Oil and gas, petrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals rely heavily on complex pipe systems to transport fluids, gases, and chemicals. In these applications, maintaining a tight seal, isolating equipment, and facilitating maintenance are essential. A Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valve is such a critical component that combines these functions to enhance safety and operational efficiency. In this article, we will explore what DBB valves are, how they work, their applications, and why they are crucial in modern industrial processes.
What is Double Block and Bleed Valve (DBB)?
A Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valve is a specialized type of valve designed to provide a superior level of isolation and safety in fluid control systems. Essentially, it combines the functions of two separate valves and a bleed port into a single, compact unit.
Double Block and Bleed Valve is a single assembly of two inline block valves and one bleed valve. A DBB valve is like having three valves in one. The task of three separate valves is performed by this assembly while saving huge space, installation, and maintenance time, weight, and cost.
The main aim of using a double block and bleed valve system is to ensure that the fluid from upstream and downstream does not reach other components of the system. So, engineers can easily bleed off or drain the remaining fluid from the intermediate section and execute maintenance, repair, or replacement work. In a double block and bleed system, isolation is achieved both from upstream and downstream flow or pressure. The bleed valve is used to drain the cavity created between two block valves.
Components of DBB Valve
Let’s break down its components and functions:
Two Isolation Valves:
The “double block” part of the DBB valve consists of two isolation valves, typically ball or gate valves, arranged in series. These valves, when closed, create a double barrier that isolates the downstream and upstream piping, ensuring no flow passes through.
Bleed Valve:
The “bleed” portion of the DBB valve is a smaller valve, often a needle valve, located between the two isolation valves. Its purpose is to allow controlled bleeding of fluid or gas from the cavity between the two isolation valves. This is crucial for verifying the integrity of the seals and for safely releasing pressure.
An NPS 3/4-inch or 1-inch bleed valve is installed between two block valves for venting or draining as shown in Fig. 1.
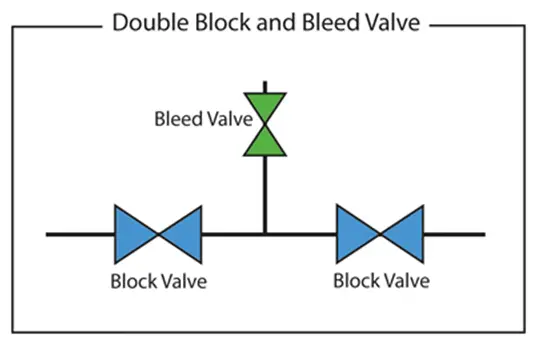
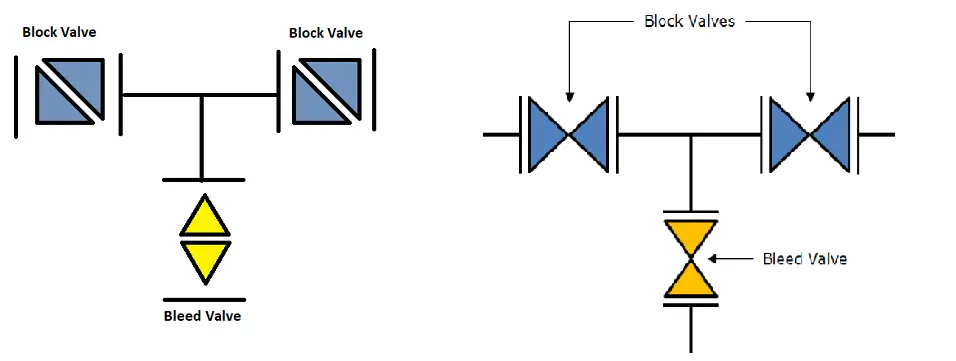
The image in Fig. 1 also serves as the double block and bleed valve P&ID symbol. In some companies, the P&ID system for the DBB valve can be represented as shown in Fig. 2.
Working Principle of a Double Block and Bleed Valve
Two block valves provide isolation from the upstream and downstream flows. A set of gate, ball, needle, or globe valves is normally used as the block valves that are placed back to back. In the center cavity of the two-block valves, a third valve known as the bleed valve is positioned. Fig. 3 shows a typical double block and bleed valve diagram.

