Hot Tap or Pipe Hot Tapping is a proprietary method for adding a branch connection to a “hot” or operating line. The hot Tapping process allows a connection into a pressurized in-service operating system, by drilling or cutting. The hot tap procedure involves attaching a branch connection and valve on the outside of an operating pipeline, and then cutting out the pipeline wall within the branch, and removing the wall section through the valve.
In general, hot taps are done in a piping system. But, it can also be done on pressure vessels and storage tanks to add nozzles. Hot tapping is a highly dangerous operation. Therefore, hot tapping must only be used as the last resort when it is impractical to shut down the system. While preparing a hot tapping specification, care needs to be exercised in inspection, design, and testing. It must be ensured that this operation is done in a safe and reliable manner. Each hot tapping needs to be properly designed, the location of hot tapping thoroughly inspected, and the installation procedures reviewed before starting the operation.
A. What is Hot Tapping?
Hot-tapping is a method of making connections to piping (or other equipment) by attaching a fitting to the system, usually by welding, followed by cutting through the pipe wall at the point of attachment utilizing a hot-tapping machine. This operation is carried out on a live (hot) system without
decommissioning or interrupting flow.
Hot tapping is a multi-disciplinary operation that typically involves various departments, each with its own responsibilities. As a result, effective coordination and careful planning among these departments are essential for successful execution.
B. Some Definitions or Terminologies related to Hot-Tapping
| Term | Definition |
| Run pipe | The pipe into which a hot tap is to be made |
| Branch pipe | The pipe which is to be connected to the run pipe by means of the hot tap. |
| Coupon | Section of pipe cut out during the hot-tap cutting operation |
| In-service welding | Welding on a piping system that is flowing or under pressure |
| Lock plug | Plug which can be set into position inside a hot-tap connection flange in order to retain internal pressure. |
Stopple
A proprietary device, to be used in conjunction with a hot tap that blocks a “hot” line is called “Stopple”.
C. Codes and Standards for Hot Tapping
There are various codes and standards that are followed for Hot Tapping in live piping and pipeline systems. Some of them are:
- Design Codes: ASME B31.1, B31.3, ISO 13623, ASME B31.4 and B31.8, ASME Sec. VIII Div.1 and 2
- Fabrication Codes: ASME BPVC Sec. VIII Div.1
- Welding Codes: ASME BPVC Sec. IX
- NDT Codes: ASME BPVC Sec. V
- Shell DEP 31.38.60.10
- API 570
- API RP 2201
D. Hot Tapping Procedure | Activity Steps for Pipe Hot Tapping Job
The following activities are involved in performing Hot Tapping Jobs in any project:
- Justification
- Design
- Construction planning
- Operations planning
- Verification
- Execution
- Completion
There has to be an agreement that the hot tap for the particular case is technically feasible and justified. During the design data gathering of the existing main pipe, connection design, confirmation of technical feasibility, setting the hydro test pressure, etc. has to be decided. In the next step, welding procedure, welder qualification, safety plan, on-site checks (e.g., inspection of the hot-tap and weld area by visual inspection and NDT), etc. need to be performed. Operations planning involves activities like control of operating conditions, work permits, and emergency procedures. Before execution, all required barriers and mitigations for safe work execution are to be verified to work as planned and that no hydrocarbons are present in the welding area or space. The next step is execution which involves welding, inspection, pressure testing, perforation, etc. The final step is completion which involves activities like reinstatement, updating records, and handover.
Hot Tap being highly hazardous, all activities need to be ensured following a detailed Hot-Tap Procedure Check List.
