What is Piping Strainer?
Piping Strainers (or filters) arrest debris such as scale, rust, jointing compound, and weld metal in pipelines, protecting equipment and processes. A strainer is a device that provides a means of mechanically removing solids from a flowing fluid or gas in a pipeline by utilizing a perforated or mesh straining element. Pipe Strainers are very important components in piping systems to protect costly equipment from potential damage caused by foreign particles carried by the process fluid. Piping Strainers are also known as Strainer Filters.
The following figure shows various types of pipe strainers normally used in Pump or Compressor Suction lines in the process piping industry.

Application of Piping Strainers
To ensure against the untimely shutdown of equipment, strainers should be installed ahead of pumps, loading valves, control valves, meters, steam traps, turbines, compressors, solenoid valves, nozzles, pressure regulators, burners, unit heaters, and other sensitive equipment. The most common range of strainer particle retention is 1 inch to 40 microns (0.00156 inches ).
Strainers in Sensitive Static Equipment
Even though static equipment is normally not considered as that sensitive, still sometimes strainers are installed near the following equipment.
- Heat exchanger
- Meters
- Steam trap
- Spray nozzles
Strainers in Sensitive Dynamic Equipment
For the following sensitive and vibration-prone equipment use of a strainer is a must.
- Pumps
- Compressors
- Turbines
Types of Piping Strainers/Strainer Types
Depending on the use, two types of strainers are found in industries.
- Permanent Strainers and
- Temporary Strainers
Permanent Pipe Strainers
These strainers will be installed permanently in the piping system. Examples of permanent strainers are
- Y type strainers(Fig. 2)
- Basket Type strainers( Simplex & Duplex construction) (Fig. 3) and
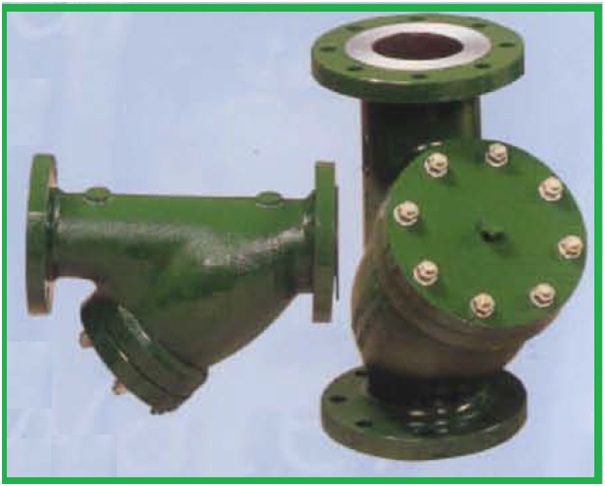
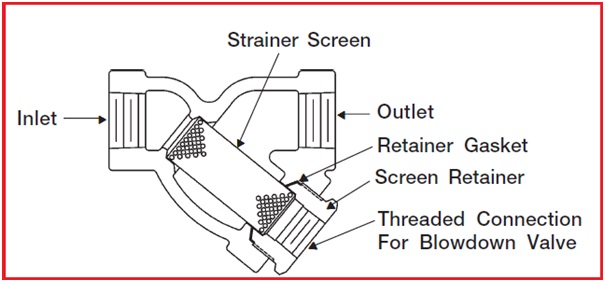
Y-Type Strainers
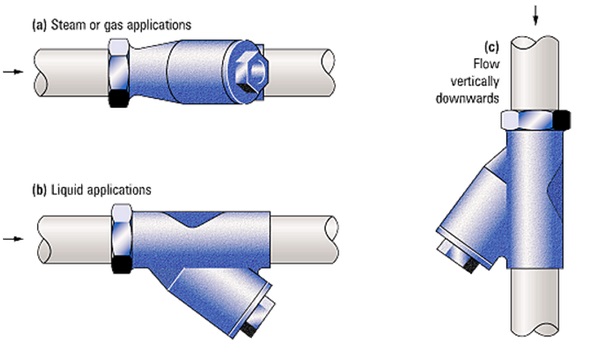
This type of strainer got its name from the shape as it resembles the alphabet “Y”. They are low-cost strainers and are used in pressurized lines with low debris or foreign particle concentration. They can be installed in horizontal or vertical lines keeping the filtering element towards the ground. As the retaining capacity of Y-Strainers (Fig. 2) are normally small, they must be cleaned frequently.
