In the engineering world, piping engineers play a vital role in the design, construction, and maintenance of piping systems. Whether in oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, or power generation, these professionals ensure that fluids and gases are transported safely and efficiently.
1. What is a Piping Engineer?
A piping engineer is responsible for the design, analysis, and maintenance of piping systems that transport various substances, including liquids, gases, and slurries. Their work is critical in industries like oil and gas, petrochemicals, water treatment, and power generation, where the integrity and efficiency of piping systems directly impact safety, productivity, and environmental compliance.
2. Piping Engineer Types
Piping Engineer is one of the famous engineering groups in the Oil & Gas, Petrochemical, Refinery, Chemical, Power, Steel, Water, and Pharmaceutical sectors. They are responsible for designing the piping systems that carry water, steam, gas, oil, two-phase mixture, waste, or other fluid. They are involved in the design, erection, troubleshooting, and all other aspects of the creation of these piping systems. Depending on the job profile they perform, there are various types of piping engineers. Let’s start to explore Piping Engineer types through this article.
Broadly, Piping Engineers can be grouped into the following classes:
- Piping Design Engineer or Piping Layout Engineer
- Piping Materials Engineer
- Piping Stress Engineer
- Piping Field Engineer/ Piping Commissioning Engineer
2.1 What is a Piping Design or Layout Engineer?
Piping Design Engineers deal with the piping routing design of the entire plant. They utilize various design software such as SP3D, PDMS, CADWORX, SOLIDWORKS, AutoCAD, PDS, Microstation, E3D, etc. They use their knowledge to define the most suitable economic pipe routing, type of fittings, space requirement, and various parameters in the design. A major part of their job involves coordination with other departments and the resolution of conflicts as and when they occur.

2.1.1 Roles of a Piping Design Engineer
In addition to the above, they are responsible for the following jobs:
- Preparing Work Instruction for Designers.
- Discussing and Analyzing problems that arise during Design.
- Preparing Piping MTO
- Providing technical support to the team.
- Planning and Scheduling work activities for the piping team.
- Reviewing Vendor drawings, Interdisciplinary item checking.
- Click here to know more about the major qualities that are required to be a good piping design engineer.
2.2 What is a Piping Material Engineer?
A Piping Material Engineer prepares project piping class and material specifications. They prepare MTO, and review valves and special items. Click here to know the complete roles and responsibilities of a Piping Material Engineer.
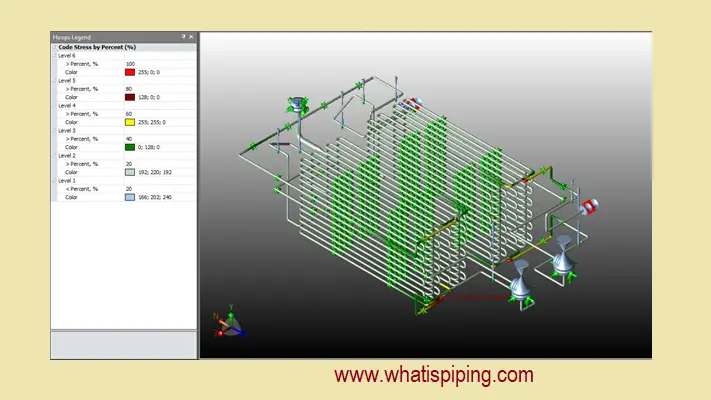
2.3 What is a Piping Stress Engineer?
A piping Stress Engineer is a Piping professional who provides technical expertise in piping design. They develop Static and Dynamic piping models and analyze system stresses using pipe stress analysis software like Caesar II, CAEPIPE, AUTOPIPE, & PASS/START-PROF, Rohr-2, etc. He is the final barrier to whether the piping design is good to proceed with fabrication/construction or not. He verifies the piping layout and supports and ensures sufficient flexibility of the piping system. Click here to know the complete roles and responsibilities of a Piping Stress Engineer.
2.4 Field Piping Engineer / Piping Commissioning Engineer
There are also piping engineers who specialize in field jobs. Their task is to ensure all the piping that has been installed is based on the design. They will solve any problems on-site and communicate to the design engineering department in case there are any changes required. They will work from the installation of the piping until the commissioning. Sometimes, the piping design engineers are deputed to the site to perform the field piping engineering job.
In Subsea structures or small-scale projects, all the above tasks (all jobs of design engineer, materials engineer, stress engineer, and field engineer) are done by a single piping engineer.