E. Components of Hot Tapping
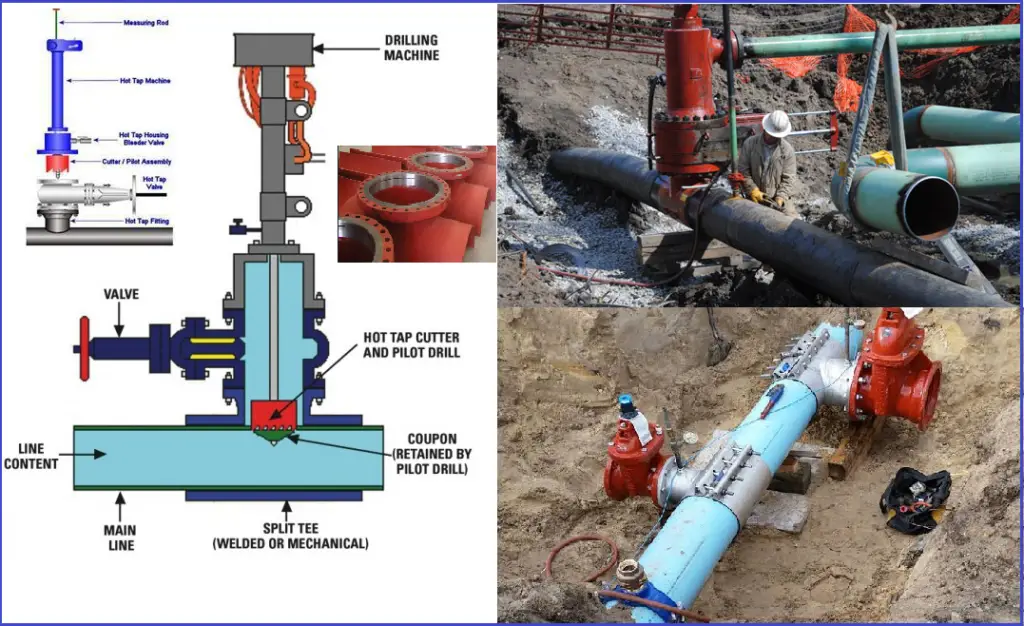
Refer to Fig. 1. A typical hot-tapping system consists of
- Tapping fittings.
- Isolation valve.
- Hot tapping machine which includes the cutter, and housing.
Drilling machine or Cutter: The drilling machine usually consists of a mechanically driven telescoping boring bar that controls a cutting tool. A pilot hole into the pipeline wall is bored by the cutting tool in order to center a hole saw that cuts out the “coupon,” or curved section of the pipeline wall.
Fitting: Connection to the existing pipe is made within a fitting, which can be a simply welded nipple for a small (e.g., one inch) connection to a larger pipeline, or a full-encirclement split-sleeve tee for extra support when the branch is the same size as the parent pipeline. The tee wraps completely around the pipeline, and when welded, provides mechanical reinforcement of the branch and carrier pipe.
Valve: The valve on a hot tap connection can be either a block valve or a control valve for the new connection, and must allow the coupon (section of pipeline wall cut out by the drilling machine) to be removed after the cutting operation. Suitable valves include a ball valve or gate valve, but not a plug valve or butterfly valve.
F. Limitations of Hot Tapping
Hot tap connections shall not be made in any of the following cases:
1. Limited by Fluid Types:
Lines carrying the following shall not be hot-tapped.
- Acid
- Caustic
- Elemental sulfur
- Oxygen
- Chlorine
- Ammonia
- Potentially toxic materials
- Any material that may cause metallurgical damage when heated.
2. Limited by Flammability of Fluid:
Hot taps are not suitable for pipes or vessels containing materials that are flammable below atmospheric pressure or mixtures that will support combustion.
3. Limited by Material Degradation:
Hot taps are not suitable if the pipe material to be welded may suffer metallurgical or physical degradation from the heat of welding.
4. Limited by PWHT Requirement:
Piping requiring post-weld heat treatment, for any reason, shall not be hot-tapped.
5. Limited by Pipe Cladding or Pipe Lining:
Hot tapping shall not be performed in piping, or vessels that are clad or lined
6. Limitation due to Maximum and Minimum Temperature:
Lines with surface temperatures above 370 degrees C or below -20 degrees C are not suitable for hot tapping.