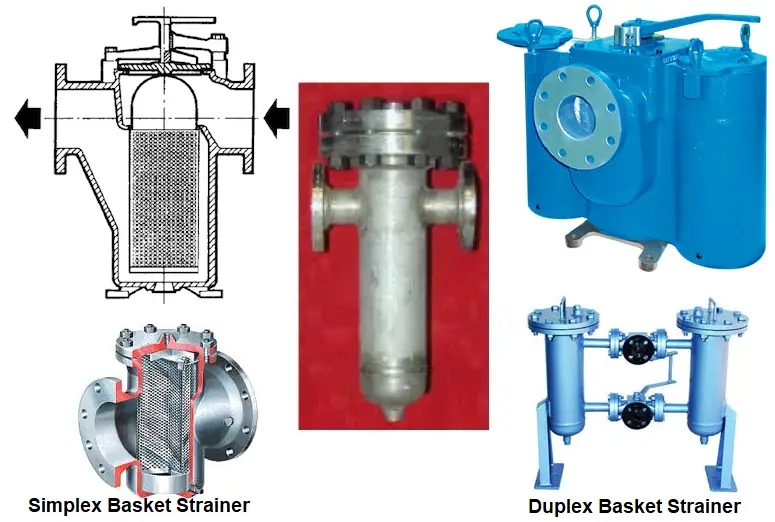
Basket Strainer / Bucket Strainers
Basket Strainers or Bucket Strainers are closed vessels with a filter screen inside them. They have a high capacity to retain foreign particles and are hence widely used. Basket strainers (Fig. 3) are used only in horizontal lines; mostly for liquid services with high flow capacity. Bucket strainers can be independently supported like equipment in case their weight is more, or they can be supported inline from pipe supports. As they resemble the alphabet “T” of the English language, they are often termed as T-Strainers.
Basket Strainers are of three types
- Simplex Style Basket Strainer (Fig. 3) and
- Duplex Style Basket Strainer (Consists of two parallel basket filters with by-pass Valves as shown in Fig. 3)
- Automatic Strainers
Basket filters can be easily cleaned by opening the top cover. Duplex Basket strainers are cleaned online when the pipeline is in operation simply by diverting the flow to the other filter.
Automatic strainers have self-cleaning baskets that are controlled by using pressure drop settings or times; Hence, the cleaning operation is never interrupted.
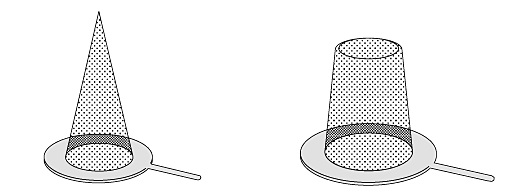
Temporary Pipe Strainers
Temporary strainers are used for a small period of time. Examples of temporary strainers are
- Cone-type strainer and
- Truncated Cone type strainer
Refer to Fig. 4 which shows typical cone and truncated cone-type temporary strainers.
Design standards for Piping Strainers
Strainers or filters are normally designed following the below-mentioned International Standards:
- ANSI B 16.34
- PED 97/23/EC: Pressure equipment design
- BPVC: ASME Boiler & Pressure vessel code, Section-VIII Div.1
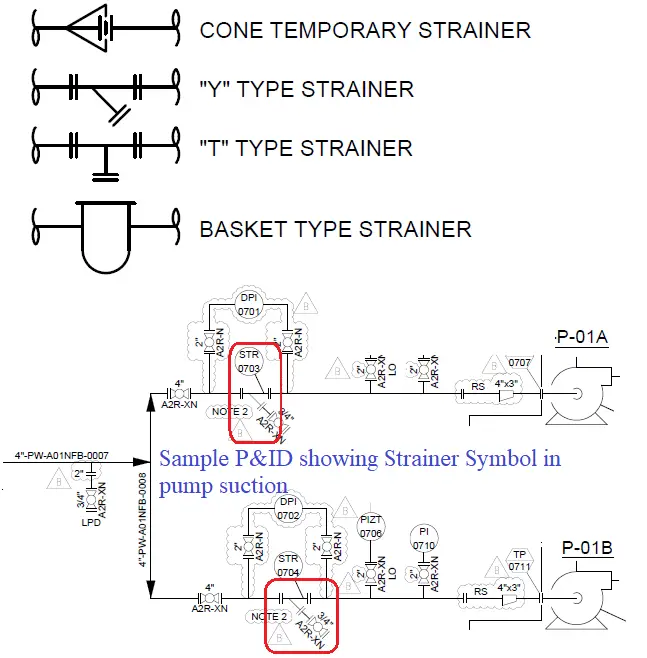
Pipe Strainer Symbol
Depending on the pipe strainer type, symbols for pipe strainers are also different. Common pipe strainer symbols are shown below in Fig. 5.
