What is a Level Gauge or Level Indicator?
Level gauges or level indicators are instrument devices that are installed in plants for determining the liquid level in process equipment like drums, vessels, tanks, etc. The level gauge instrument or level instrument has several parts like a head, float, measuring tape, bottom anchored bracket, guide wires, elbows, anchors, coupling, pipe support brackets, and pipework. To suit the requirement of the industry, various types of level gauges (Fig. 1) are available.
Level gauges are widely used for a wide variety of applications requiring level monitoring. Some of the applications include:
- Industrial processes involve storing or filling liquid in containers.
- Process control systems for managing flow rates of various equipment.
Major industries that use level gauges are
- Chemical and Petrochemical
- Pharmaceutical
- Medical
- Manufacturing
- Food and Beverages
- Marine
- Fuel and Energy Management
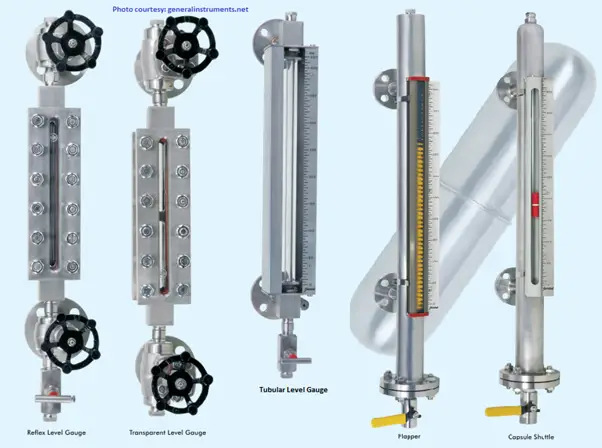
How many Types of Level Gauges are there?
Depending upon application and level measuring techniques, the following types of Level gauges are found:
- Transparent level gauge
- Reflex level gauges
- Magnetic level gauges
- Tubular level gauge
- Bi-color level gauge
Transparent Level Gauges
They are made of two transparent glass plates which are fitted with liquid cavities on both sides. By detecting the dissimilarity of transparent characteristics of the two media, Transparent Level gauges determine the fluid level. In some applications, an illuminator from which rays emit is used to make the liquid level easier to see. Such level indicators can be used for almost all installations.
Transparent Level Gauges are sometimes fitted with Mica shields for the purpose of protecting the glass surfaces from the corrosive action of the process fluid.
What is Reflex Type Level Gauge?
The reflex-type level gauge operates by detecting the dissimilarity in the refraction index between fluids and vapors. This type of level gauge works based on the refraction and reflection laws of light.
They are frequently used in vessels or containers. They are durable, can sustain high temperatures and pressure, and are normally made of carbon steel or stainless steel. In the gas or steam phase, the light is reflected by the prismatic grooves of the glass, which therefore gives a clear appearance. In the liquid phase, the light is absorbed, thus providing a dark indication of the level on the sight glass which is a transparent tube, clamped to the gauge body. Reflex Level gauges are frequently used as they have low initial cost, low operating cost, and easy level reading.
Magnetic Level Gauges
Magnetic level indicators are used to control the fluid level. Operating based on Archimedes’ Buoyancy Principle, such level gauges are highly durable and find their application in high-pressure temperatures and highly toxic, explosive, poisonous, or corrosive environments. These types of level instruments are able to detect the inter-phase level.
Magnetic level indicators consist of a float in a pipe chamber that moves up and down with the level. A flag follower is clamped with a chamber. The individual flags comprise an alignment magnet that couples with the float magnets as the float moves up or down within the piping column.
Float movement rotates the flags and changes their color, the position of the follower, or the point at which the flags change color, represents the true level.
Tubular Level Indicators
The tubular Level indicator is the simplest form of Level indication. Used in low-pressure, non-toxic services, Tubular level gauges detect and report the process fluid level through the direct reading of level in tanks or vessels. It consists of a Glass tube, Packing Material, end blocks, Vent plug, Drain valve, isolation valve, etc.
Bi-Color Level Gauges
Bi-color level gauges are basically transparent gauges having a liquid chamber in a wedge-shaped section. The illuminator on the backside of the device is fitted with two color filters; red and green. When red color light radiations hit the water, they get alerted to one side and absorbed. When the same light hits the steam, the light passes through and shows up as a red color. The reverse happens for light passing through green filters. This allows users to tell how much of each media is in the system.
These are specifically used to measure the media level in a boiler and detect levels by distinguishing the index of refraction between the steam and water. The gauge uses high-quality mica sheets to guard against the wet steam generated in a boiler drum.
Depending on the specific application liquid level gauges are usually termed drum level gauges, tank level gauges, oil level gauges, propane level gauges, fuel level instruments, water level gauges, etc.
Measuring Range of Level Indicators
The measuring range is the level range that the devices can measure and the range is determined by the maximum and minimum media levels. While choosing a level gauge, this parameter must be examined accounting for anticipated media-level fluctuations.
Parameters for Level Gauge Sizing and Selection
The main parameters that affect the level gauge selection and sizing are:
Properties of liquid: Predicting the Properties such as density (specific gravity), viscosity, conductivity, dielectric constant, etc are absolutely critical for the selection of instruments. These properties are responsible for the proper functioning and accuracy of the equipment.
Condition of the liquid: The liquid condition like foaming, frothing, Emulsion, sand, Wax, scaling, etc must be accurately specified to select the required accessories to reduce the effect on the Instrument.
Nature of the Liquid: The nature of liquids like corrosive, non-corrosive, and hazardous depends on their properties and uses to study the compatibility of the material of construction of the level measurement system.
Accurate prediction of vapor space: This is required since vapors can disrupt the functioning of sensors, build pressure, and in turn result in incorrect readings.
Operating conditions: Various operating parameters like temperature and pressure conditions to which the liquids are subjected must be specified. Level-measuring instruments have minimum and maximum limits for these parameters. Considering these limits help to select the Instrument which will withstand them.
Accurate Level Sketch: The accurate level sketch depicting various levels inside the equipment for determining the nozzle positions on the equipment.
Features of Level Gauges
Level indicators have the following characteristics:
- They are mechanical devices.
- They do not require a power source to operate.
- They provide a visual level indication.
Level Gauge Sizes
Level gauges are sized by the body length and the sight length. The body length of a level gauge is measured from the extreme top to the bottom of the gauge. Whereas the sight length represents the available viewable window length. The minimum and maximum level readings that can be obtained from a given size gauge are dependent on the sight length of the level instruments.
How to Order a Level Indicator?
While selecting and placing an order the following points need to be mentioned:
- Process conditions with Temperature range, Maximum operating pressure, Fluid Density
- Center-to-center distance
- End connections (flanged or screwed)
- Device Medium
- Mounting Options and
- Application of the instrument
Few more Resources for you..
What is FMS or Flow Metering Skid?
Types of Flowmeters and their Applications
Overview of Piping – Instrument Interface: An article
An article on Temperature Measurement by Filled Thermal Systems
An article on Conductivity Analyzers
The safe way to install restriction orifices
Other Oil and Gas Instrumentation related Articles

Excelente publicación de indicadores de nivel para los diseñadores de tuberías.
Yo ya he leído varios artículos tuyos acerca de tuberías, muy buenos.
Felicidades y gracias por tu aportación.
Please explain more the level guages
What is the minimum distance kept for level gauge from bottom of tank to bottom of the gauge
TIA: Enquiry – Level indicator/Level gauge for 10.5m height Water tank 600KL capacity.
Hi
I have a question
For what pressure & temperature has been Reflex level gauge designed?
If possible give me a value