7. Limitation by Other Process Conditions
Some standards provide additional reservation parameters for hot tapping. Some examples are:
- The operating pressure during hot tapping should not be more than 70 bar (g)
- The minimum velocity of liquid flow during hot tapping welding should be more than 0.43 m/s to provide cooling during the hot tap welding process. Again, the maximum velocity for liquids should be limited to 1.75 m/s to prevent rapid cooling. Similarly, for purge gas, the minimum velocity to be maintained is 0.4 m/s and the maximum velocity is 9 m/s.
8. Some other limitations are
- Equipment Availability: There must be a hot tapping machine available for the temperature pressure and size of the shell.
- Tanks: Hot taps on tanks shall be located at least 1 m below the liquid level.
- Compressed Air: Compressed air, when there is any possibility of hydrocarbon contamination, shall not be hot tapped, without thorough internal cleaning, or the introduction of inert gas, prior to welding.
- Debris Damage: Hot taps shall not be made upstream of any equipment that may be damaged by chips, shavings, and other debris introduced into the line by the hot tapping process. Hot tapping shall not be allowed until systems have been put in place that will positively trap foreign matter.
- Minimum Wall: The minimum wall thickness for hot tapping is 5 mm. This wall thickness must be verified by ultrasonic testing on the parent pipe.
- Hot tap welding is not to be performed on wet surfaces.
G. Hot Tapping Design
1. Base Material
The material of the run and branch pipe for the hot tapping welding shall be compatible in terms of weldability; the same P-Number can be considered as the basis for compatibility.
2. Dimensions of the Connection:
The dimensions of the connection, the hot tap valve, and the clearances shall be within the limits specified for the hot tapping equipment to be used. This requires data from the most likely contractor or specification of a list of allowable hot-tapping machines for that project. The minimum bore of the valve used shall be large enough to pass the cutter or stopple plug.
3. Size to Size Taps:
A tap equal to the nominal size of the header, such as required for the stoppling of a pipeline, shall be made only when the accurate positioning of the cutter can be guaranteed. This is accomplished by the use of a shop-fabricated split tee. In all other cases, the taps are only allowed at least one pipe size smaller than the pipe to be tapped.
4. Welding on Pipelines under Pressure:
Before welding on lines under pressure, the existing pipe wall shall be determined. A maximum working pressure shall be calculated in accordance with the appropriate ASME B31 code, using the actual wall minus 2.5 mm. The 2.5 mm wall thickness takes into account the molten and heat-affected portion of the base metal which does not contribute to pressure containment.
5. Control of Cuttings:
When using gate valves for hot tapping, orient the valve so that chips from the cutting procedure will not fall into areas where the action of the valve is inhibited. If this is not possible, the hot tap valve shall be provided with a valved drain of not less than 3/4 inch NPS to permit flushing of the valve if needed.
6. Removal of Hot Tap Valve:
When the hot tap valve is to be removed after tapping, as in the case of stoppling, a Lock-O-Ring flange and plug, or approved equal, shall be used unless the equipment can be depressurized and drained prior to removal of the valve.
7. Guide Bars:
When hot taps are made in pipelines that require scraper bars, a Lock-O-Ring, or approved equal, flange and plug and matching insert with bars attached, shall be installed.
8. Loads during Hot Tapping
During the stress analysis of hot tapping of the pipeline or piping system the following loads need to be considered:
- Piping Transmitted Loads
- Internal Pressure
- Hot-Tapping Loads
This will ensure that the hot tap weld will withstand all the loads during the hot tapping operation.
H. Hot Tap Fitting Installation
Positioning the Split Tee and Cutter
The welded branch or split tee shall be accurately positioned so that the axis of the cutter will intersect the axis of the pipe or vessel being tapped at a 90-degree angle unless an angled tap has been specifically approved in the hot tapping procedure. The branch position shall be verified by the assigned inspector prior to making the cut.