Materials of Construction of Piping Strainers
Strainer Body
The body of the strainer can be made from
- Forging
- Casting( but flanges shall be an integral part of the body) or
- Fabrication
Common materials used for the strainer body are iron, steel, stainless steel, bronze, chrome molly, and plastics.
Piping Strainer Internals
Strainers internal must be corrosion resistant and they have to be in contact with dirt or debris continuously. Common materials used are
- Stainless steel
- Special care shall be taken for Produced water service
- copper and aluminum

End connections of Piping Strainers
Strainers are connected to piping by the following end connection types
- Flanged
- Socket Welded or Threaded
Screens or Filters for Piping Strainers
Two types of screens used in strainers :
- Perforated screens
- Mesh screens
Perforated screens
Perforated screens or strainers are formed by punching a large number of holes in a flat sheet of the required material using multiple punches. These are relatively coarse screens and hole sizes typically range from 0.8 mm to 3.2 mm
Mesh screens
Fine wire is formed into a grid or mesh arrangement. This is then commonly layered over a perforated screen, which acts as a support cage for the mesh.
- Mesh Screen terminology: e.g. 3 mesh screen
- We shall always ask the process to give Maximum allowable pressure drop at % clogged condition.
- Mesh screens are usually specified in terms of ‘mesh’; which represents the number of openings per linear inch of screen, measured from the center line of the wire.
- Mesh is not the only thing to be asked for but hole size is also important.
- The corresponding hole size in the mesh screen is determined from knowledge of the wire diameter and the mesh size
Selecting Mesh Size for Piping Strainers:
While selecting the proper mesh size the following factors must be considered.
- the maximum particle size that the downstream equipment can handle safely.
- the working temperature and pressure ranges.
- the maximum allowed pressure drop.
- the fluid service or nature of the conveyed fluid.
Strainer options
Nowadays various strainer options are available to the user like
- Magnetic inserts
- Self-cleaning strainers
- Mechanical-type self-cleaning strainers
- Backwashing type strainers
- Temporary strainers
Y type Pipe strainer on various fluid
Selection of Pipe Strainers
The success of a specific type of pipe strainer solely depends on the proper selection of the piping strainer. The main parameters that affect the piping strainer selection process are:
- Flow Rate: A flow rate in excess of 150 GPM requires a basket strainer.
- The dirtiness of the flowing fluid: The basket strainer has more dirt-holding capacity as compared to the Y-strainers.
- Application Requirement:
- A y-type pipe strainer is suitable for applications requiring frequent cleaning.
- For continuous operation, the ideal choice will be a duplex basket-type pipe strainer.
- Strainer Orientation: For vertical orientation, Y-type is the only option.
- Pressure Loss: Basket strainers exhibit less pressure loss as compared to Y-strainers. That’s why when there is doubt a basket strainer can easily be installed. It will cost more but serve all the purposes.
Note that, purchasing a spare pipe strainer is always a good engineering practice to avoid unnecessary delays in cleaning and installation for line operation.
Pipe Strainer Dimensions
Dimensions of pipe strainers vary with respect to flange rating, end connection, and pipe strainer types. For flanged piping strainers, with an increase in flange rating the dimension and weight increase. Normally, the pipe strainer dimensions are vendor specific. This is the reason during the initial stages of piping design the length of piping strainers is kept as hold in piping isometrics. Later, when the specific vendor data is available the same is updated in piping isometrics and adjustments are made in piping length. The following table provides some typical pipe strainer dimensions and weights for Y-type and Basket-type strainers as samples. However, Final vendor details need to be verified.