The same double block and bleed arrangement can be obtained using three separate valves. But the single unit double block and bleed valve saves huge space, weight, installation time, and cost. Also, from the operation and maintenance viewpoint, single-unit double block and bleed valves are better as potential leak paths are significantly reduced in a single unit. Pressure drop is also minimized.
The operation of a DBB valve is relatively straightforward:
- Normal Operation: In typical operational conditions, both isolation valves are open, allowing fluid or gas to flow through the valve as if it were a regular pipeline. The bleed valve remains closed.
- Isolation: When maintenance or repairs are needed, the DBB valve offers a unique advantage. By closing both isolation valves, it effectively seals off the section of the pipeline in which it is installed. This isolation ensures that no fluid or gas can pass through.
- Bleeding: After isolation, the bleed valve can be opened to release any trapped fluid or gas between the isolation valves. This step is crucial for safety and maintenance purposes, as it prevents pressure buildup that could be hazardous.
The main function of the bleed valve is
- to drain/vent the cavity created between two isolation valves.
- flow diversion
- sampling and injection point connection
- integrity or maintenance check connection to monitor leakage
Bleed valves can be vented to the atmosphere directly or a hose connection/piping system can be used for a closed disposal system.
Types of Double Block and Bleed Valves
Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valves ensure safe and dependable isolation of process fluids through a combination of block valves and a bleed valve. Depending on configurations, there are three types of DBB valves that are widely used:
- Single valve systems,
- Dual valve systems, and
- Expanding gate valves.
Single Valve DBB
Single Valve DBB systems combine both block and bleed functions within a single valve body, featuring two separate sealing surfaces for effective isolation and a bleed function to vent trapped pressure. When closed, the primary and secondary seals create a double barrier, preventing fluid flow and ensuring isolation. A bleed port situated between the seals allows for the venting of any pressure or fluid once isolation is achieved, making the section safe for maintenance or inspection. Upon re-opening, the seals retract, restoring normal flow. The compact design of Single Valve DBB systems minimizes the need for additional piping and space, simplifying installation and maintenance. These systems are particularly useful in applications with space limitations and where moderate isolation integrity is sufficient.
Dual Valve DBB
Dual Valve DBB systems consist of two separate block valves and an independent bleed valve positioned between them, providing enhanced isolation integrity and maintenance flexibility. The first block valve is closed to prevent fluid from entering the isolated section, followed by the closure of the second block valve to create a dual barrier that ensures reliable isolation. Once both valves are closed, the bleed valve can be opened to vent any trapped pressure or fluid between the block valves, ensuring safety for maintenance personnel. During maintenance, the bleed valve is opened first to eliminate trapped pressure, followed by the opening of the block valves to restore normal operation. This setup offers enhanced safety through an additional layer of protection against leaks or failures and allows for independent maintenance of each block valve without compromising isolation integrity. Dual valve DBB systems are particularly suitable for high-integrity applications such as oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing plants, and other critical isolation scenarios.
Expanded gate valve DBB
Expanding gate valves are a type of DBB valve that utilize an expanding gate mechanism to achieve effective isolation, featuring a gate that expands laterally against the valve seats to create a tight seal. When the valve is closed, the gate presses firmly against the seats on both sides, establishing a double block and ensuring a strong barrier against process flow. A bleed port located between the expanded gates can be opened to vent any trapped pressure or fluid once the gates are fully expanded. Upon opening the valve, the gate retracts from the seats, allowing fluid to flow through. This mechanism provides a positive seal with minimal leakage, ensuring high integrity isolation, while its robust design is suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Expanding gate valves are commonly employed in the oil and gas industry, particularly in critical service scenarios where reliable isolation is crucial.
Codes and Standards for Double Block and Bleed valves
Double Block and Bleed Valves or DBBVs are designed and manufactured based on any of the governing codes
- API 6D
- API 607
- API 6FA
- BS6755-Part 2
- ASME B16.34
- EEMUA 182
- API 598
- BS EN ISO 17292
- ISO 14313
Benefits of Double Block and Bleed Valve
The advantages of double block and bleed valve can be summarised as follows:
- Compact design
- Provides sealing against pressure from both the upstream and downstream ends of the valve.
