 X 6 | 219.1 | 168.3 | 178 | 168 |
| 8 X 8 X 5 | 219.1 | 141.3 | 178 | 162 |
| 8 X 8 X 4 | 219.1 | 114.3 | 178 | 156 |
| 8 X 8 X 3-1/2 | 219.1 | 101.6 | 178 | 152 |
| 10 X 10 X 8 | 273.0 | 219.1 | 216 | 203 |
| 10 X 10 X 6 | 273.0 | 168.3 | 216 | 194 |
| 10 X 10 X 5 | 273.0 | 141.3 | 216 | 191 |
| 10 X 10 X 4 | 273.0 | 114.3 | 216 | 184 |
| 12 X 12 X 10 | 323.8 | 273.0 | 254 | 241 |
| 12 X 12 X 8 | 323.8 | 219.1 | 254 | 229 |
| 12 X 12 X 6 | 323.8 | 168.3 | 254 | 219 |
| 12 X 12 X 5 | 323.8 | 141.3 | 254 | 216 |
| 14 X 14 X 12 | 355.6 | 323.8 | 279 | 270 |
| 14 X 14 X 10 | 355.6 | 273.0 | 279 | 257 |
| 14 x 14 X 8 | 355.6 | 219.1 | 279 | 248 |
| 14 X 14 X 6 | 355.6 | 168.3 | 279 | 238 |
Considerations and Installation Tips
When working with cross fittings, there are a few considerations and installation tips to keep in mind:
- Material Selection: Choose the appropriate material based on the application and compatibility with the fluid or gas being transported.
- Proper Sizing: Ensure the cross fitting’s size matches the pipes’ diameter to prevent any flow restrictions or pressure issues.
- Secure Connections: Use appropriate methods, such as soldering, threading, or gluing, to ensure tight and leak-free connections.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically inspect the cross fittings and the entire piping system for any signs of damage or wear, and perform maintenance as needed to prolong their lifespan.
In conclusion, cross fittings are an essential component in the world of plumbing and piping systems. Their ability to facilitate efficient flow distribution, compact design, and versatility across various applications make them a go-to choice for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike. Whether it’s for residential plumbing, HVAC systems, or industrial processes, cross fittings play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of fluid and gas transport within piping networks.
Online Courses on Piping Design and Engineering
If you wish to dig deeper and learn more about elements of piping design and engineering then the below-mentioned online courses will help you to do so:
- Designing Piping Systems: Pipe Fittings Flanges Valves
- Piping Isometrics demystified through practical examples
- Flow of fluids through piping systems , valves and pumps
- The Complete Course on Piping Components for Oil&Gas Career
- Piping Design Engineering & Piping Isometrics Masterclass
- PG Diploma in Piping Design Engineering
- Click here for other relevant piping engineering courses