3. Is Piping Engineering a Good Career?
Yes, piping engineering can be a great career choice for those interested in a stable and rewarding profession. With strong demand across industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation, piping engineers enjoy competitive salaries and ample opportunities for advancement. The role also allows for a variety of work environments, from design offices to on-site project management, and offers the chance to make a significant impact on safety and environmental compliance.
Piping engineering was one of the best career options earlier. However, from the last few years (2014 to 2020), due to lower crude oil prices, the Corona effect, and the advancement of electric vehicles, the oil market suffered a huge loss. So the number of new piping projects was declined, which reduced the requirement for qualified piping engineers. However, from early 2021 onwards, the crude oil price increased and now stabilized at higher prices, which created a good demand for piping engineers in various sectors. The demand for piping engineers in the oil and gas industry is believed to be increasing throughout recent times.
At the same time, many piping engineering institutions around the world are producing a large number of piping engineers each year. So competition is increasing each day which directly impacted the Piping Engineer’s Salary and remuneration.
Also, in recent times, there has been a sudden surge of many experienced freelancers. So many companies are providing jobs to them without the need for preparing the required infrastructure to build a design team.
4. Skills Required for a Piping Engineer
As Piping Engineering is almost 95 % technical job, to become a successful piping engineer, one needs to have good imagination, knowledge, and willingness to learn. The following skills are required for a good piping engineer:
- Observational Skills
- Analytical Skills
- Project Management Skills
- Written and Verbal Communication Skills
- Drafting Skills
Normally, Mechanical and Chemical Engineers opt for the piping engineering profession.
4.1 What is the basic knowledge required for a piping engineer?
A piping engineer should have a solid understanding of fluid mechanics to analyze the behavior of fluids within piping systems. Familiarity with industry codes and standards, such as ASME and API, is essential for ensuring compliance in design and installation. Knowledge of material properties, including metals and polymers, is crucial for selecting appropriate piping materials. Additionally, skills in stress analysis are necessary to assess how piping systems will withstand operational loads. Proficiency in design software like AutoCAD, E3D, SP3D, and CAESAR II is important for creating accurate models, while an understanding of thermodynamics helps in managing temperature variations. Strong communication skills are also vital for collaborating with multidisciplinary teams, along with basic project management and troubleshooting abilities to effectively oversee and resolve issues within piping systems.
5. Piping Engineer Jobs
There are various companies that offer jobs for piping engineers. Some of the most reputed companies are:
- Aramco
- Adnoc
- PDO
- OQ
- Occidental
- Bechtel
- Chiyoda Corporation
- Fluor
- Worley
- Larsen and Toubro
- Toyo
- Petrofac
- Technip
- Samsung Engineering
- G S Engineering
- Technimont
- Mcdermott
- Udhe
- Wood Group
- Aker Solutions
- Burns & Mcdonnell
- Toshiba
- Siemens
- Alstom
- Punj Lloyd
- Jacobs
- Bilfinger
- Enter Engineering
- Lisega
- Click here to get a list of comprehensive piping engineering companies that provide jobs to piping engineers in India.
- Top EPC companies of UAE (Abu Dhabi, Dubai, and Sharjah) to try for employment opportunities
6. Industry Applications of Piping Engineers
Piping engineers are employed in a variety of industries, each presenting unique challenges and requirements.
6.1 Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas sector, piping engineers design systems for transporting crude oil, natural gas, and refined products. This includes offshore platforms, refineries, and gas processing plants. They must account for high pressures, extreme temperatures, and potentially corrosive environments.
6.2 Chemical and Petro-chemical Processing
Piping systems in chemical plants transport a wide range of hazardous and non-hazardous materials. Piping engineers in this field focus on safety, regulatory compliance, and process optimization, often employing advanced materials and corrosion-resistant coatings.
6.3 Power Generation
In power plants, piping systems transport steam, water, and gases critical for energy production. Piping engineers must ensure that systems are designed for maximum efficiency while maintaining safety and environmental standards.
6.4 Water Treatment
Piping engineers in the water treatment industry design systems for the transportation and treatment of drinking water and wastewater. This role often involves working with environmental regulations and ensuring that systems are sustainable and efficient.