Safety Procedures
The hot-tapping contractor shall submit safety procedures with his proposal. The installation, pressure testing, welding, and cutting, shall be in accordance with the approved procedures.
I. Pressure Testing
1. Test Valve:
The hot tap valve shall have a pressure test applied to the seats and body to ensure no leaks prior to use.
2. Test Fluid:
Special attention shall be given to the possibility of boiling or flashing of the test liquid if the surface to be tapped is hot.
3. Hot Tap Test:
When the full assembly is complete, and prior to cutting the coupon, the assembly shall be pressure tested.
4. Test Pressure:
The test pressure for the hot tap connection shall be in accordance with the appropriate ASME B31 code, however, not exceeding any of the following:
(i) The minimum pressure in the pipe or vessel being tapped, while the test is in progress, plus a calculated differential pressure. The differential pressure shall be 1.25 times the allowable external pressure calculated per the ASME SEC VIII D1, paragraph UG-28. The value of L, for this calculation, shall be the total length of the split tee or the inside diameter of the welded nozzle.
(ii) The maximum test pressure of the branch connection flange, or the wall thickness.
(iii) The test pressure of the hot tap connection may be lower than the original hydrostatic test pressure of the pipe or vessel being tapped. This is acceptable since the purpose of the test is to provide some assurance of the integrity of the connection weld. It is not a proof test of the connection. The system being tapped should not be derated because of the lower test pressure of the hot tap connection.
5. Pad Vent Hole
The reinforcing pad of a welded branch shall be provided with a vent hole. The hole shall be plugged in with heavy grease before leaving the job.
6. Inspection
In addition to the hydro test, the reinforcing pad welds may be inspected by magnetic particle examination. Alternatively, dye penetrant examination may be used provided surface preparation is made as required.
Few more useful resources for you…
Piping Design and Layout Basics
Piping Stress Analysis Basics
Piping Material Basics
Piping Design Software
Piping Interface Articles
J. Hot Tapping Operation Video
Refer to the following video to visualize the hot-tapping operation.
K. FAQ on Hot Tapping
1. What is hot tapping?
Hot tapping is a technique used to create a connection to a pressurized system, such as pipelines or vessels, without shutting down the system. It allows for the installation of new valves, branches, or other equipment while the system remains in operation.
2. When is hot tapping used?
Hot tapping is typically used in situations where:
- A system cannot be taken offline due to operational needs.
- Quick modifications or repairs are necessary.
- The process requires minimal disruption to services.
3. What are the safety precautions for hot tapping?
Safety is paramount in hot-tapping operations. Key precautions include:
- Conducting a thorough risk assessment.
- Ensuring all personnel are trained and equipped with appropriate PPE (Personal Protective Equipment).
- Utilizing certified equipment and following industry standards.
- Implementing proper isolation and monitoring procedures.
4. What types of systems can be hot tapped?
Hot tapping can be performed on various types of systems, including:
- Gas and oil pipelines
- Water distribution systems
- Chemical processing facilities
- Steam and heating systems
5. What equipment is used in hot tapping?
Common equipment for hot tapping includes:
- Hot tap machines
- Tapping valves and fittings
- Isolation valves
- Pressure monitoring instruments
- Safety equipment (e.g., fire extinguishers, emergency shutdown systems)
6. How is the hot tapping process carried out?
The hot-tapping process generally involves the following steps:
- Preparation: Assess the site and gather necessary equipment.
- Isolation: Isolate the area around the intended tap.
- Installation: Attach the tapping machine and valve to the existing pipeline or vessel.
- Tapping: Cut into the system under controlled conditions, allowing flow to continue.
- Completion: Secure the new connection and perform pressure tests to ensure integrity.
7. What are the potential risks of hot tapping?
Potential risks include:
- Leaks or spills if not properly managed.
- Equipment failure or accidents due to high pressure.