| Pipe Size (Inch) | Pressure rating | Y Type Strainer Length- Flange face to Flange Face (mm) | Y Type Pipe Strainer Weight (Kg) | Basket Strainer Length- Flange face to Flange Face (mm) | Basket Pipe Strainer Weight (Kg) |
| 1/2″ | 150 | 170 | 3 | ||
| 3/4″ | 150 | 170 | 3.5 | 224 | 7 |
| 1″ | 150 | 185 | 5.5 | 225 | 13.5 |
| 1-1/2″ | 150 | 270 | 10 | 240 | 19 |
| 2″ | 150 | 275 | 16 | 315 | 27.5 |
| 3″ | 150 | 360 | 30 | 365 | 46.5 |
| 4″ | 150 | 435 | 50 | 445 | 70 |
| 6″ | 150 | 560 | 92 | 600 | 167 |
| 8″ | 150 | 655 | 180 | 715 | 310 |
| 10″ | 150 | 880 | 340 | 855 | 550 |
| 12″ | 150 | 970 | 385 | 1015 | 600 |
| 1/2″ | 300 | 175 | 3.5 | – | – |
| 3/4″ | 300 | 175 | 4.5 | 224 | 7.5 |
| 1″ | 300 | 195 | 6.5 | 232 | 14.5 |
| 1-1/2″ | 300 | 275 | 11.5 | 245 | 21.5 |
| 2″ | 300 | 315 | 18 | 321 | 29.5 |
| 3″ | 300 | 405 | 35.5 | 375 | 49 |
| 4″ | 300 | 490 | 65.5 | 455 | 92 |
| 6″ | 300 | 582 | 125 | 620 | 225 |
| 8″ | 300 | 730 | 233 | 740 | 405 |
| 10″ | 300 | 910 | 420 | 890 | 655 |
| 12″ | 300 | 1070 | 445 | 1050 | 700 |
Comparison between Filter and Strainer
Nowadays, the terms filter and strainer are used interchangeably in industries. However, there are differences between the two. The main differences between a Filter and a Strainer are tabulated below
| Filter | Strainer |
| A device that eliminates unwanted particles from the fluid is known as a filter. | Strainer also serves the same function. |
| The filtering medium in a filter is normally disposable. | Strainer uses a Reusable filter that is used again after cleaning. |
| The Filters normally filter out smaller particles (smaller than 40 microns). | Strainers remove comparatively larger particles ( larger than 40 microns) |
| Normally filters remove elements invisible to the naked eye. | Dirt removed by strainers is visible. |
| Filters remove particles by obstruction as well as chemical action. | Strainers remove particles by construction only. |
| Filters use soft media on hard surfaces to remove contaminants. | Strainers use hard mesh or rigid materials to remove debris. |
Few more Resources for you..
Piping Design and Layout
Piping Stress Analysis
Piping Interface
Piping Materials


It’s really interesting how much variety you can find in strainer baskets. I would imagine that the hole size of the mesh you use should be determined by the location in the pipe. It would need to be small enough to catch any unwanted debris, while also not disrupting the flow of the pipe. Are there different types of strainers for fluid and gas pipelines?
Very knowledgeable post. This website is very good for knowledge related to oil and gas .
As explained in the post, there are two elements: the First one is perforated plate and the second one is the Mess.
Now as per post, the Mess will be wrapped around the perforated plate. And perforated plate will provide support to the mesh.
While purchasing the Strainers, I always came across the term “Perforation Ratio”.
Can the Author or any other member of the portal explain the term “Perforation Ratio”?
Post talk about the different types of Strainers.
Can anybody explain:
# Where to use “T- Type Strainers”?
# Where to use “Y- Type of Strainers”?
# Where to use “Basket Type Strainers”?
# Where to use “Temporary Strainers”?
Author presents exemplary outlook of the subject matter. expertise. no single stone is left to present its case.
i was looking for selection criteria for different types of strainers.
Dear Sir,
Kindly explain how to design Y strainer, what are the parameters we have to consider,
how we derive body thickness, cover flange side pipe diameter etc..??
please explain.
Hi all
I need some information about how to determinte a hole size of Perforated screens
Detailed post very helpfull
You may have come across the term Ratio in a strainer. It is basically the Net Free Area of the element through which the fluid can pass through divided by the cross sectional area of the inlet pipe
Very informative and detailed in an easy manner.
how could we calculate the pressure drop during the strainer?