- The capability of venting the cavity in between the block valves.
- Around 60% savings in weight and 70% savings in installation time.
- High reduction of leak paths, ensuring low probability of hazard. Improved safety in operation.
- Great savings in space as compared to a conventional arrangement using separate valves.
- Can be used as chemical injections and sample points.
- Prevent product contamination.
- Remove equipment from service for cleaning or repair
- Reduced Stresses from load and vibration
- Uninterrupted flow for negligible pressure drop
Applications of Double Block and Bleed Valve
Double Block and Bleed Valve or DBB is widely used in systems requiring critical isolation. The major uses of DBB Valve include
- Oil & Gas, Chemical, and Petrochemical industries.
- LNG and Natural Gas industrial processes.
- Isolate instrumentation such as level gauges, pressure indicators, etc.
- Liquid pipelines and manifolds.
- Prevent product contamination.
- Transmission and storage, refined products transmission lines.
- Meter Calibration.
- Chemical injection and sampling.
- Liquid service near waterways or municipalities.
- Instrument drain connections.
- Remove equipment from service for repair or cleaning.
Factors affecting Double block and Bleed Valve (DBB) Selection
The parameters that affect the selection of a double block and bleed valve are
- Process Media and Application
- Temperature and Pressure
- Toxicity and Operating Environment
- The material of Valve Parts
Depending on requirement various types of DBB Valve configuration is available in the market. In general, three types of double block and bleed valves are available; Single unit DBB, Cartridge Type Standard Length DBB, and Three Piece Non-Standard Length DBB.
Why DBB Valves Are Crucial
- Safety: DBB valves are essential for maintaining safety in high-pressure systems. By providing double isolation and a bleed port, they reduce the risk of hazardous incidents during maintenance or emergencies.
- Efficiency: DBB valves streamline maintenance procedures by allowing technicians to isolate specific sections of a pipeline without shutting down the entire system. This minimizes downtime and improves operational efficiency.
- Cost Savings: Reduced downtime, minimized risk of leaks, and increased system reliability contribute to significant cost savings over the long term.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industry standards and regulations require the use of DBB valves for critical applications. Using DBB valves helps ensure compliance with these safety standards.
DBB vs DIB
A double isolation and bleed valve, or DIB, is a single valve with two seating surfaces. In a closed position, each of these seating surfaces provides a positive seal against pressure from a single source. There is a means of draining/venting from the cavity between seating surfaces. So, DIB looks almost similar to DBB and is quite confusing among many. The main differences between DBB and DIB valves are listed below:
| Double Block and Bleed Valve (DBB) | Double Isolation and bleed valve (DIB) |
| A DBB Valve provides sealing against pressures from both sides of the valve. | A DIB provides an additional sealing against pressure from one side of the valve. |
| A DBB Valve has two unidirectional self-relieving seats which are independent of outside mechanisms for pressure relieving. | A DIB uses one or two bi-directional seats which are not self-relieving requiring an external pressure-relieving mechanism. |
| In a DBB, if the first seal leaks, the second will not provide sealing in the same direction. | DIB provides an additional pressure barrier from the main pressure barrier. |
Double Block and Bleed (DBB) valves are indispensable in the oil and gas industry, providing a reliable means of isolating and managing sections of pipelines and process systems. Their ability to offer double isolation and safe depressurization makes them a critical component in maintaining safety and efficiency in operations. By understanding their functionality, advantages, and applications, industry professionals can better appreciate the role of DBB valves in ensuring the safe and effective operation of oil and gas facilities.

Hi, Anup .
It is good initiative , that you open this blog. Iwould like to understand, from your many experienced of hands on experienced, how do differentiate the lethal service and toxicity service.? May i know what is the criteria for one to conlclude whether this liquid is lethal / toxic. Hope you can enlighten me.
thank you
Hi Anup,
Thanks for posting this topic and its helping a lot. If you can help answer my question: Regarding requirement to have DBB at sampling point at sour services, do you know what codes or ASTM or API mention about this?
Thanks in advances for your kind help to answer my question.
Take care