- Exposure to hazardous materials.
- Fire or explosion in certain environments.
8. How do you ensure a successful hot tap?
To ensure success:
- Plan thoroughly and conduct proper training.
- Use high-quality equipment and follow industry standards.
- Monitor conditions continuously during the operation.
- Conduct post-operation inspections to verify the integrity of the new connection.
9. Are there regulations governing hot tapping?
Yes, hot-tapping operations are subject to various industry regulations and standards, which can vary by region and industry. Always consult local regulations and follow best practices outlined by organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) or the American Petroleum Institute (API).
10. Who should perform hot tapping?
Hot tapping should only be performed by trained and experienced personnel familiar with the specific processes and equipment involved. Many companies specialize in hot tapping services, providing skilled technicians to ensure safe and efficient operations.
11. What is a hot tap used for?
A hot tap is used to create a connection to a pressurized pipeline or vessel without shutting down the system. This method allows for the installation of new valves, branches, or other fittings while the system continues to operate, facilitating modifications, repairs, or maintenance without interrupting service.
12. Why do we need hot tapping?
Hot tapping is essential for maintaining continuous operations in critical systems where downtime is costly or impractical. Industries such as oil and gas, water distribution, and chemical processing often rely on hot tapping to enable timely upgrades, repairs, or expansions while minimizing disruption to ongoing processes and ensuring safety.
13. What are the benefits of hot tapping?
The benefits of hot tapping include reduced downtime, increased operational efficiency, and cost savings. By allowing modifications to be made without shutting down the system, hot tapping minimizes interruptions to service, thus preserving production schedules and avoiding the financial impact of system shutdowns. Additionally, it enhances flexibility in managing system upgrades and maintenance.
14. What are the disadvantages of hot tapping?
Despite its advantages, hot tapping poses several disadvantages, including potential safety risks such as leaks, explosions, or equipment failure if not executed properly. The process requires specialized equipment and trained personnel, which can increase project costs. Additionally, there may be limitations based on the type of material or conditions within the existing pipeline that could complicate the hot-tapping operation.
15. What are the differences between hot tapping and cold tapping?
The primary difference between hot tapping and cold tapping lies in the operational status of the system being tapped. Hot tapping involves making a connection while the system is pressurized and in operation, allowing for immediate flow without interruption. In contrast, cold tapping is performed on a system that has been depressurized and shut down, requiring more extensive planning and potentially longer downtime. Consequently, hot tapping is generally more complex but offers the advantage of maintaining continuous service.
L. Detailed Course on “Hot Tapping in Pipeline and Piping Industry”
If you still have doubts or want to get more insights on the topic, you can join the detailed online course on “Hot Tapping in Pipeline and Piping Industry” by clicking here

We need to hot tap 26″ line -running fluid is HSD and pipe wall thickness is 11 mm with 26″ equal split tee with 26″ isolation valve( Gate Valve).
As per existing line PMS, PWHT is required.
But for hot tapping with split tee with isolation valve
As per ASME B31.8 para 825.3 Welds in all carbon steel shall be stress relieved when the nominal wall thickness exceeds 1.25inch. Which means for 11 mm wall thickness , PWHT is not required.
Could you please confirm?
PWHT requirement as per fluid should be followed irrespective of thickness limits/ PWHT exemptions mentioned in code.
Any hot tappers, stopplers, or pipe freezers out there that want to join a technical support group? At quora.com, I started a group called “Hot Tapping, Stoppling, & Freezing Piping”. Get on Quora and join.
P.S.: I have hot tapped all of the types of pipe content that you say cannot be hot tapped, except for oxygen. I think I could even do oxygen with the right situation.
Hi sir,
good evening I’m hot tapping and line isolation oil & gas field technician.
thanks,
your information.
please confirm flowrate 22000 scmh can we do online welding , pipe wall thinness is 7.8 mm, if minummumm and maximum flow rate requirement !