6.5 Other Industries
The above-mentioned industries are the core industries for piping engineers. Additionally, the following industries recruit piping engineers at various levels:
- Mineral Industry
- Mining Industry
- Offshore Industry
- Steel Industry
- Food Processing Industry
- Pharmaceutical Industry, etc
7. How Much Does A Piping Engineer Make?
The salary of a piping engineer can vary significantly based on factors such as experience, location, and the specific industry they work in. On average, piping engineers in the United States can expect to earn between $70,000 and $120,000 annually, with entry-level positions starting around $60,000. Experienced engineers, especially those in managerial or specialized roles, can make upwards of $150,000 or more.
In addition to base salaries, many piping engineers receive benefits such as bonuses, health insurance, and retirement plans, which can enhance overall compensation. Regions with a high demand for engineering talent, such as areas with active oil and gas sectors, often offer higher salaries to attract skilled professionals.
7.1 Salary of a Piping Engineer in India
The salary of a piping engineer in India can vary widely based on factors such as experience, location, and the specific industry. Generally, here’s a rough breakdown:
- Entry-Level (0-2 years): ₹3,00,000 to ₹5,00,000 per year
- Mid-Level (3-7 years): ₹5,00,000 to ₹10,00,000 per year
- Senior-Level (8+ years): ₹10,00,000 to ₹20,00,000 or more per year, especially in managerial roles or specialized positions.
In metropolitan areas and sectors like oil and gas or chemicals, salaries may be on the higher end of these ranges. Additionally, benefits and bonuses can further enhance overall compensation.
8. Differences between Piping Engineer and Design Engineer
A piping engineer focuses on planning and designing piping systems within various structures, ensuring compliance with safety and efficiency standards. They work closely with other professionals to tackle technical challenges and ensure the systems function properly.
On the other hand, a design engineer has a wider scope, managing the overall design of project elements beyond just piping. They are tasked with conceptualizing and detailing components, systems, or structures, taking into account functionality, aesthetics, and safety considerations.
While both positions involve engineering principles and design processes, they cater to different facets of projects. Their major differences are listed below:
| Aspect | Piping Engineer | Design Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design and maintenance of piping systems for fluid transport | General design of products or systems across various domains |
| Industry Application | Primarily in oil and gas, chemical, and power generation | Broad applications including consumer products, machinery, and electronics |
| Key Responsibilities | Piping layout, material selection, stress analysis | Conceptualization, prototyping, and overall system design |
| Software Tools | CAESAR II, PDMS, AutoCAD | SolidWorks, AutoCAD, CATIA, or other design software |
| Code Compliance | Ensures adherence to piping codes (e.g., ASME, API) | Ensures design meets industry standards and regulations |
| Collaboration | Works closely with process and mechanical engineers | Collaborates with various engineering disciplines as needed |
| Problem-Solving Focus | Resolving issues related to fluid dynamics and pressure | Addressing design challenges related to functionality and aesthetics |
This table highlights the key distinctions, illustrating how each role contributes uniquely to the engineering landscape.
9. Piping Engineer Certification
Piping engineer certification is a credential that validates a professional’s expertise and knowledge in the field of piping design and engineering. These certifications demonstrate proficiency in industry standards, best practices, and technical skills essential for effective piping system design and maintenance. Obtaining certification in piping engineering can be a valuable investment in one’s career, demonstrating commitment to the profession and enhancing professional standing.
Here are some recommended piping engineering certification courses that can help enhance your skills and credentials:
- Certified Piping Designer by Piping Designers and Engineers Associations
- ASME B31.3 Process Piping Certification by ASME.
- API 570 Piping Inspection Certification by API.
- CAD Software Training (e.g., AutoCAD, CAESAR II, AutoPipe, E3D, SP3D, Rohr II, etc) by various training providers
- Piping Engineering and Designing Courses by SPED.
10. What is a Piping Engineer: Video Tutorial
The role of a piping engineer is crucial in various industries, ensuring the safe and efficient transport of fluids and gases. With a combination of technical skills, industry knowledge, and innovative thinking, piping engineers face unique challenges and opportunities.
This comprehensive understanding of the piping engineer’s role highlights not just their technical expertise, but also their contribution to the safety and sustainability of modern infrastructure. Whether you are a student considering this career path or an experienced engineer looking to broaden your horizons, the world of piping engineering offers a wealth of opportunities and challenges that are essential for our increasingly interconnected world.

Second class boiler operation
Is there any profesion certification for piping designer in Indonesia??
How can I embark a career in piping engineering ?
Am available for any company to employ me as apprentice.
Excellent post– You amaze me. Thank you for sharing. Your content was both useful and fantastic. We’ve learn a lot from this.